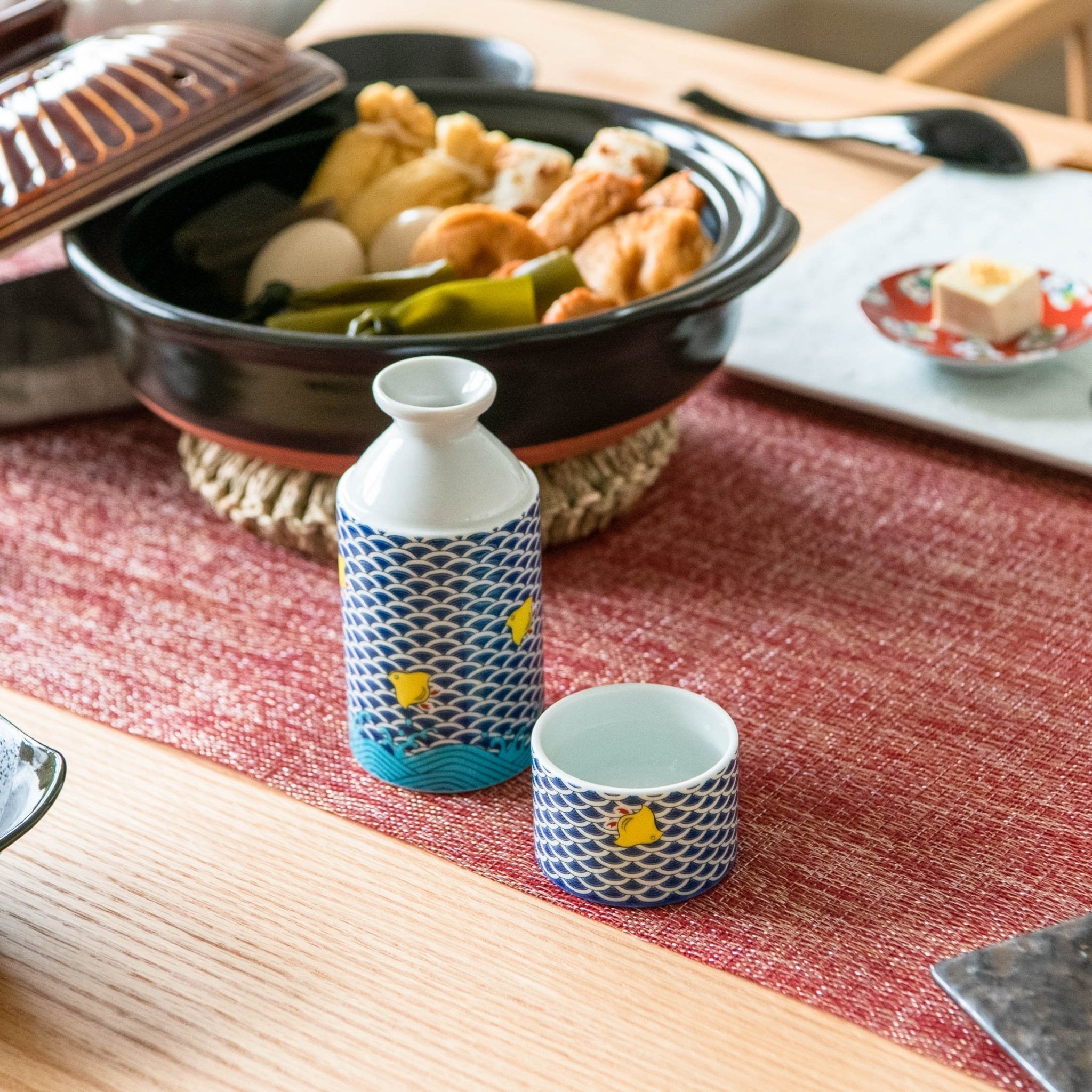
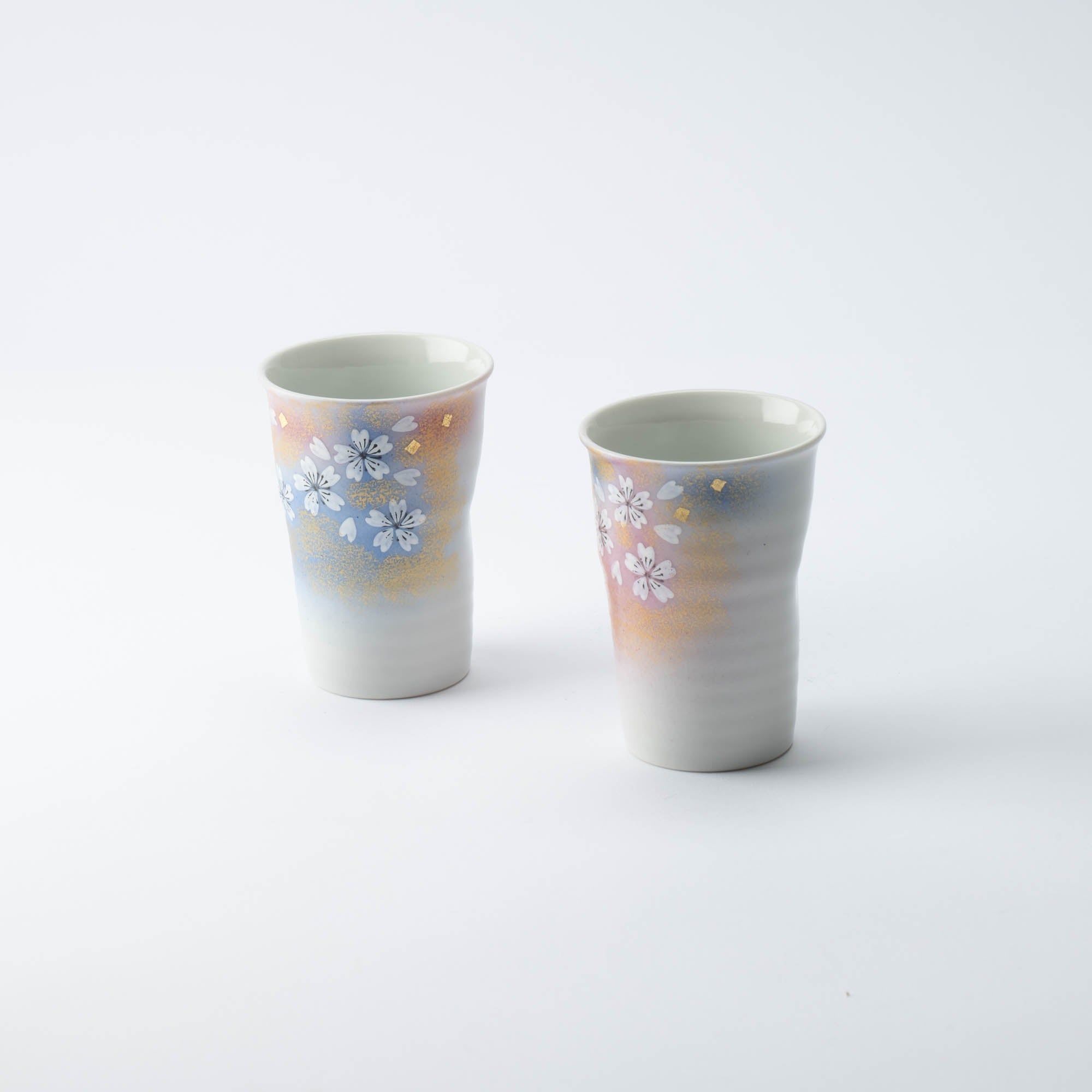
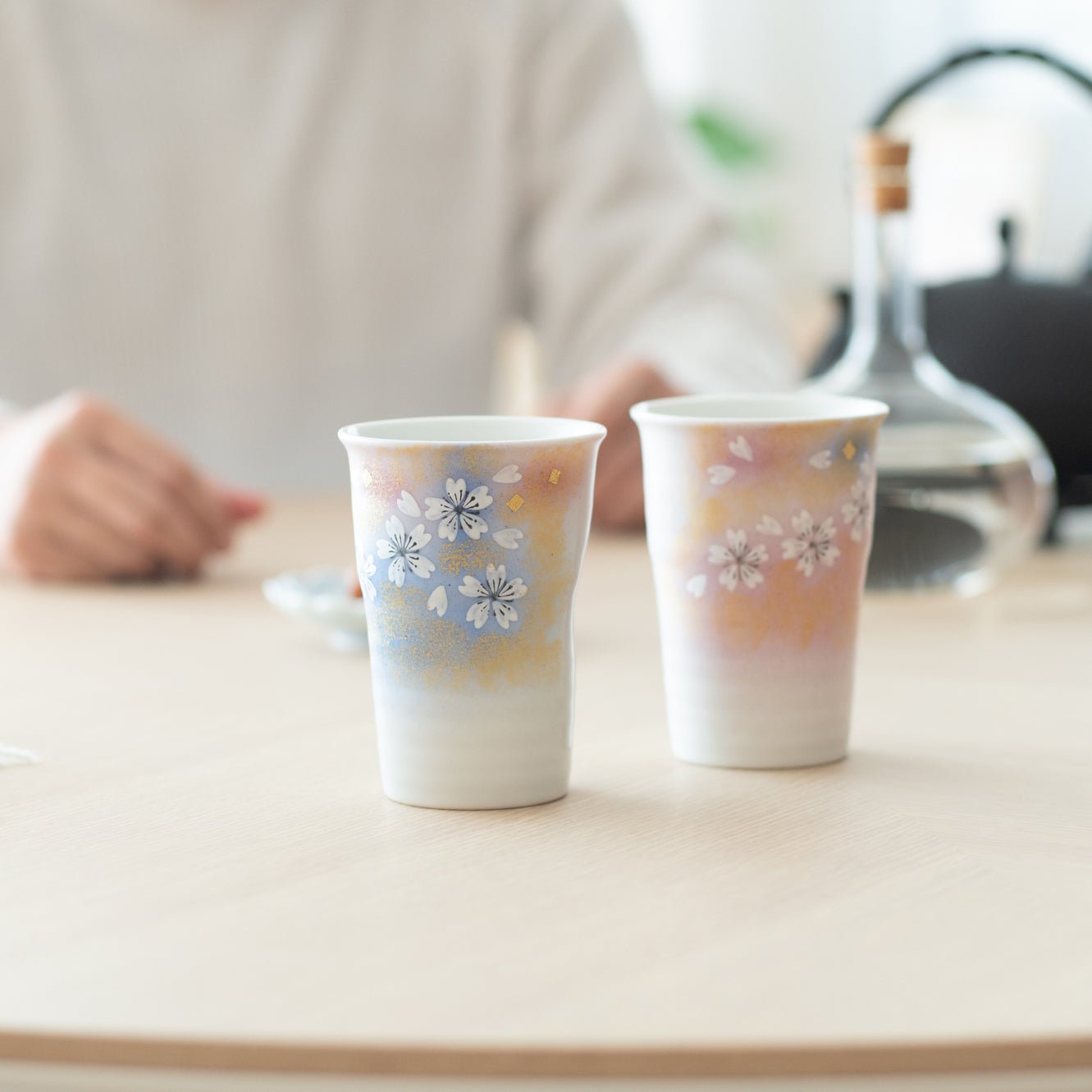
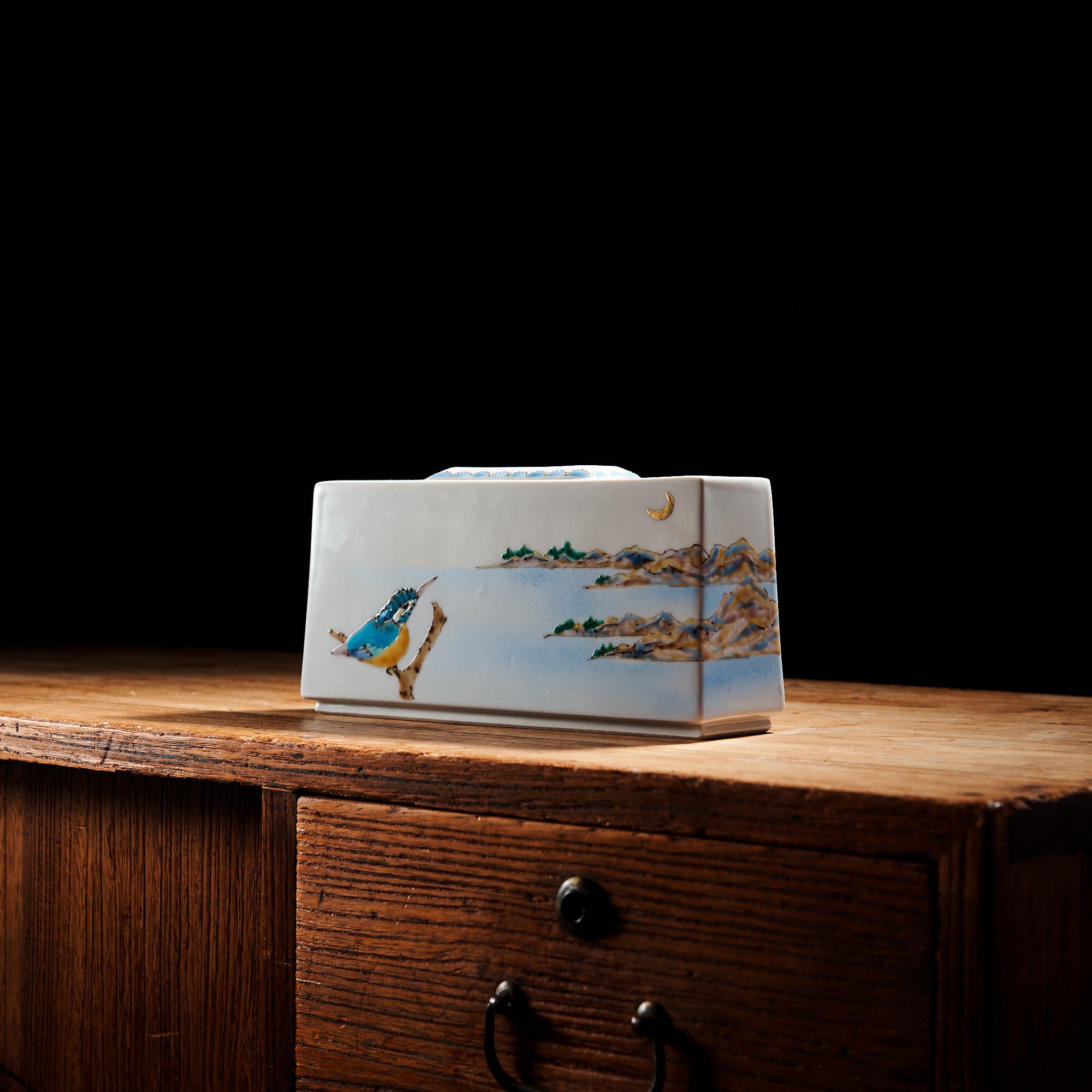
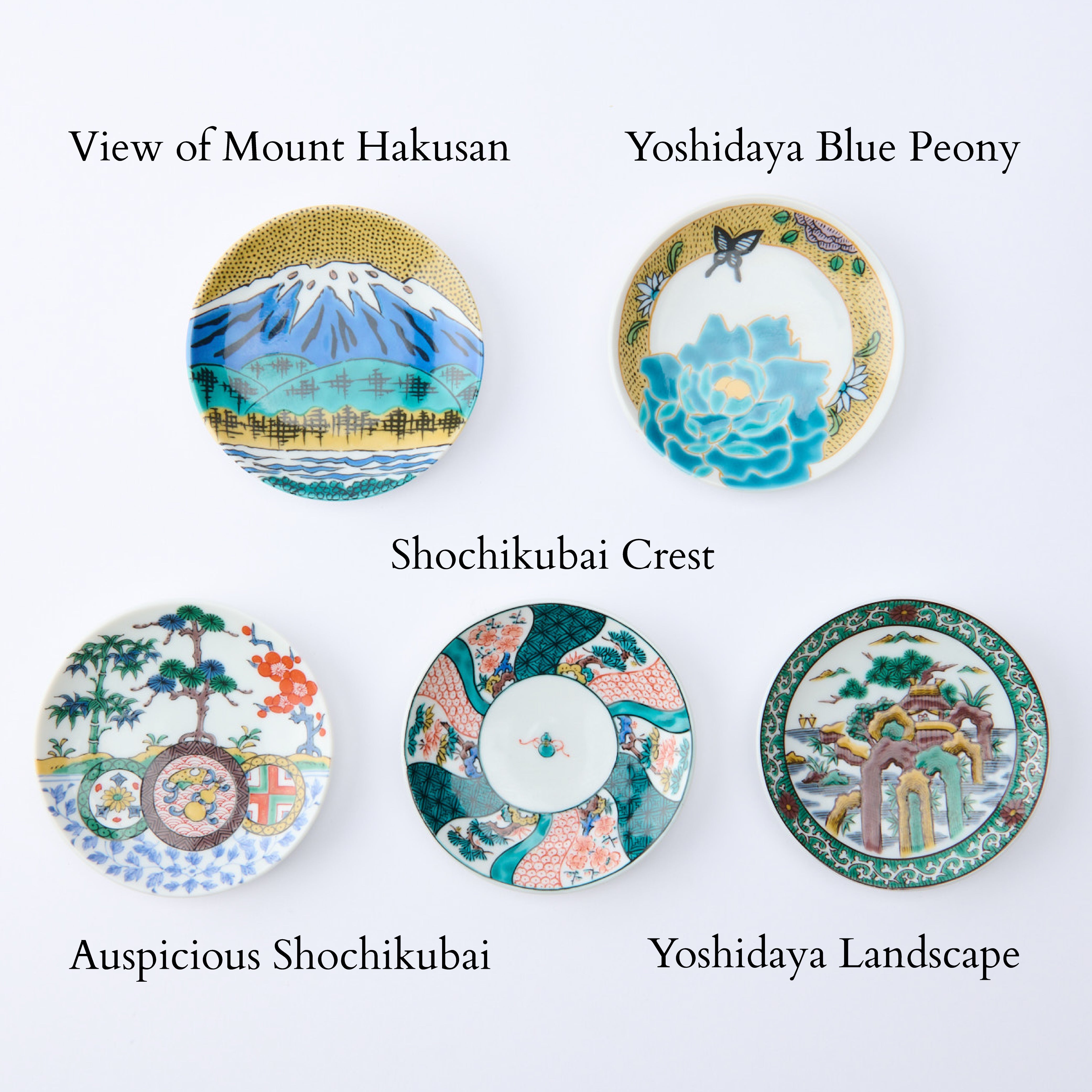
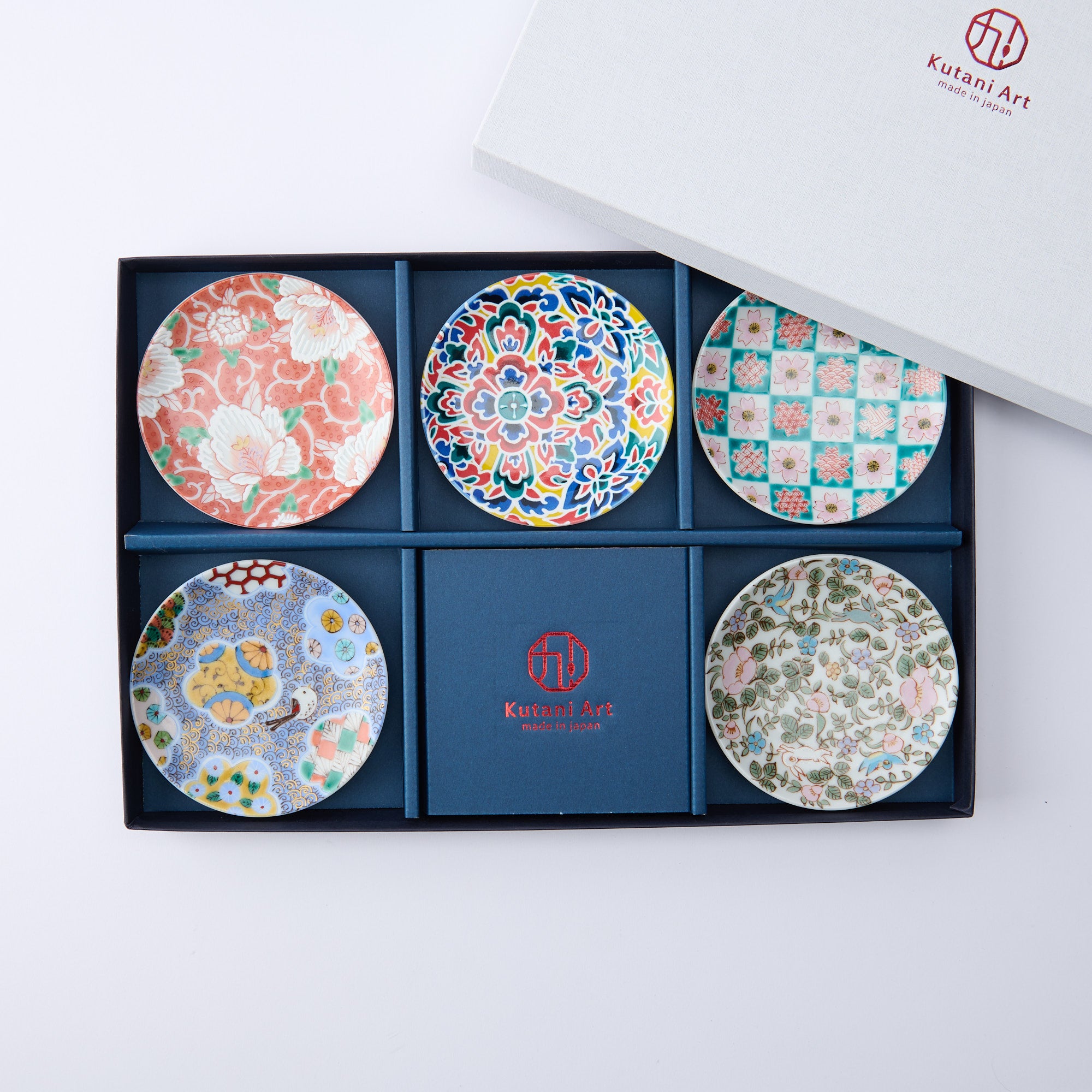
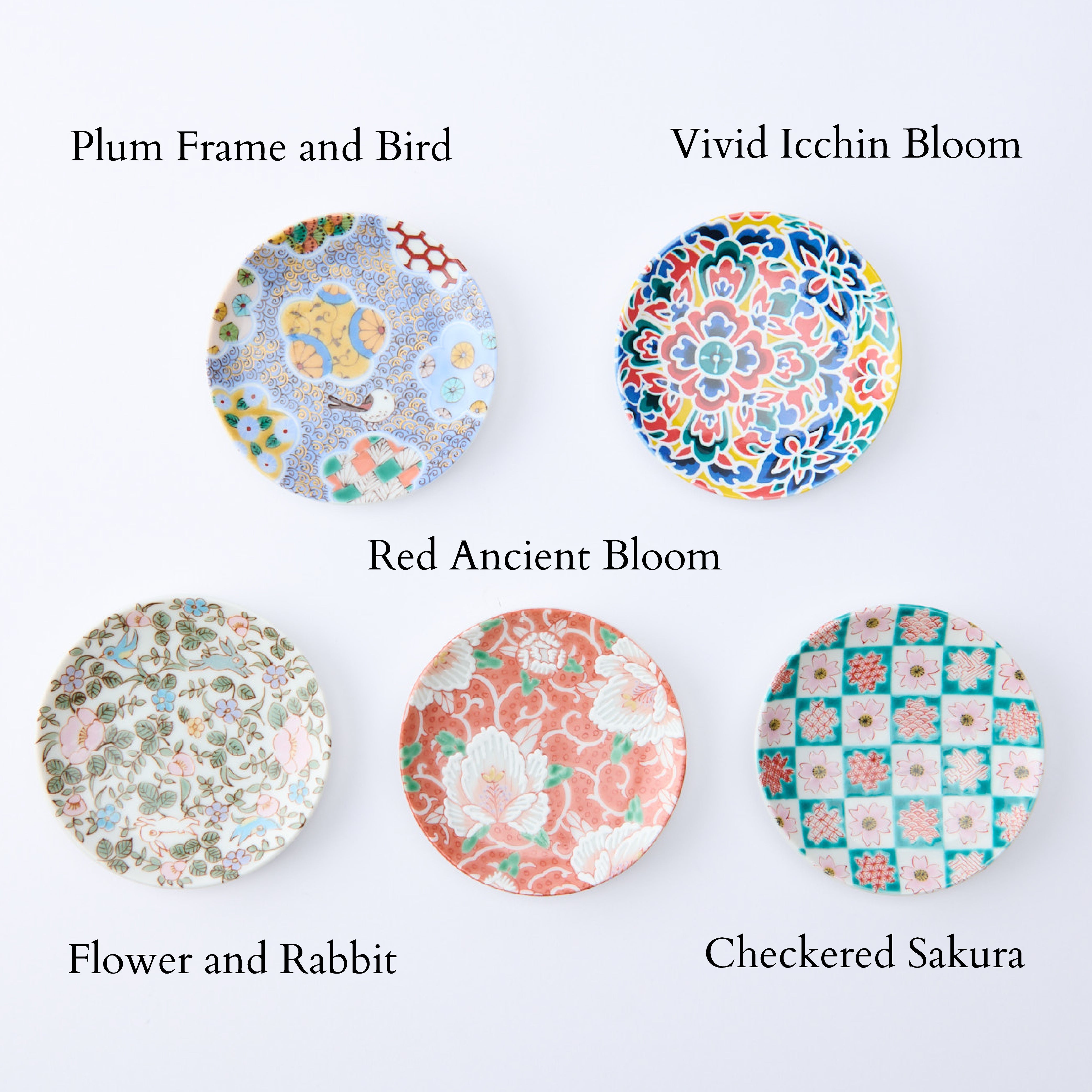
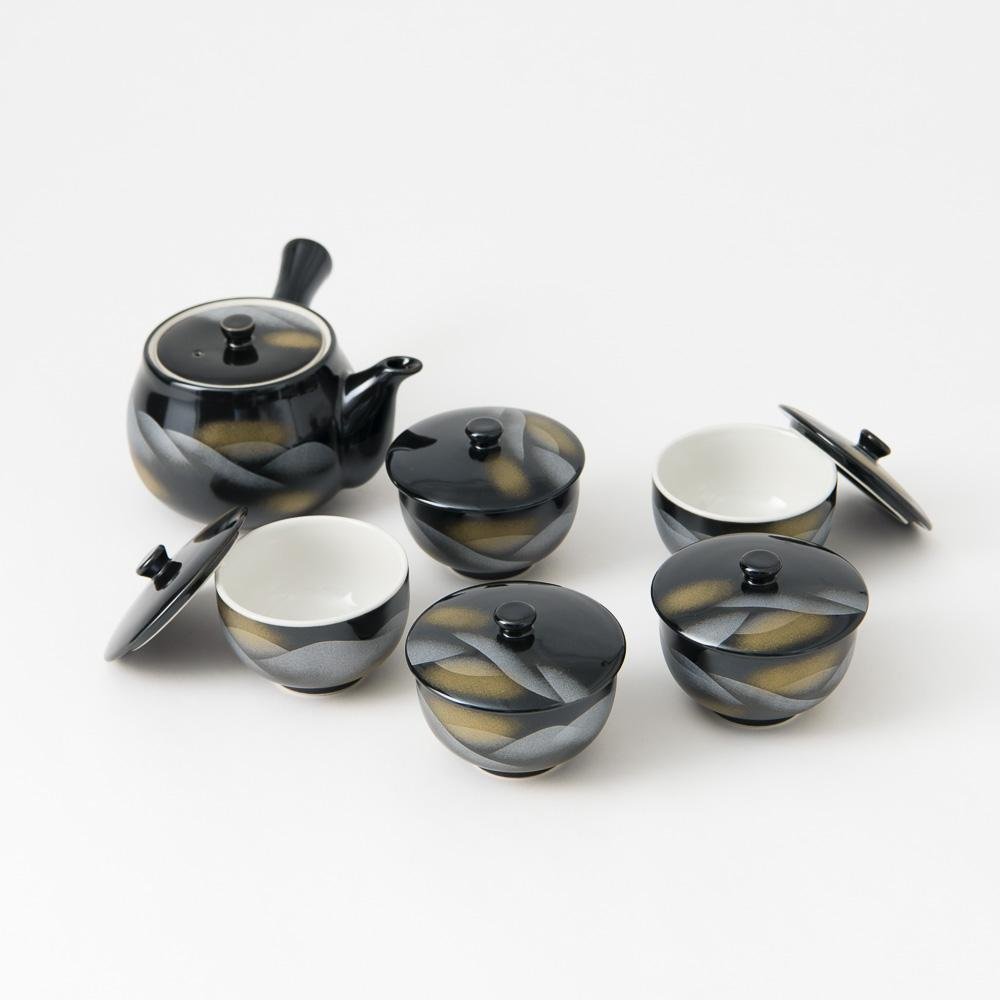
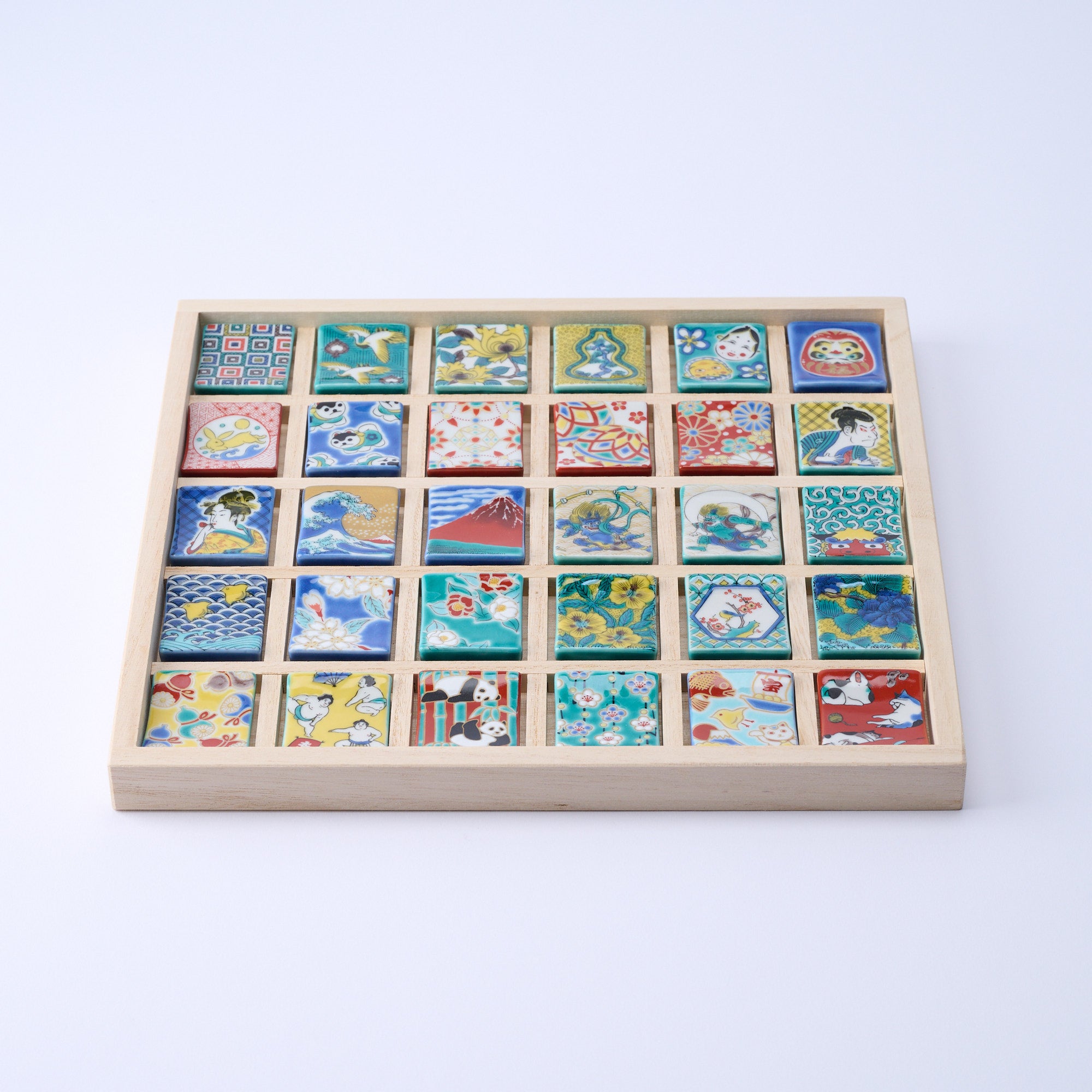
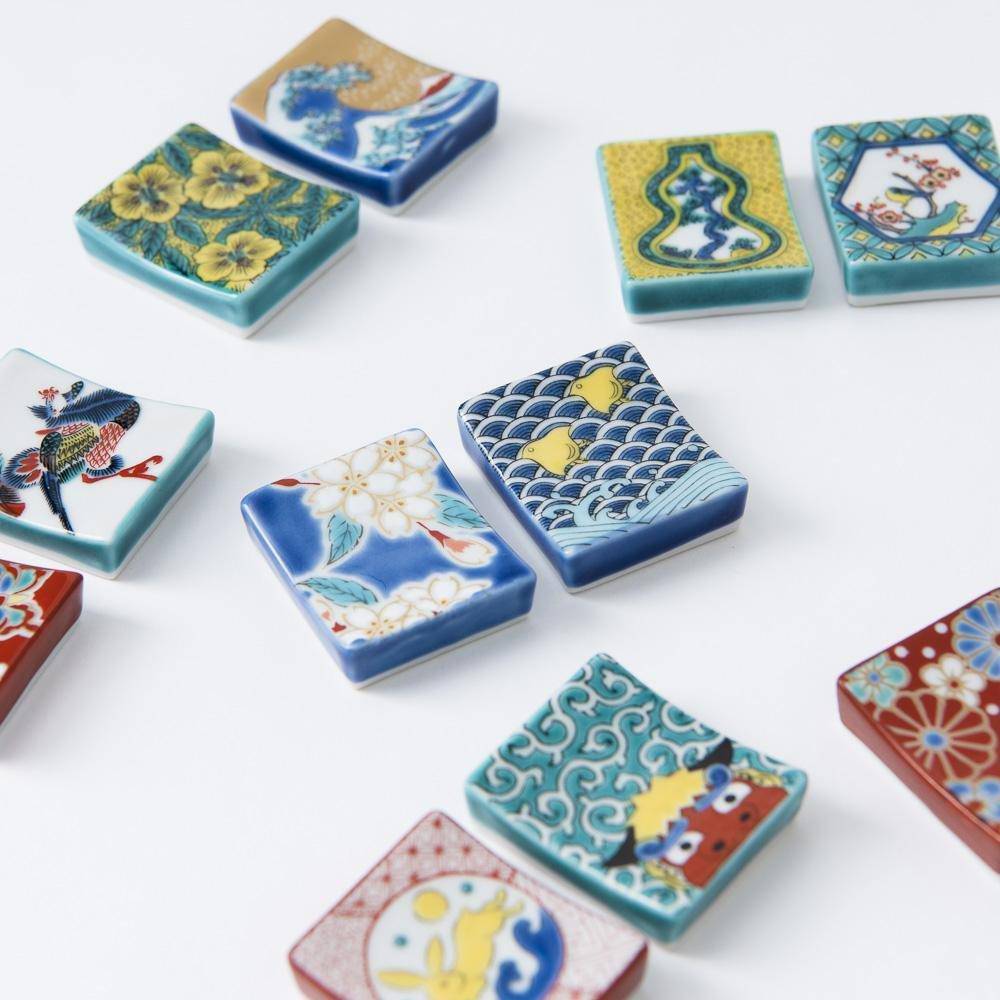
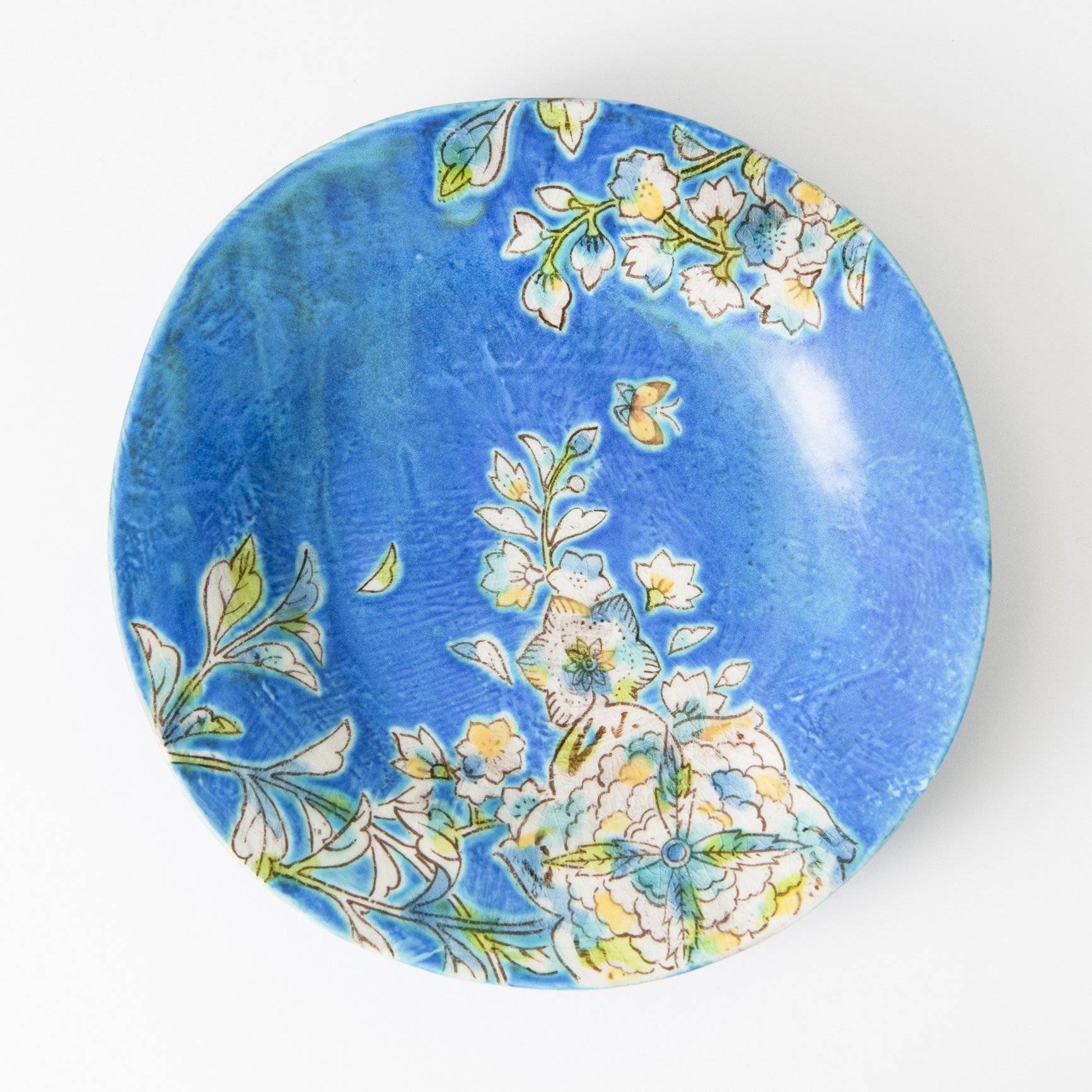
Colors that Tell a 350-Year Story
Kutani Ware
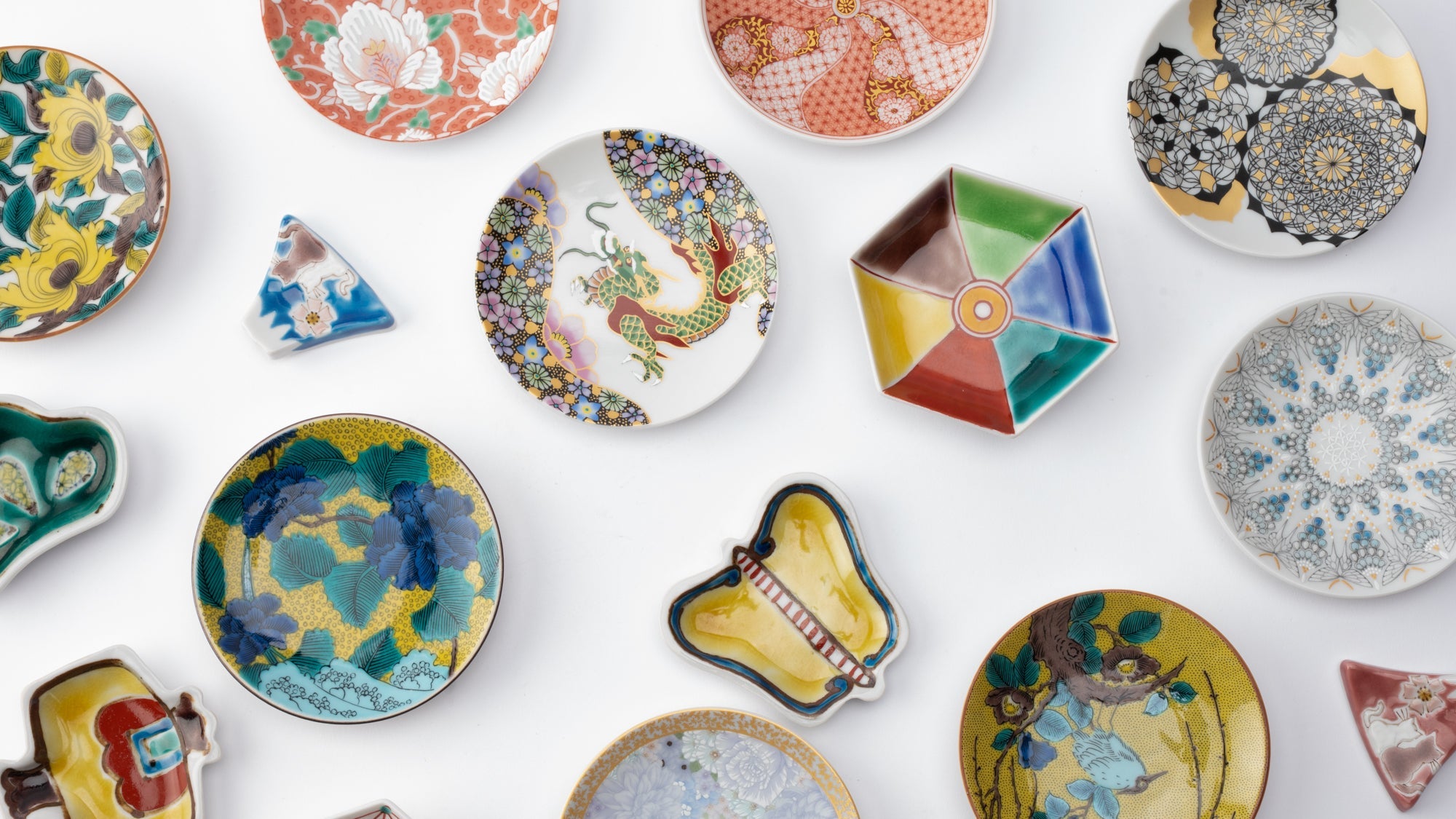
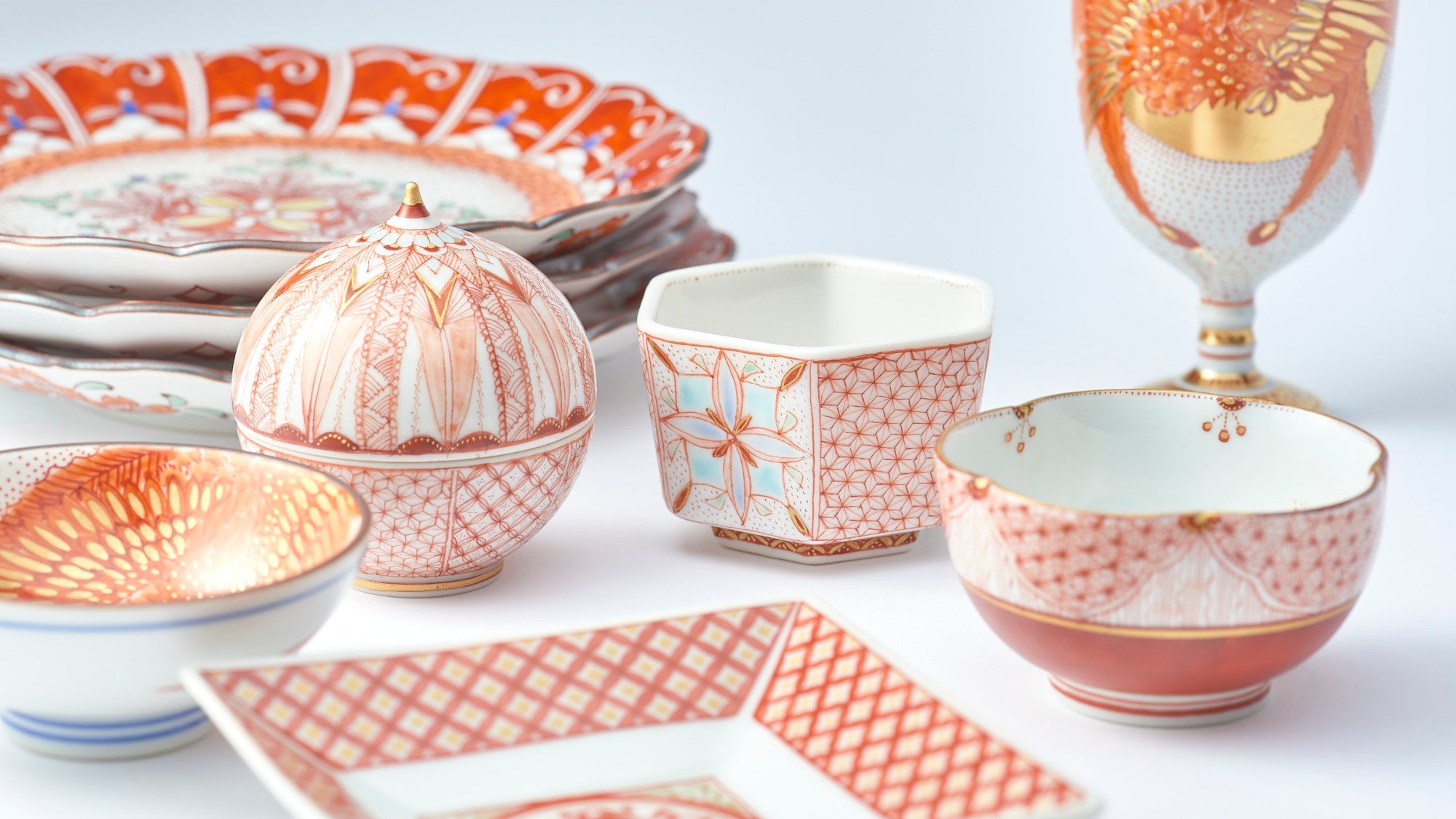
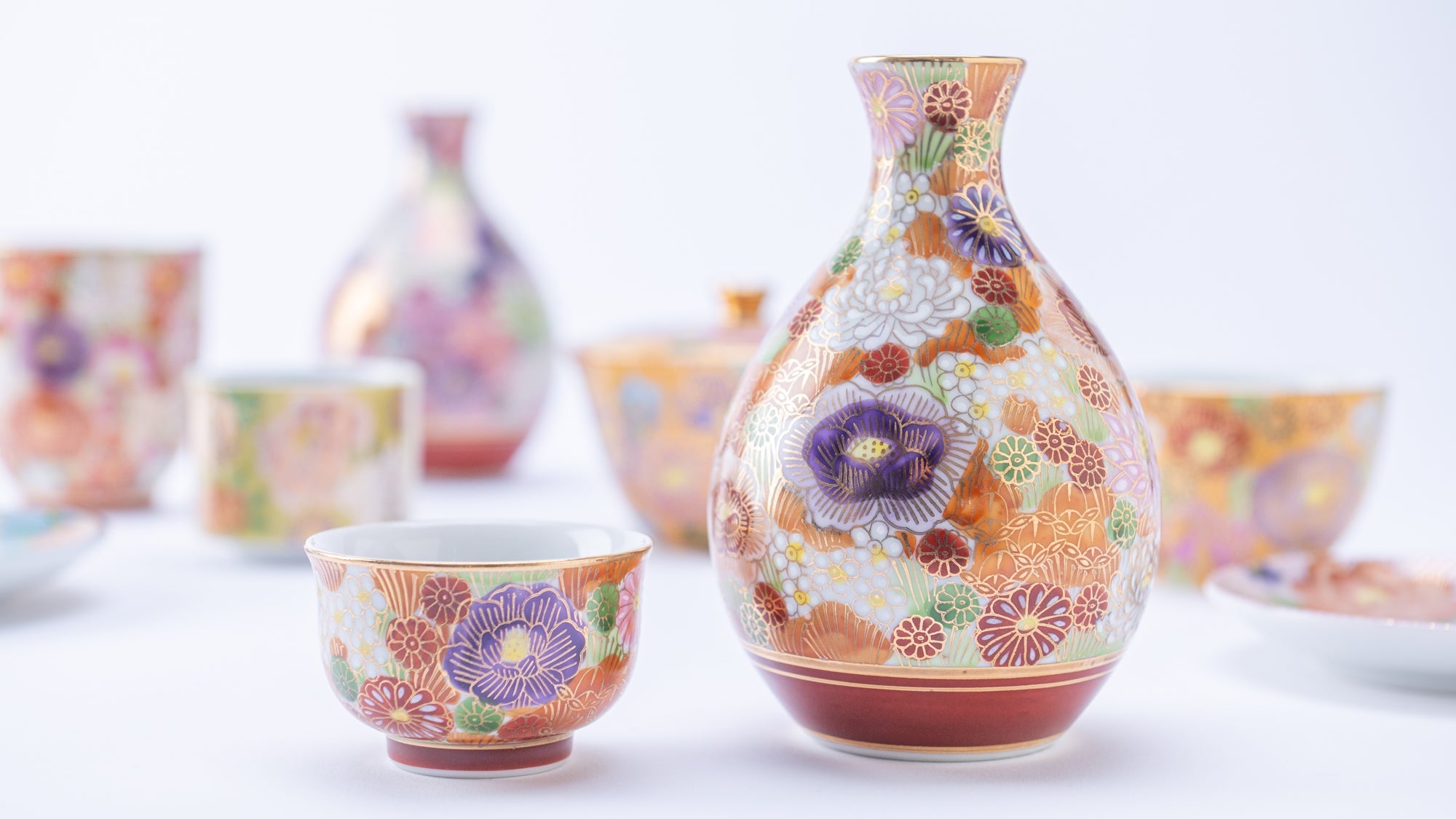
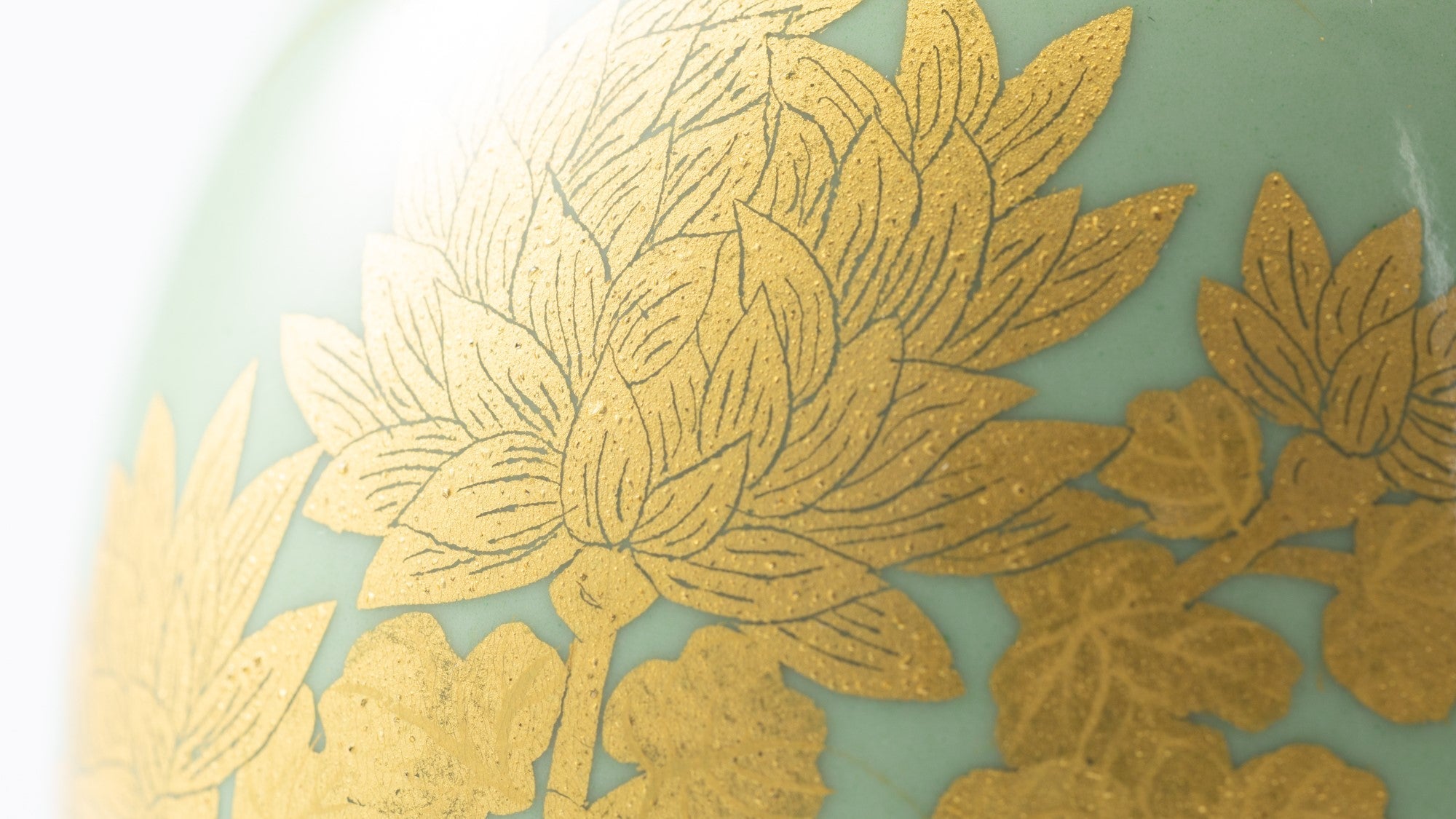
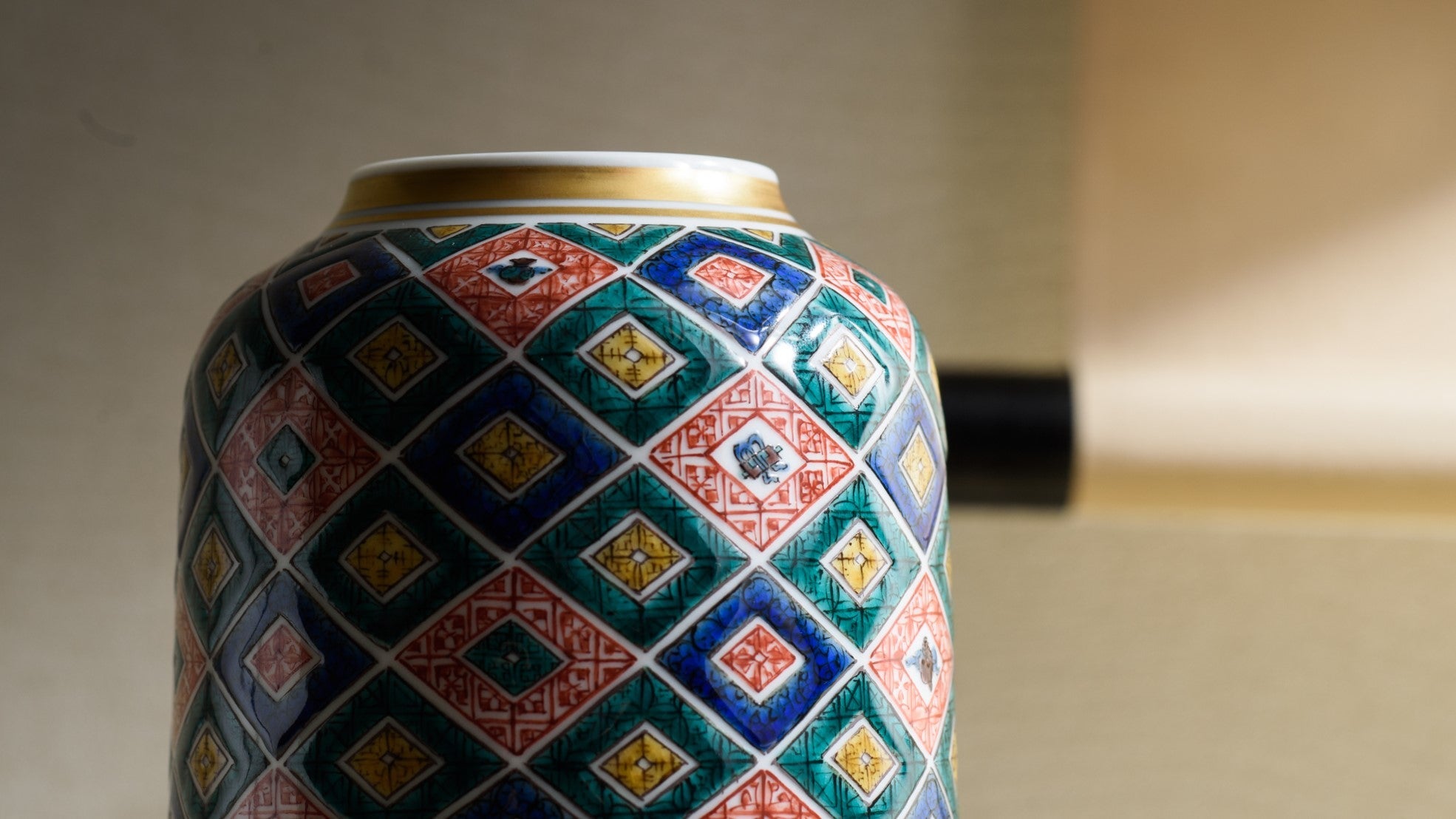
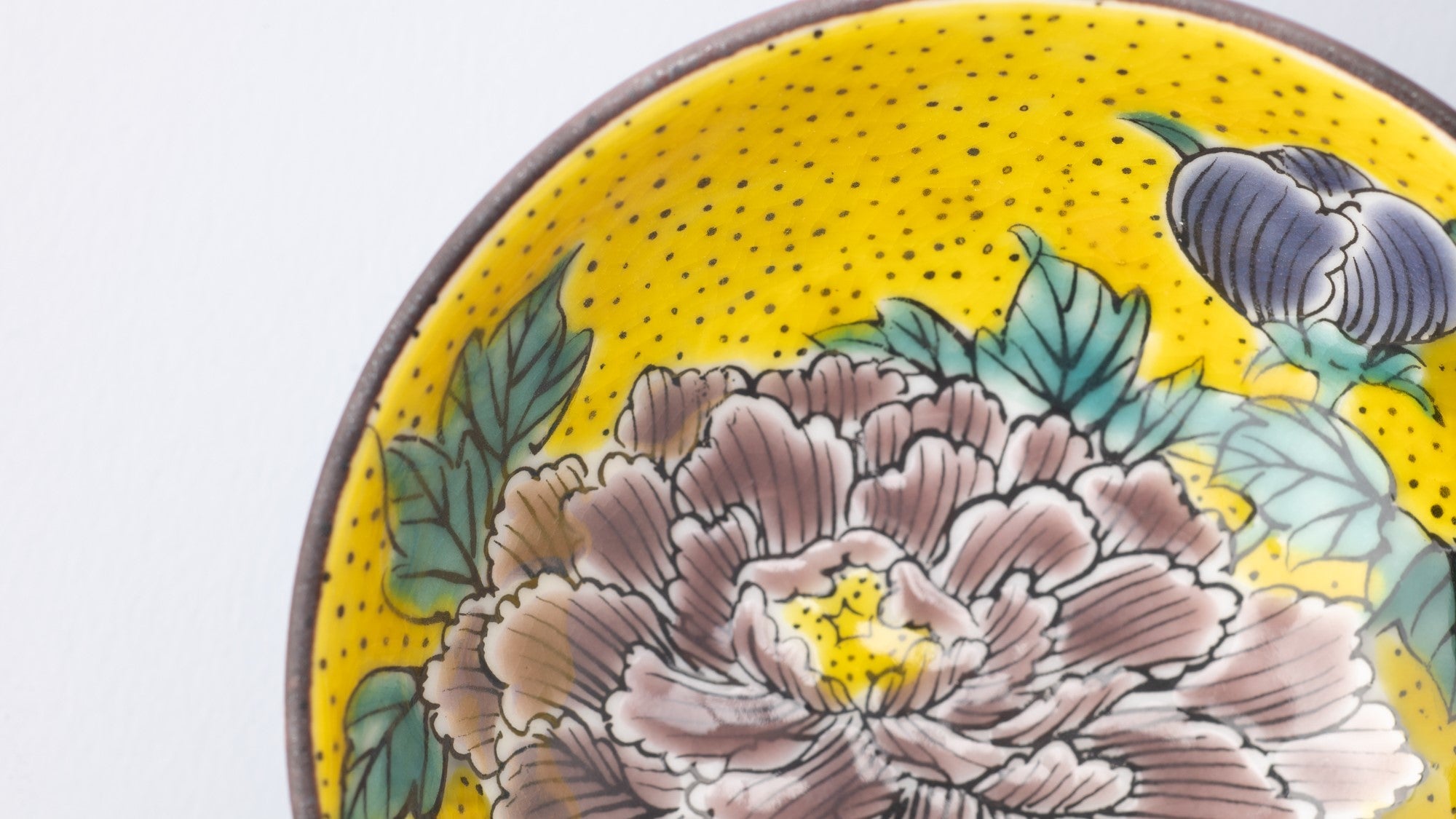
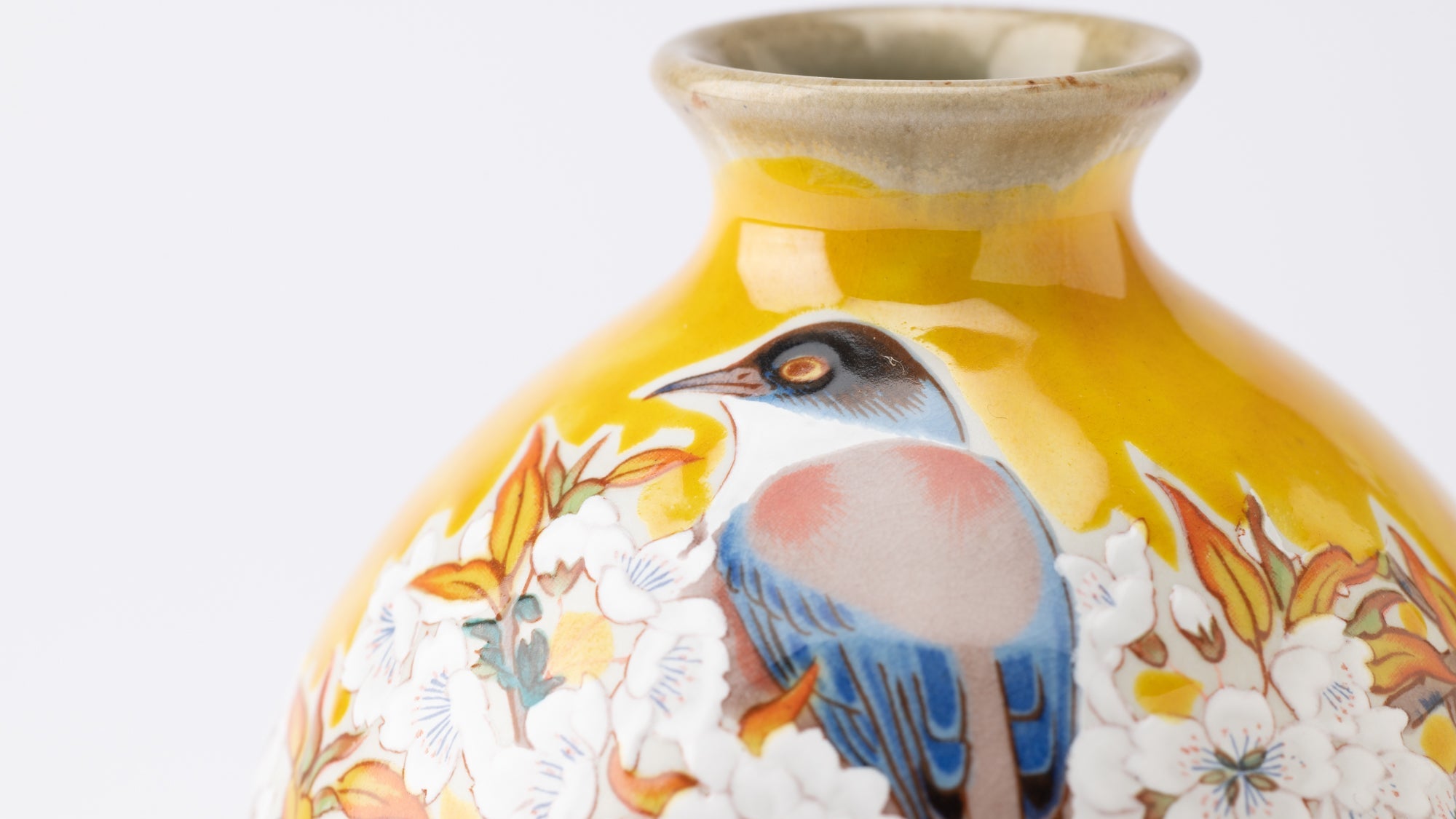
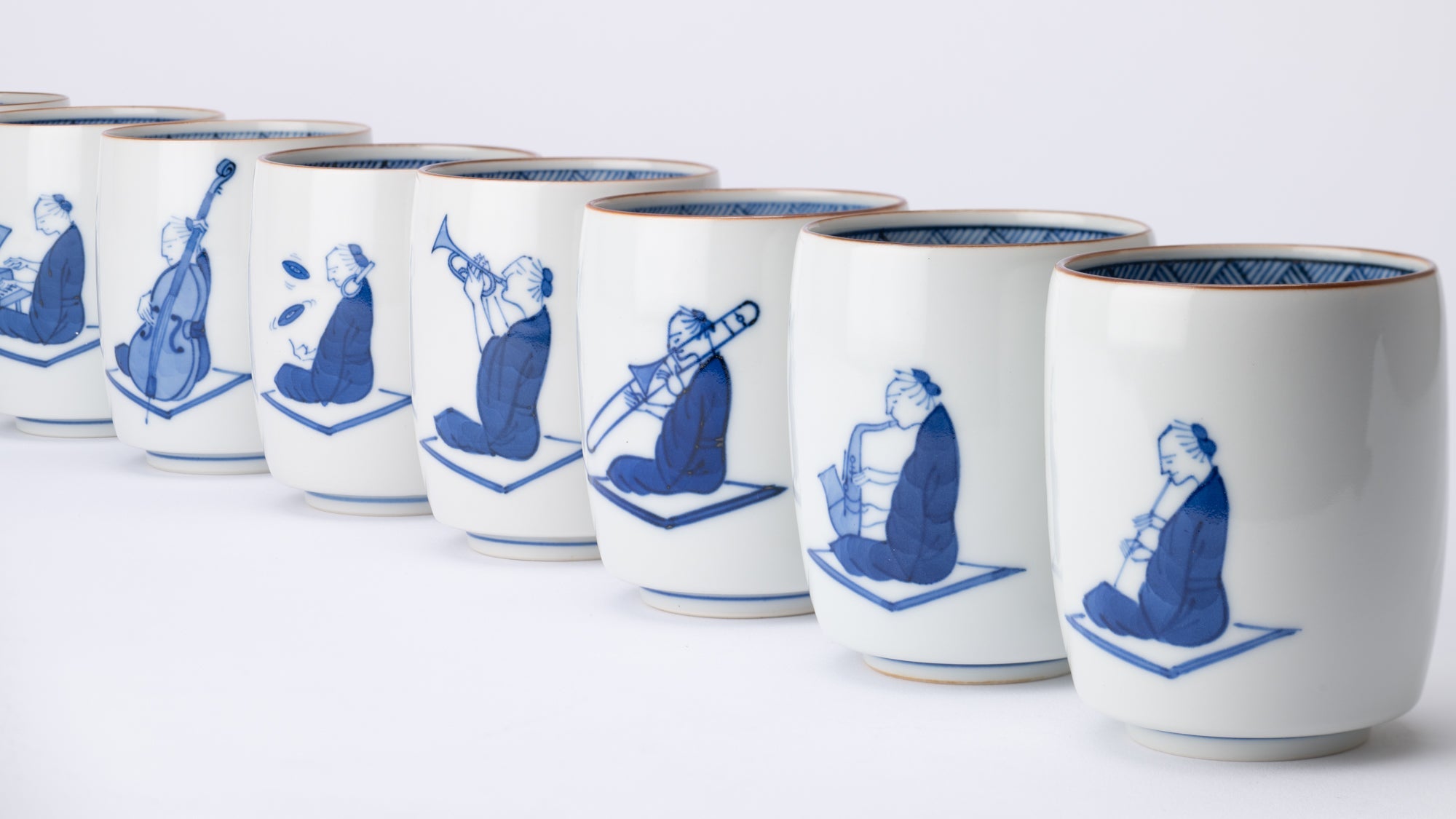
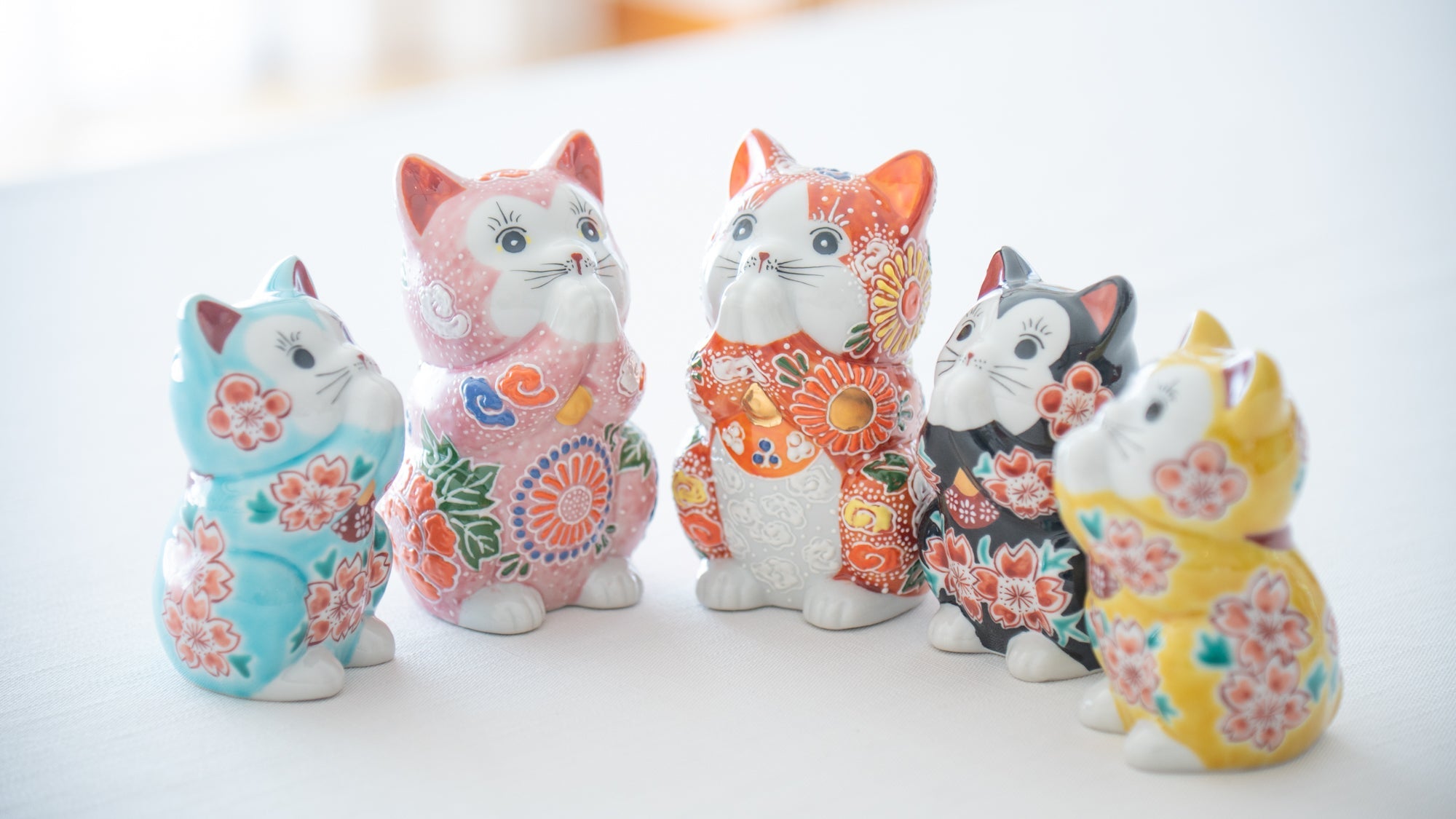
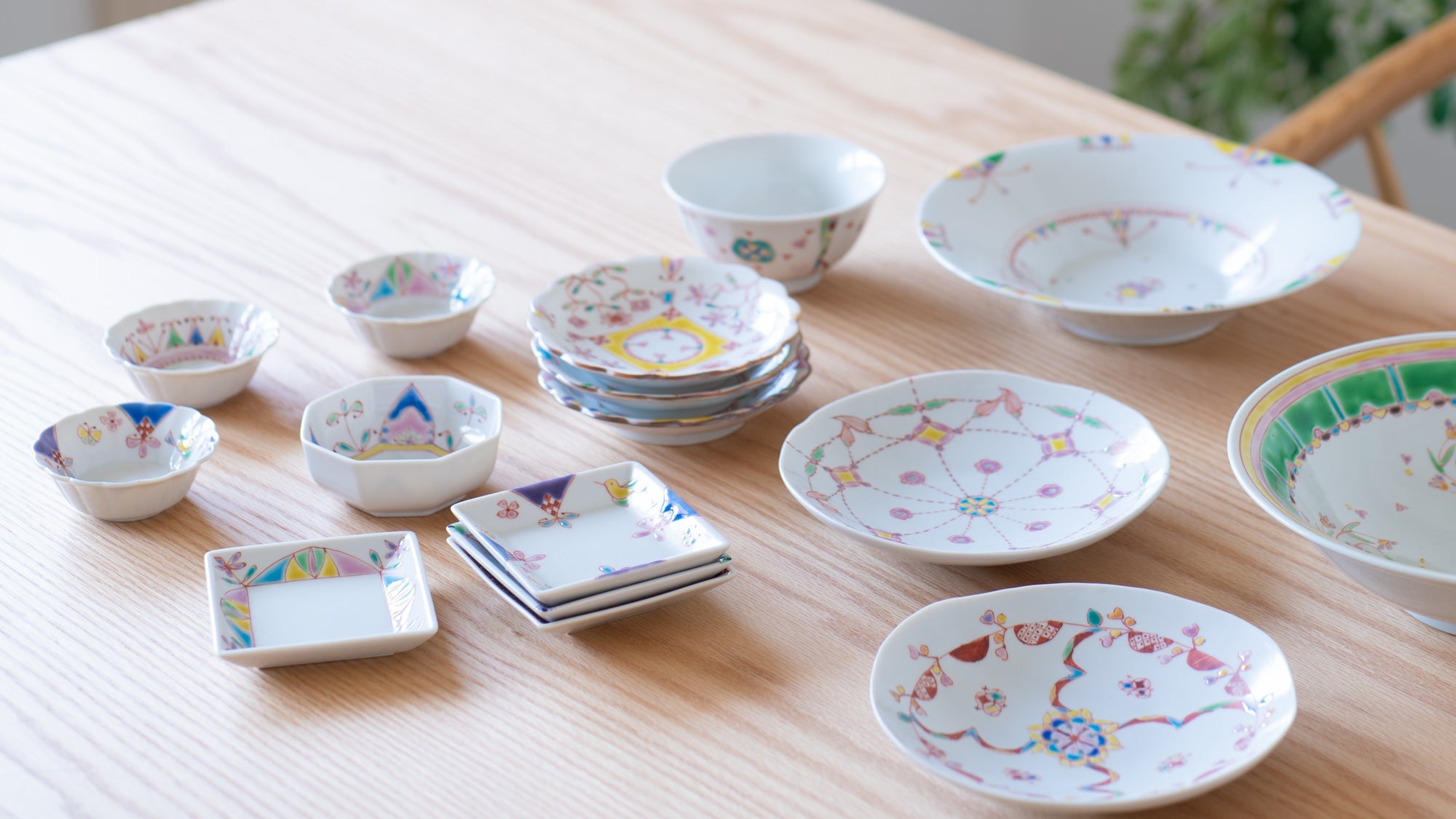
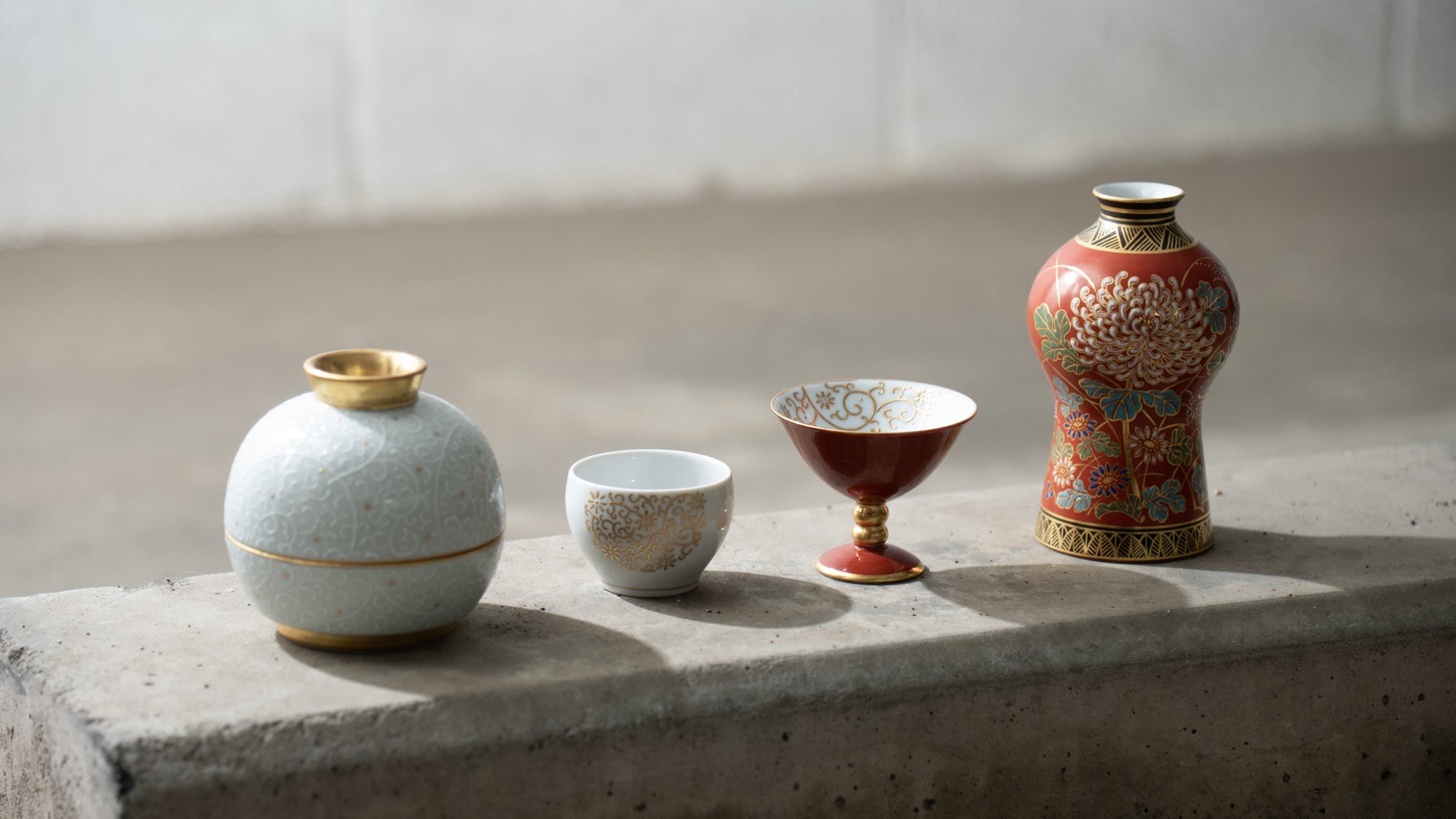
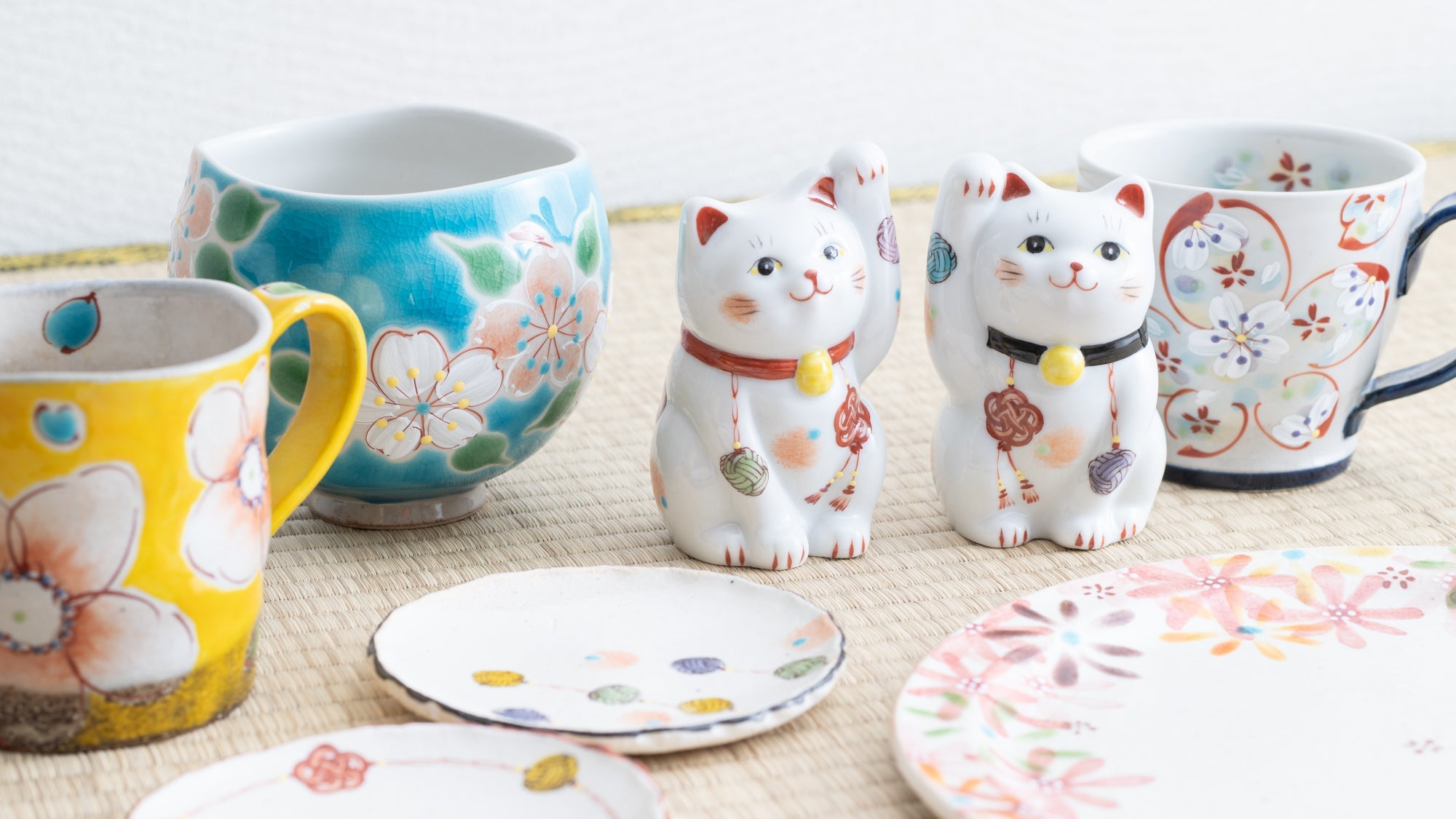
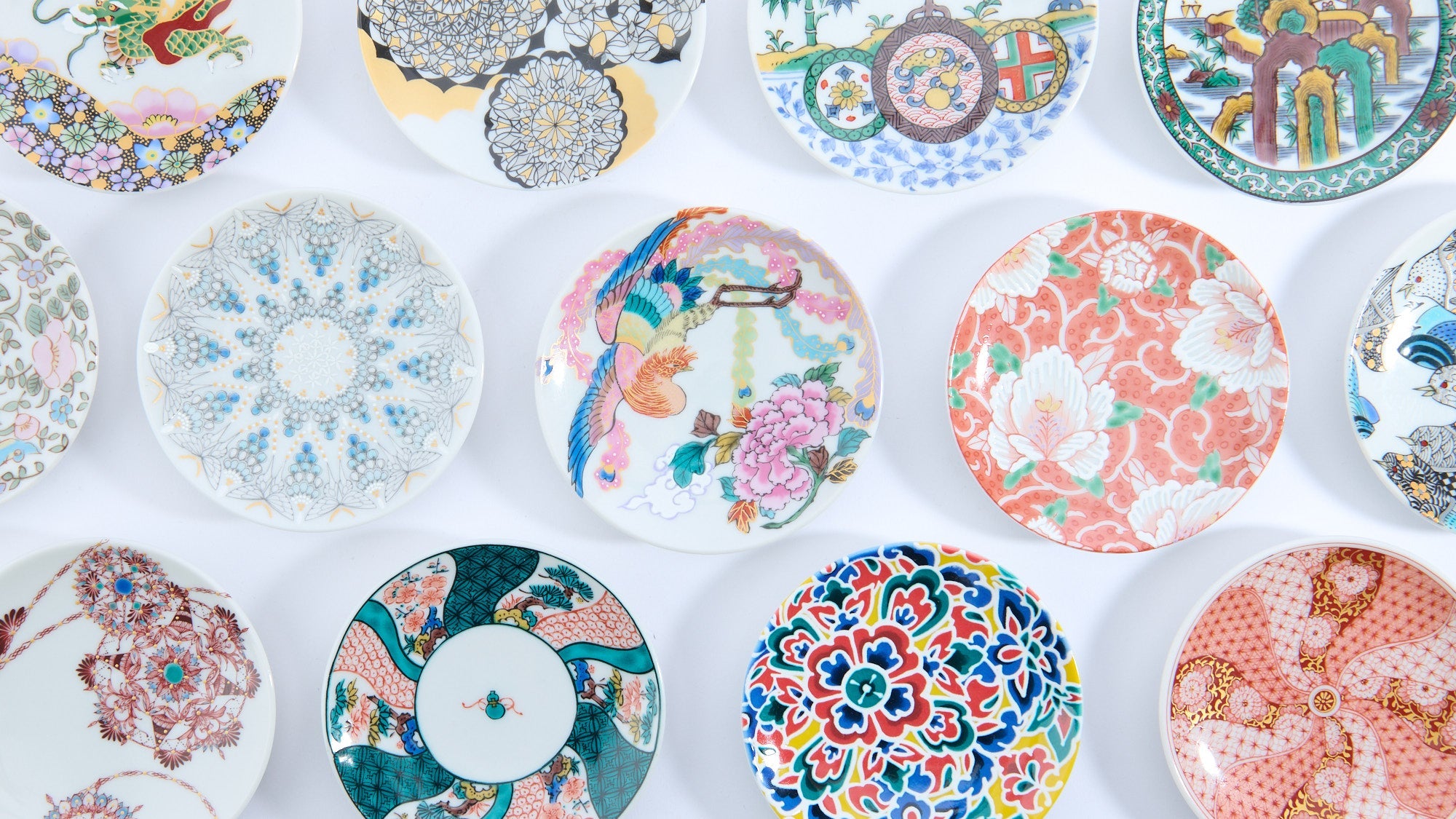
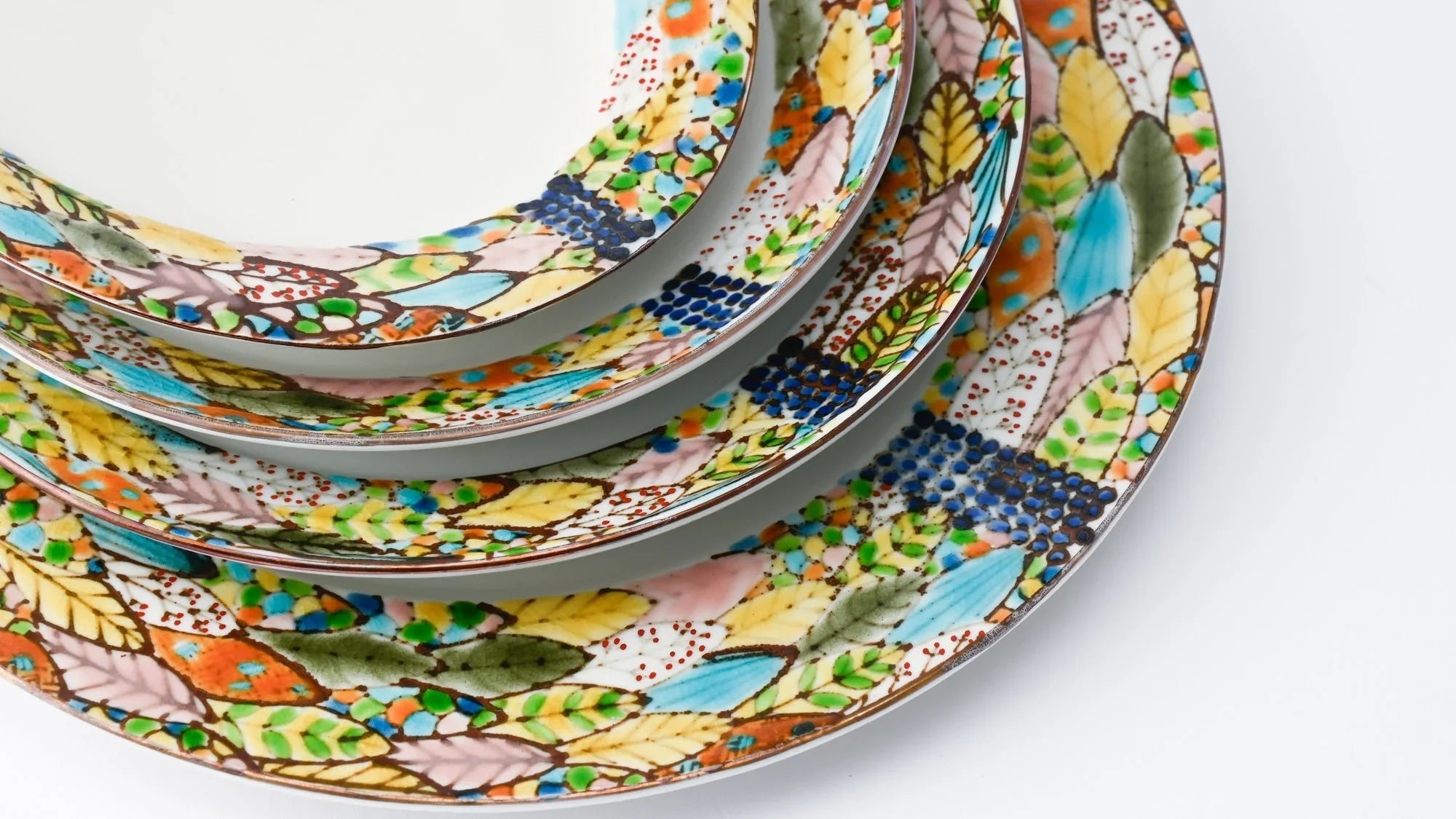
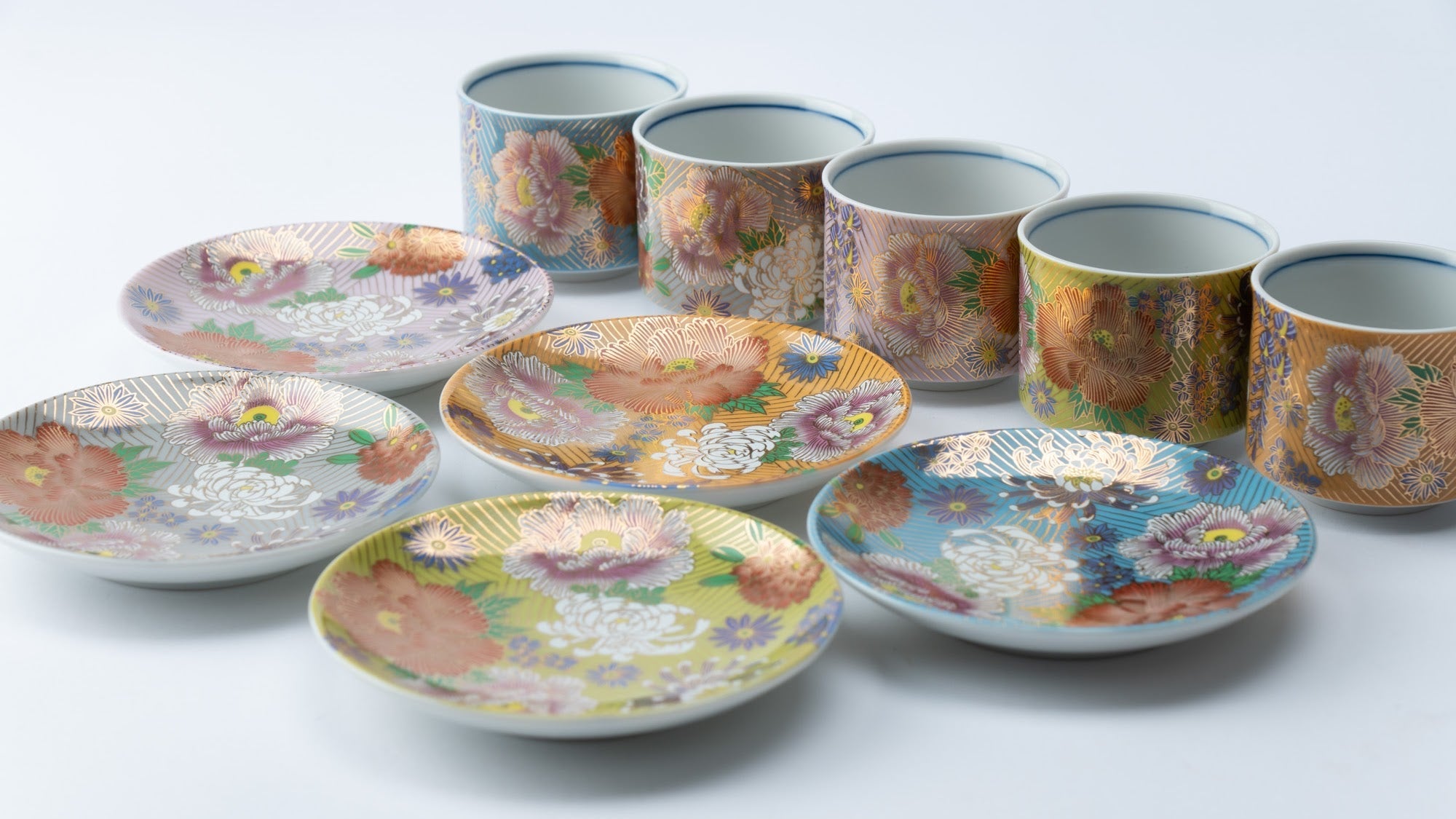
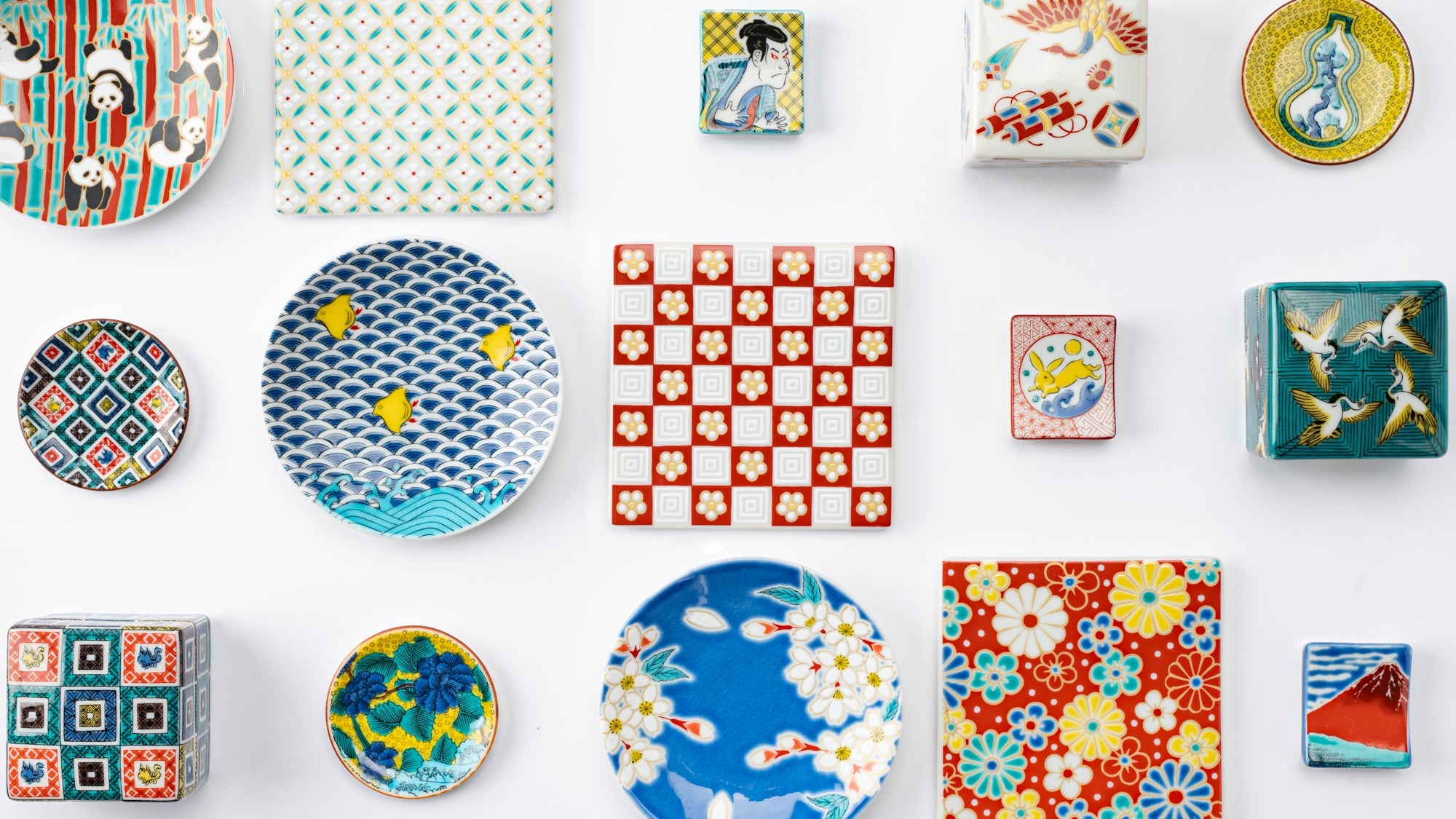
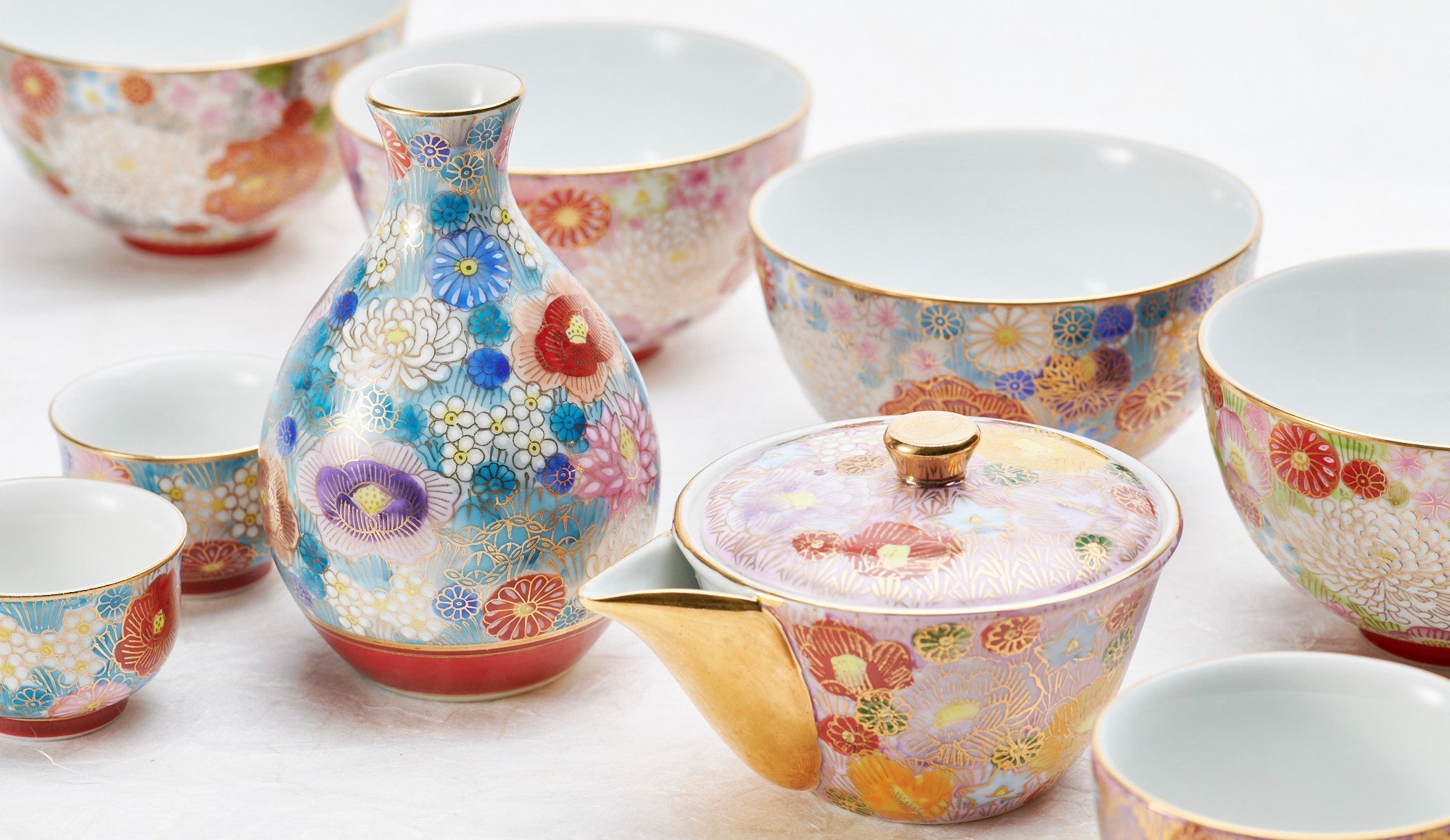
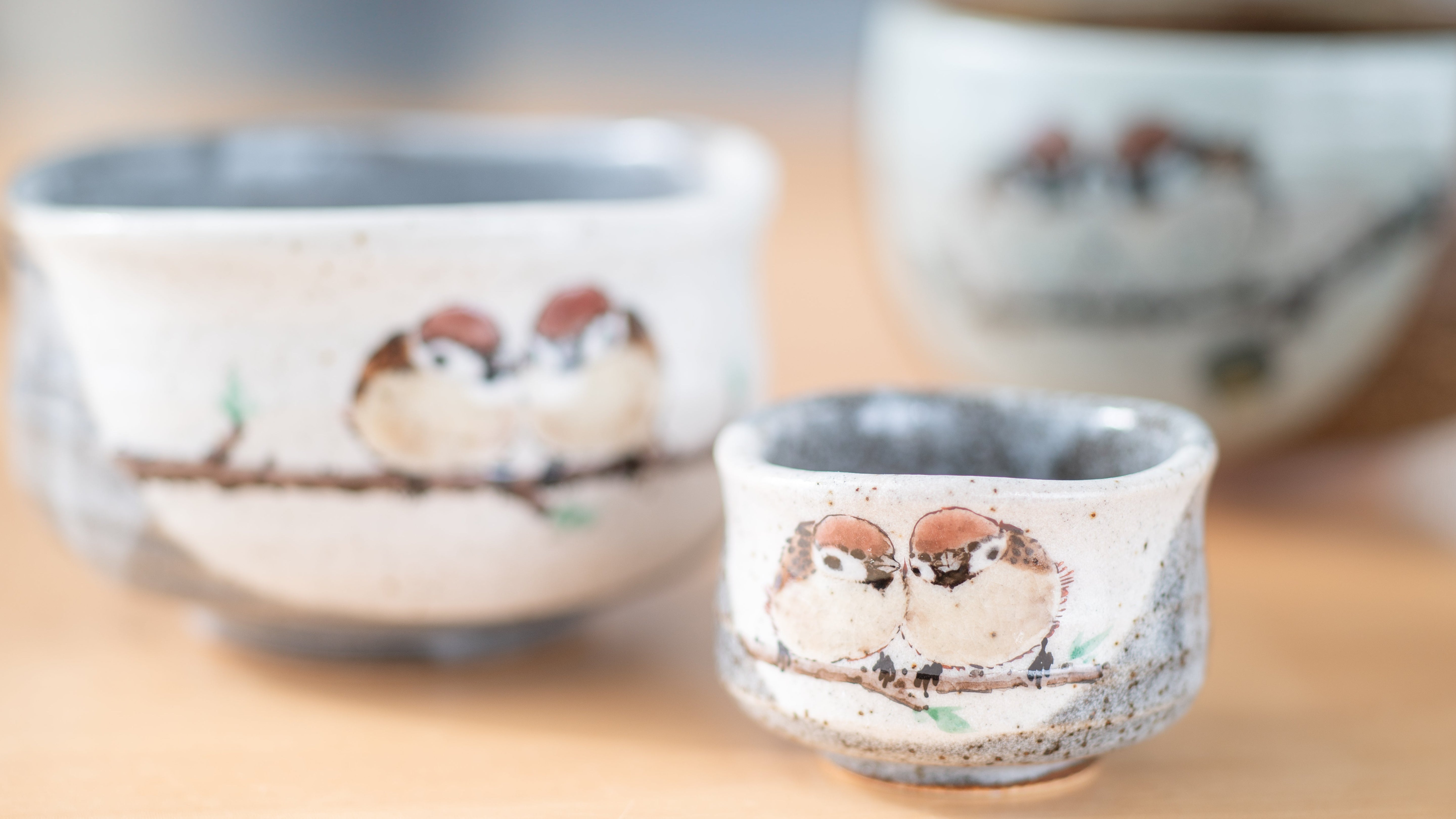
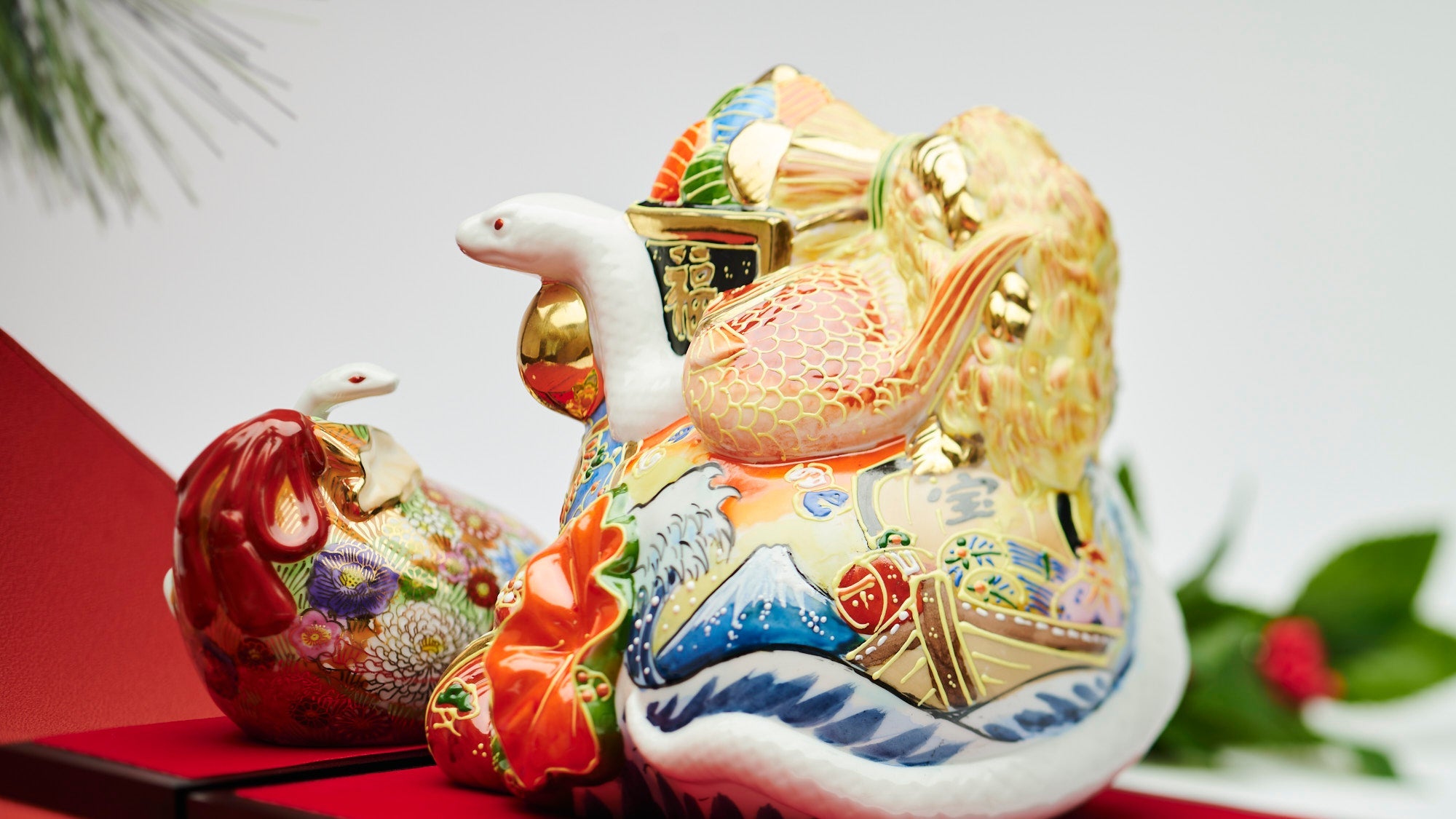
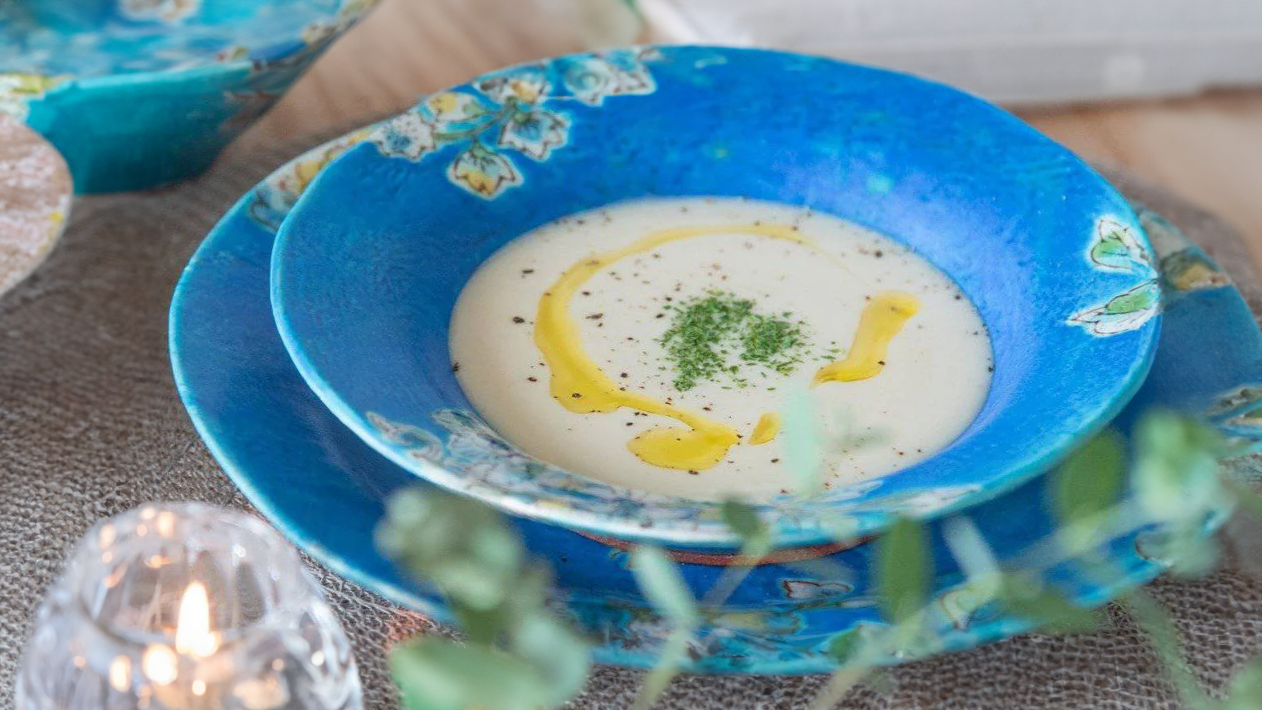
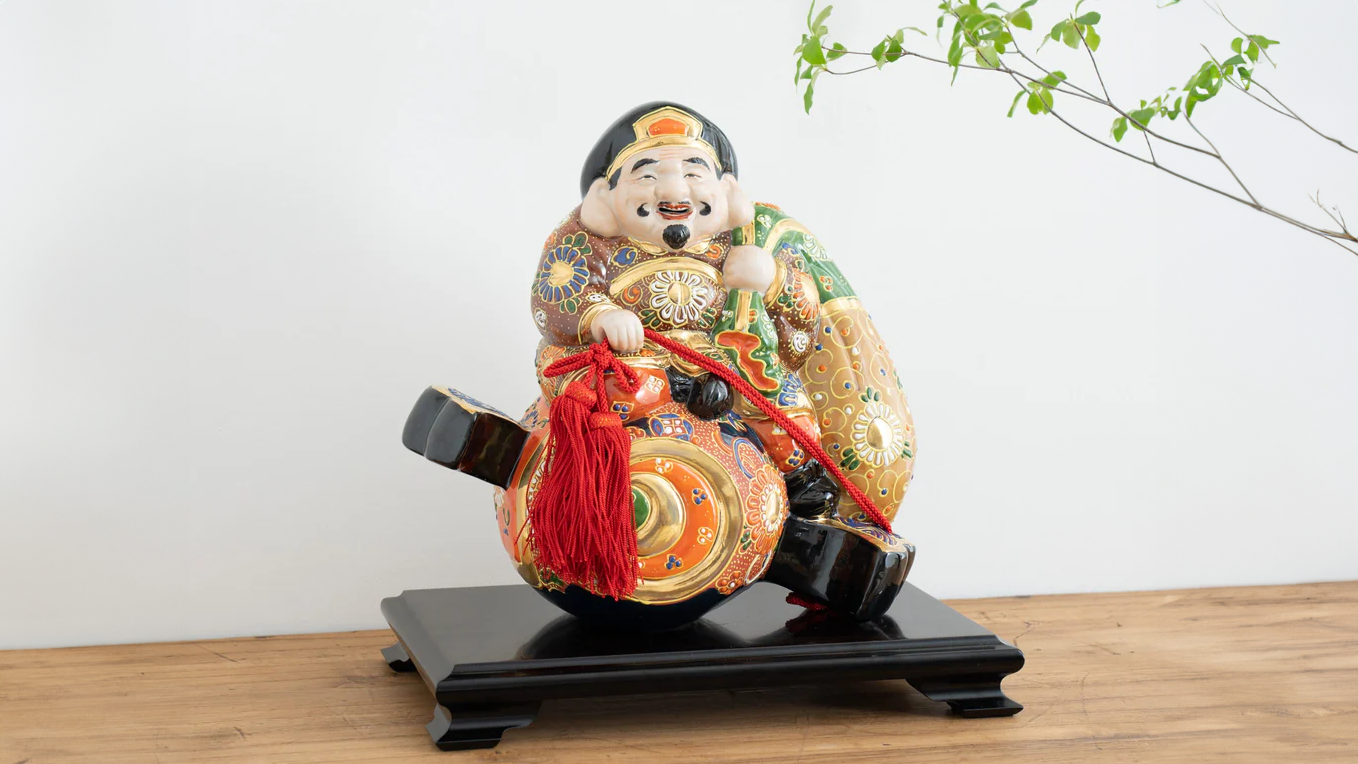
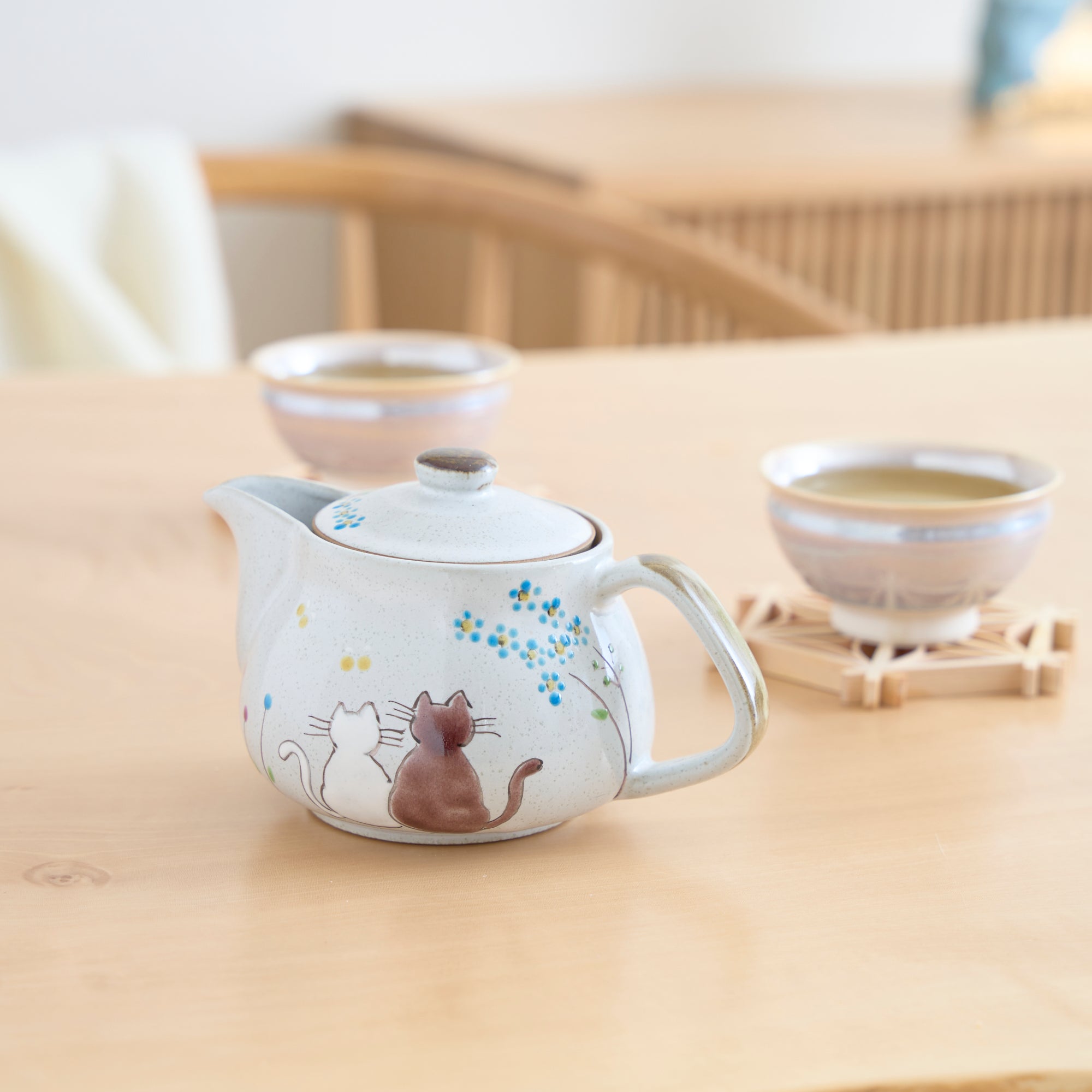
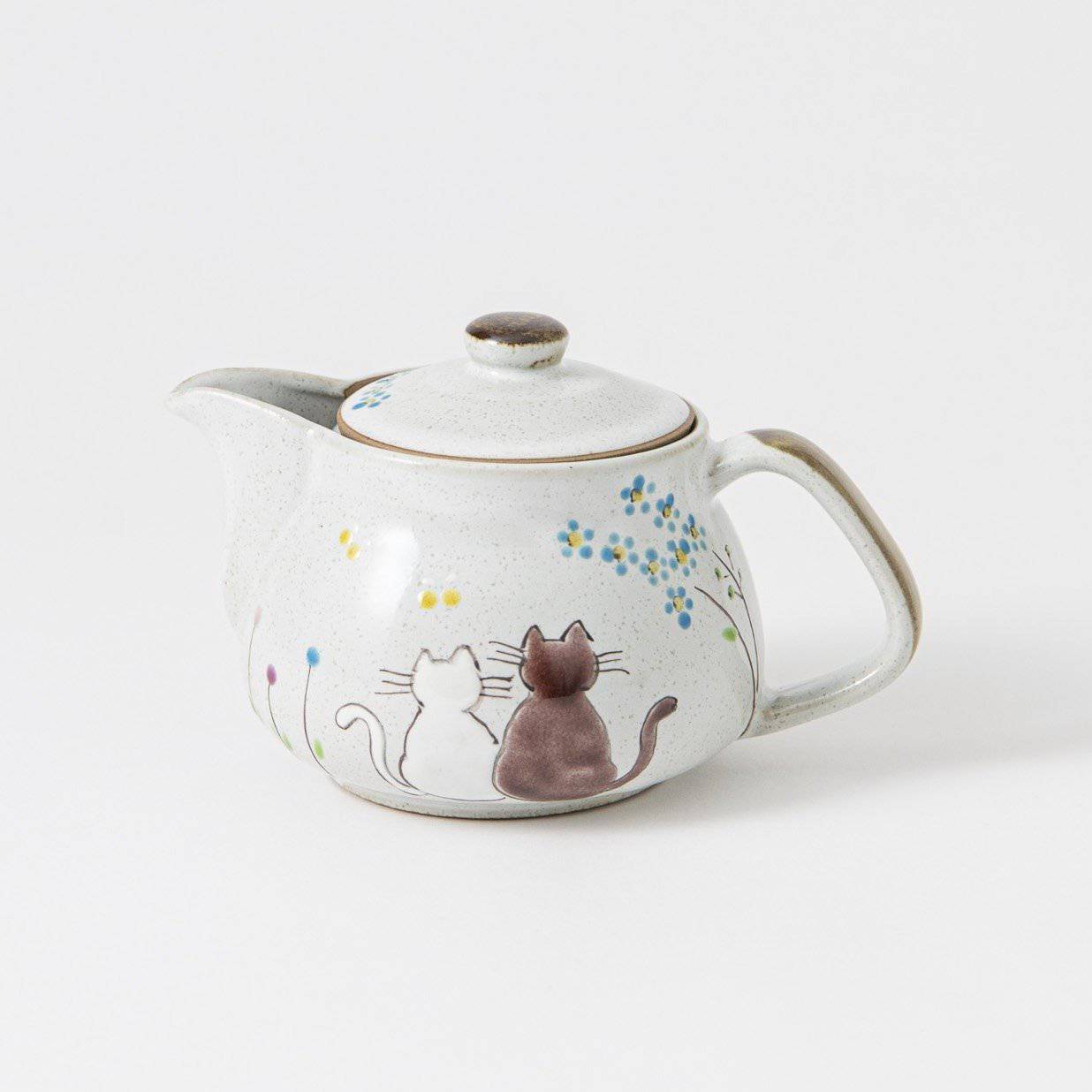
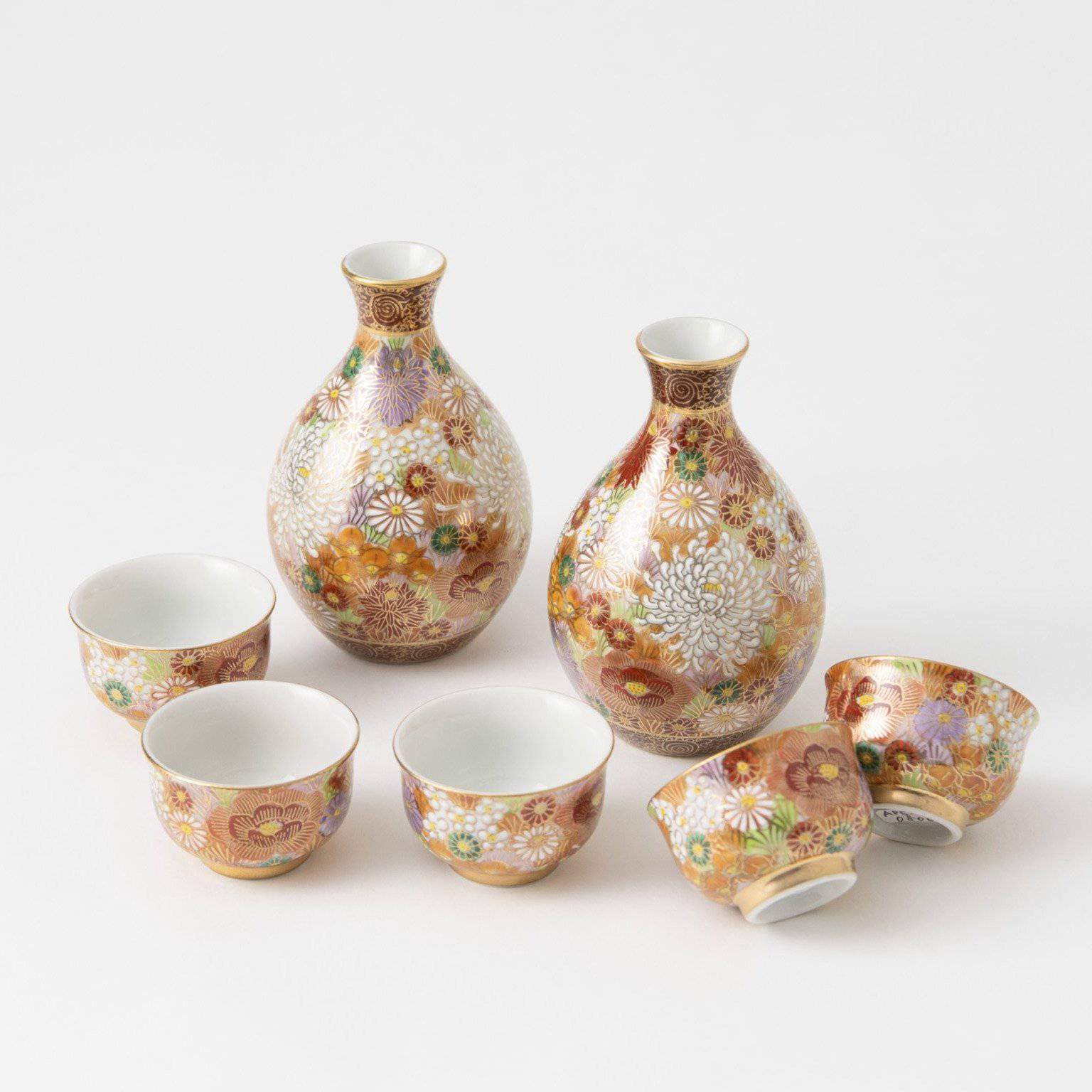
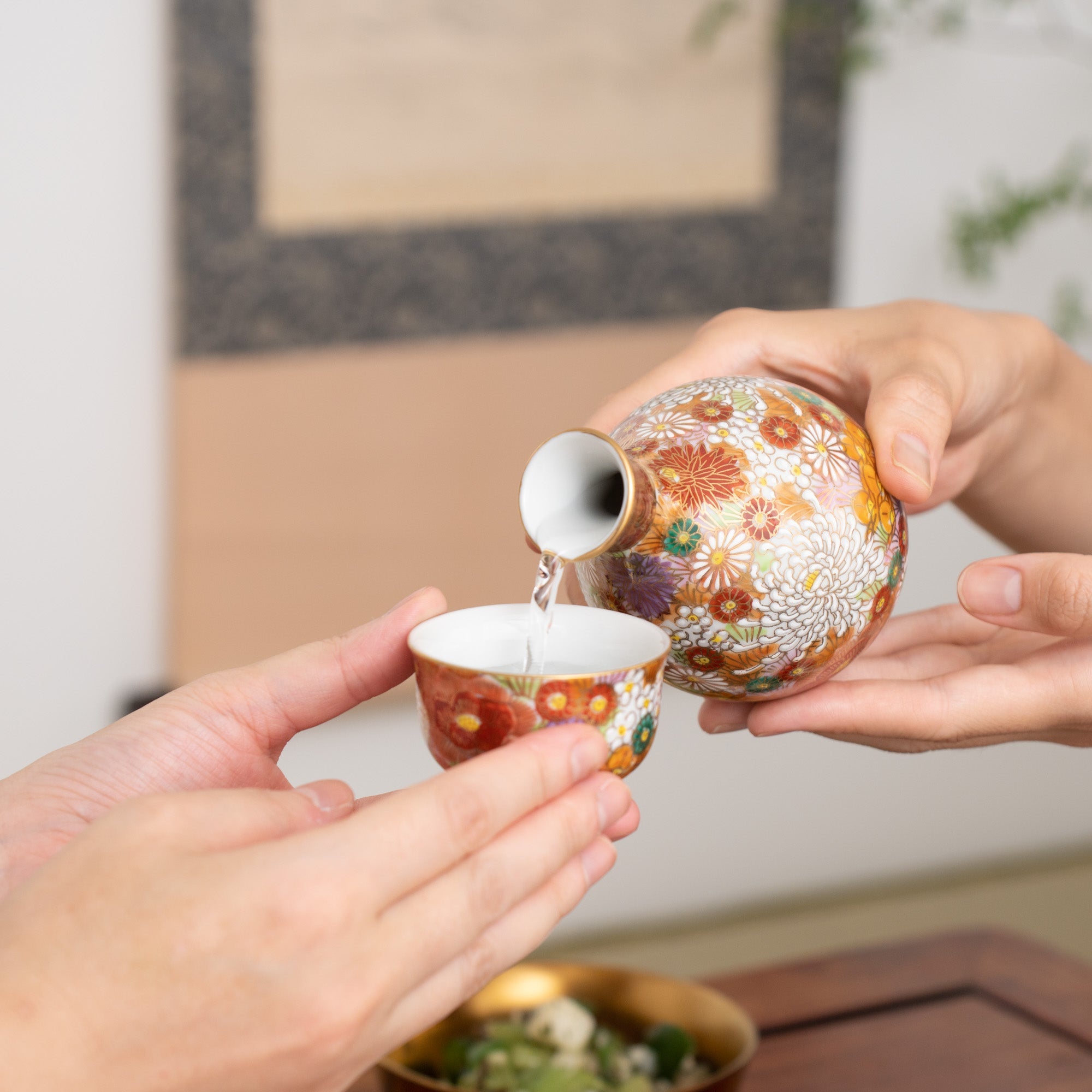
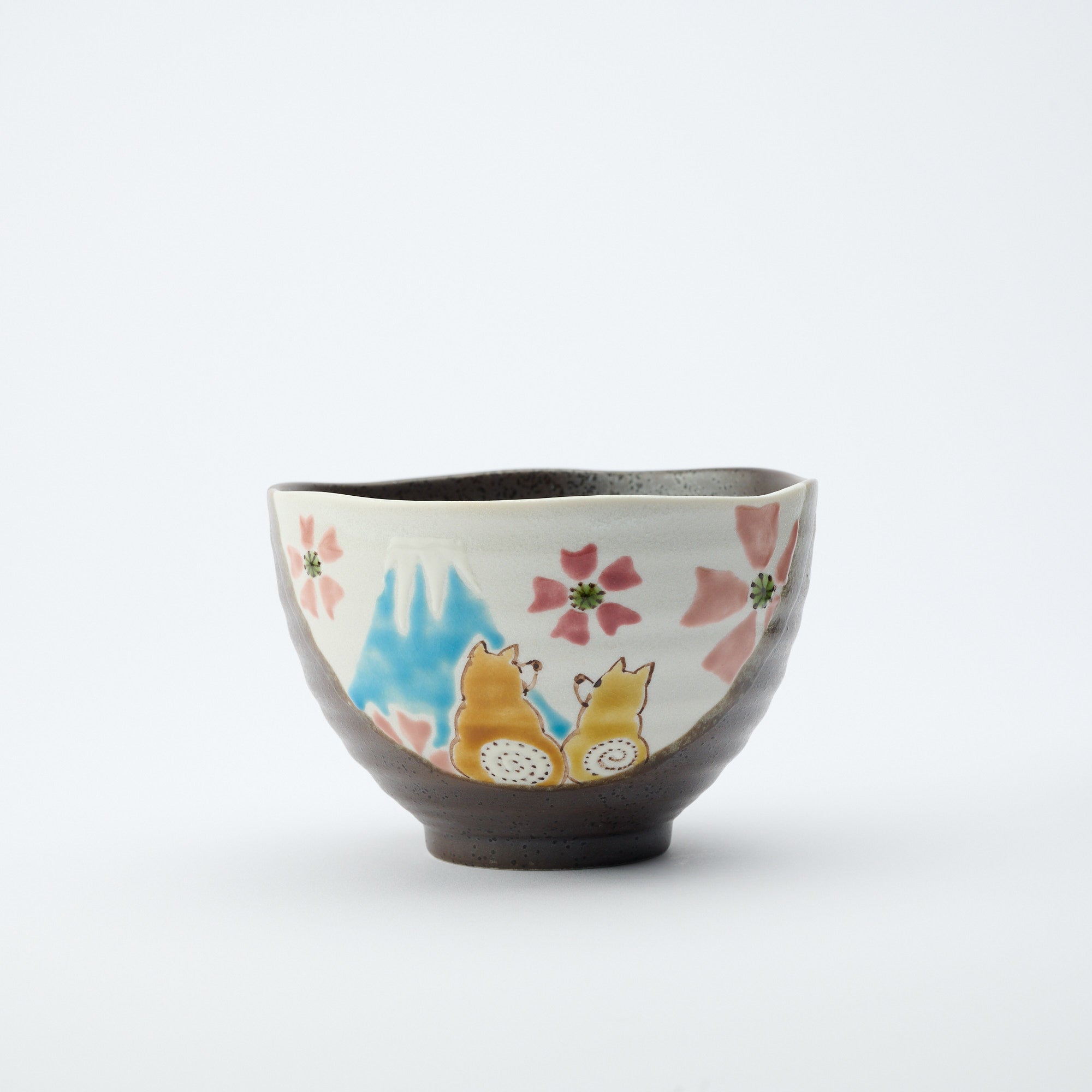
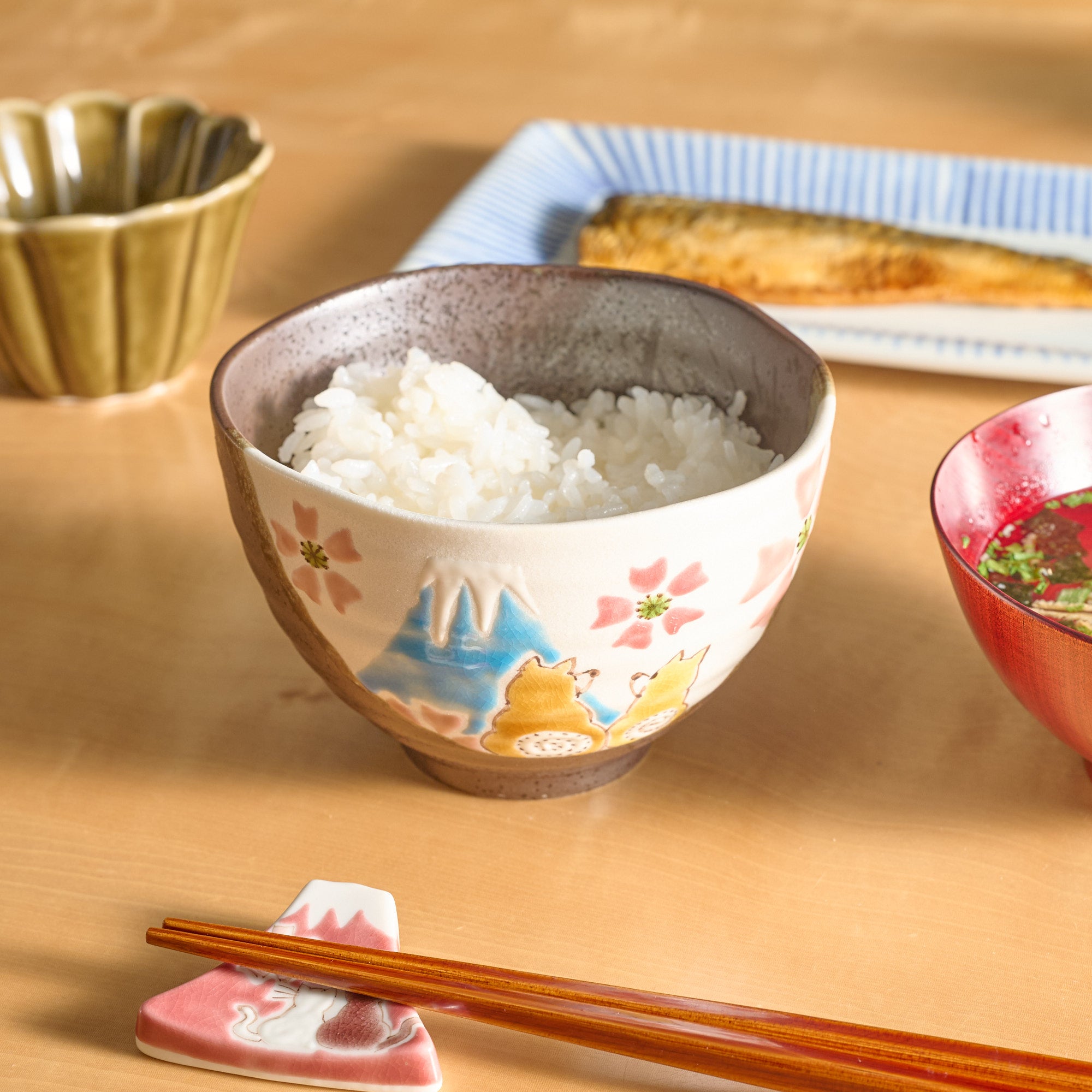
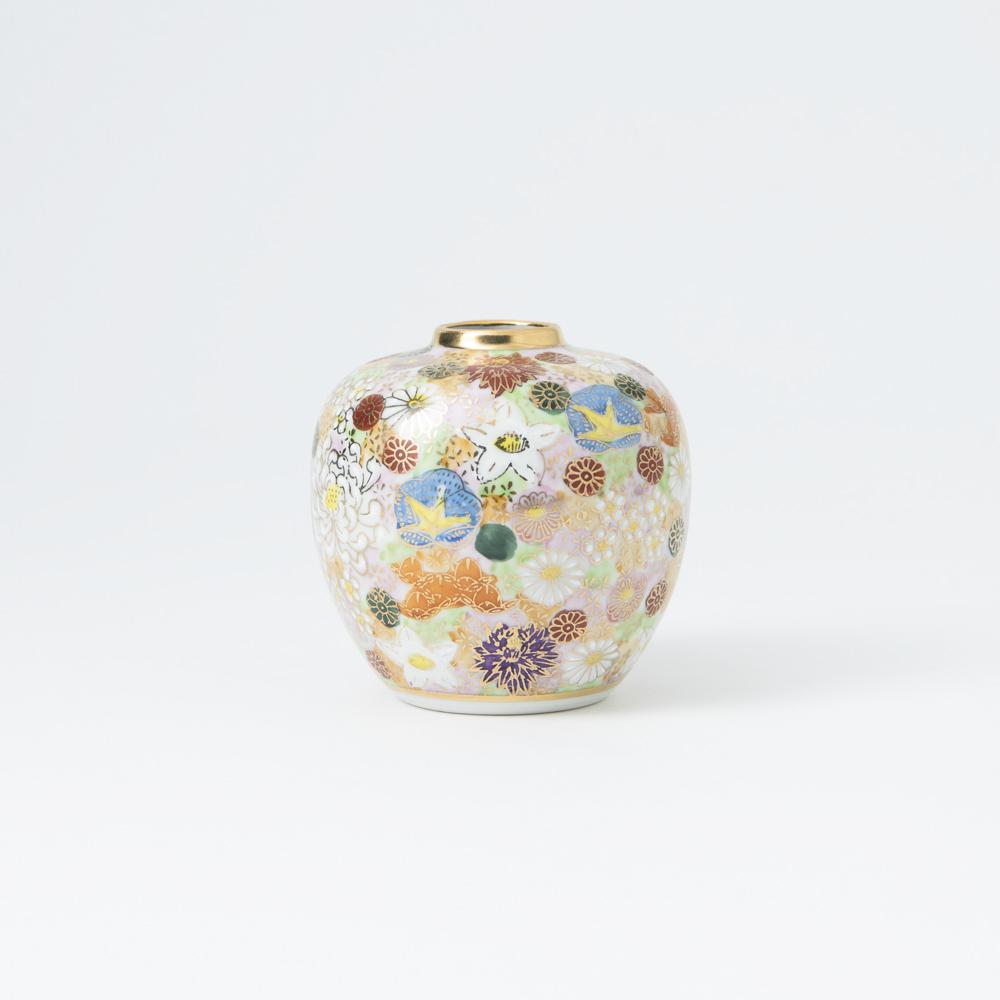
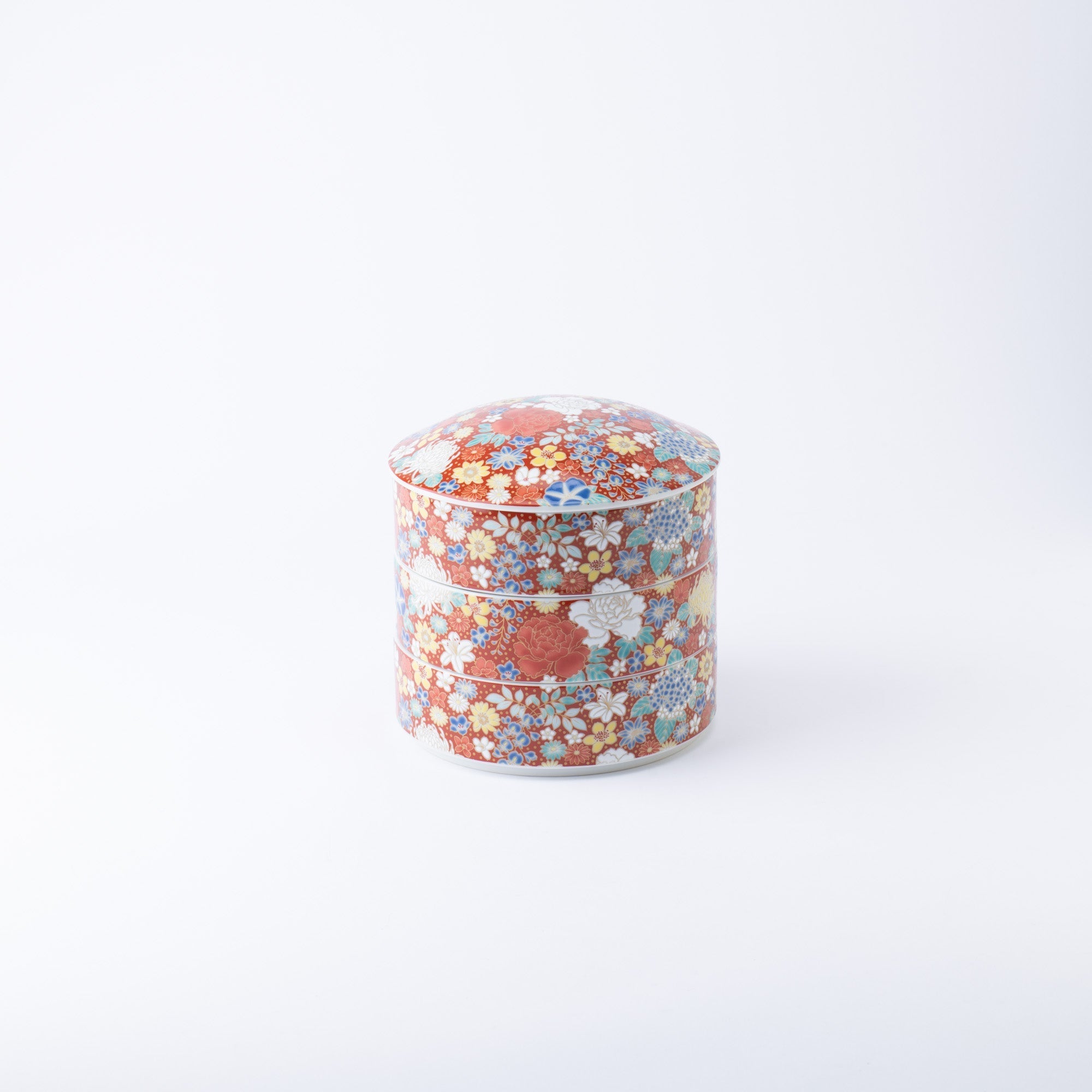
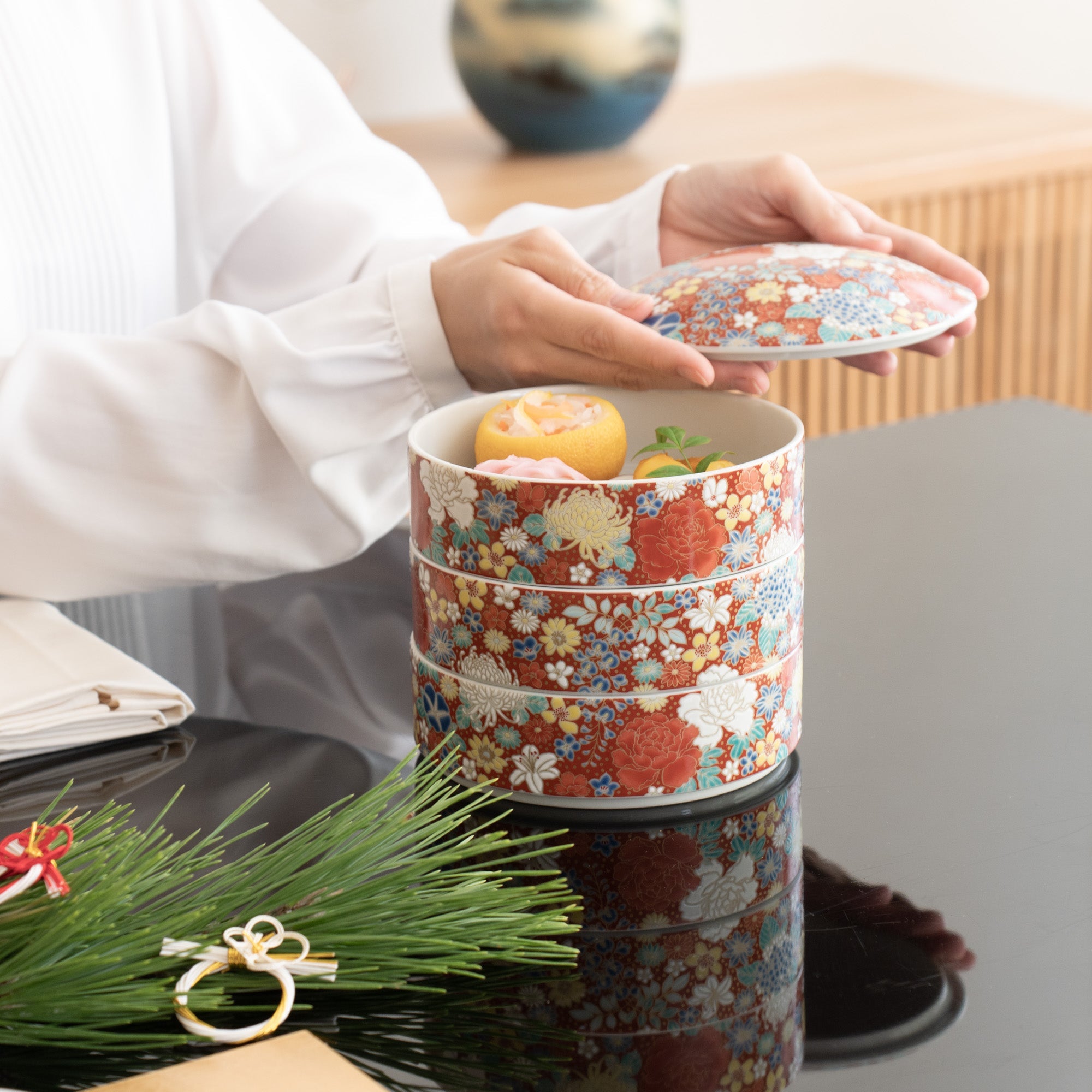
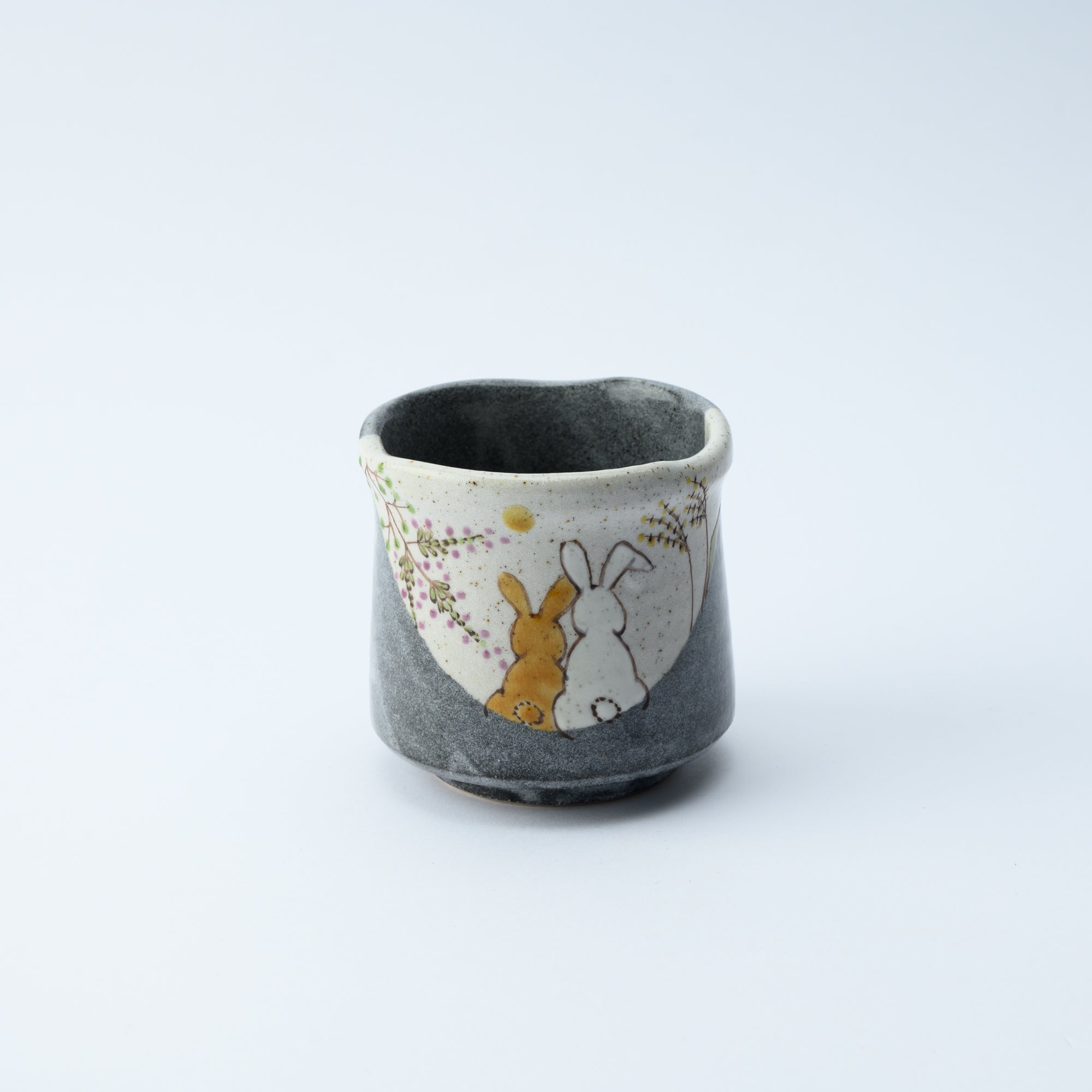
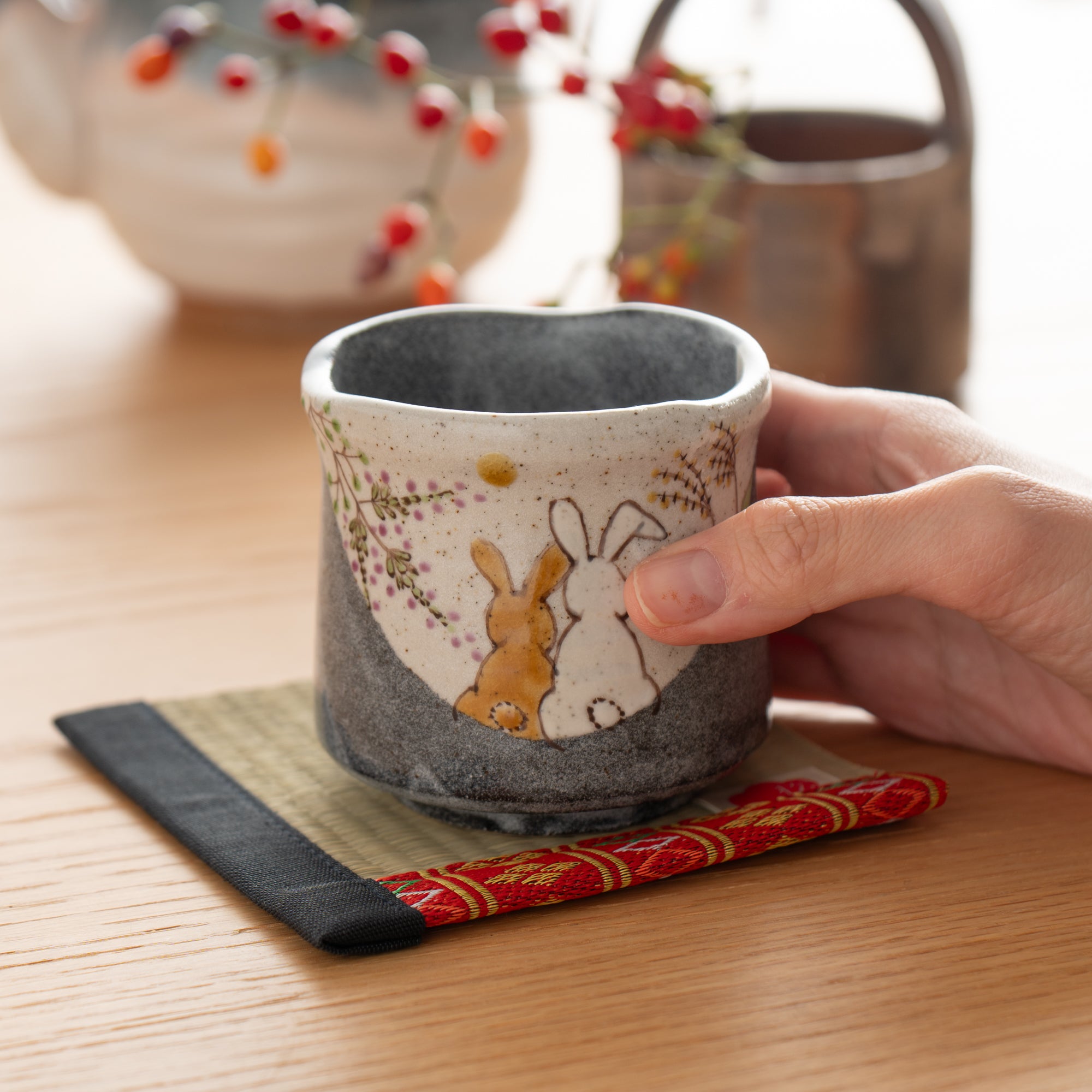
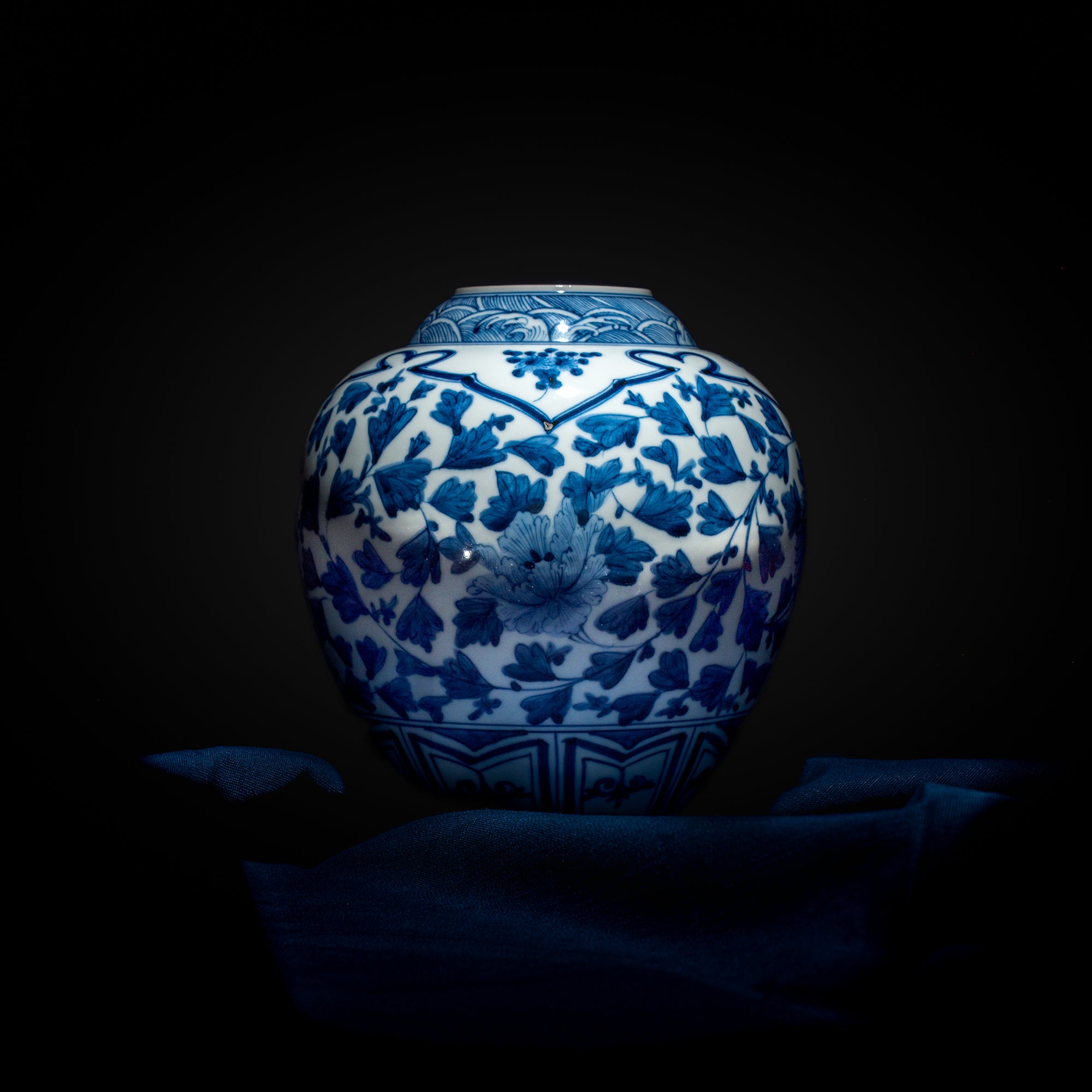
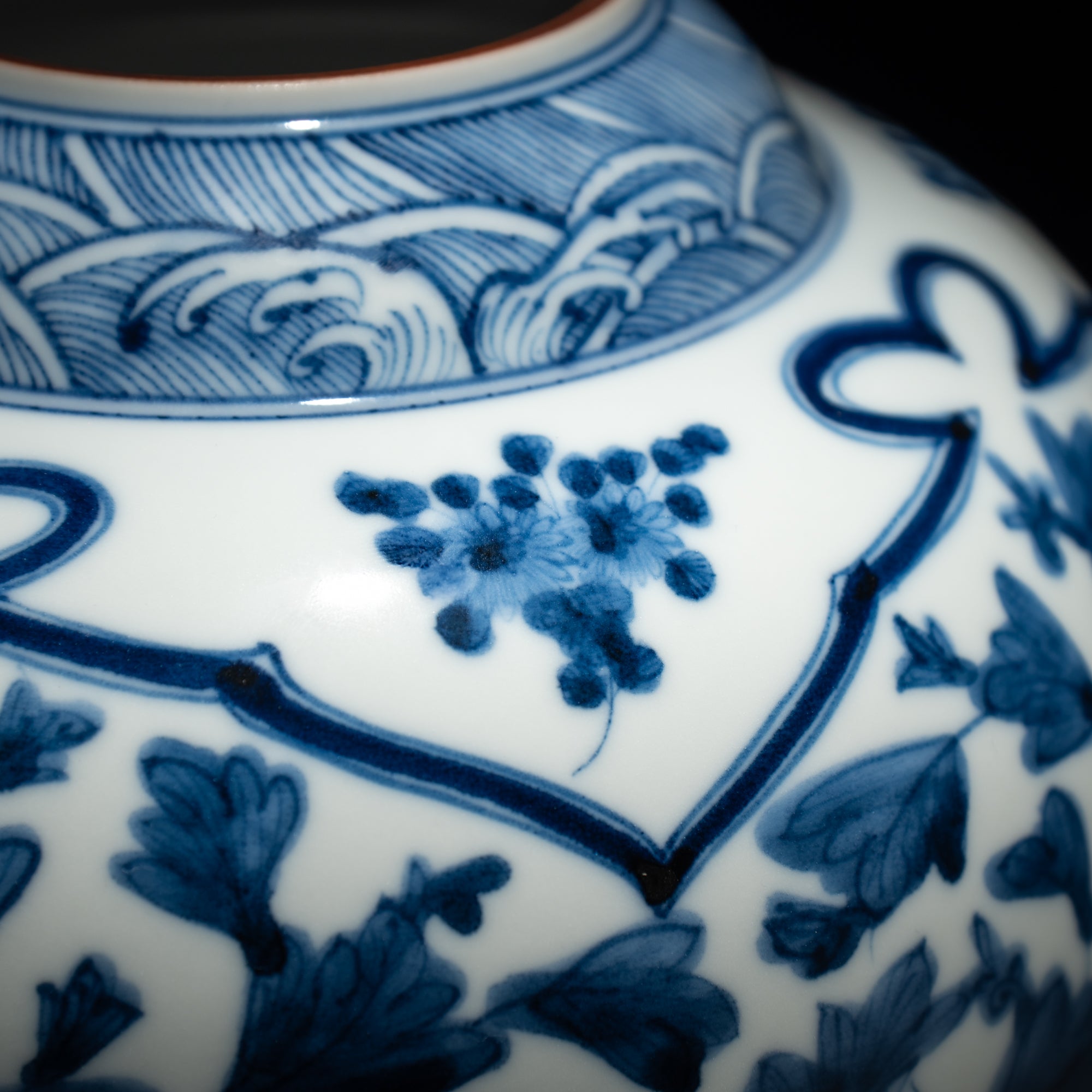
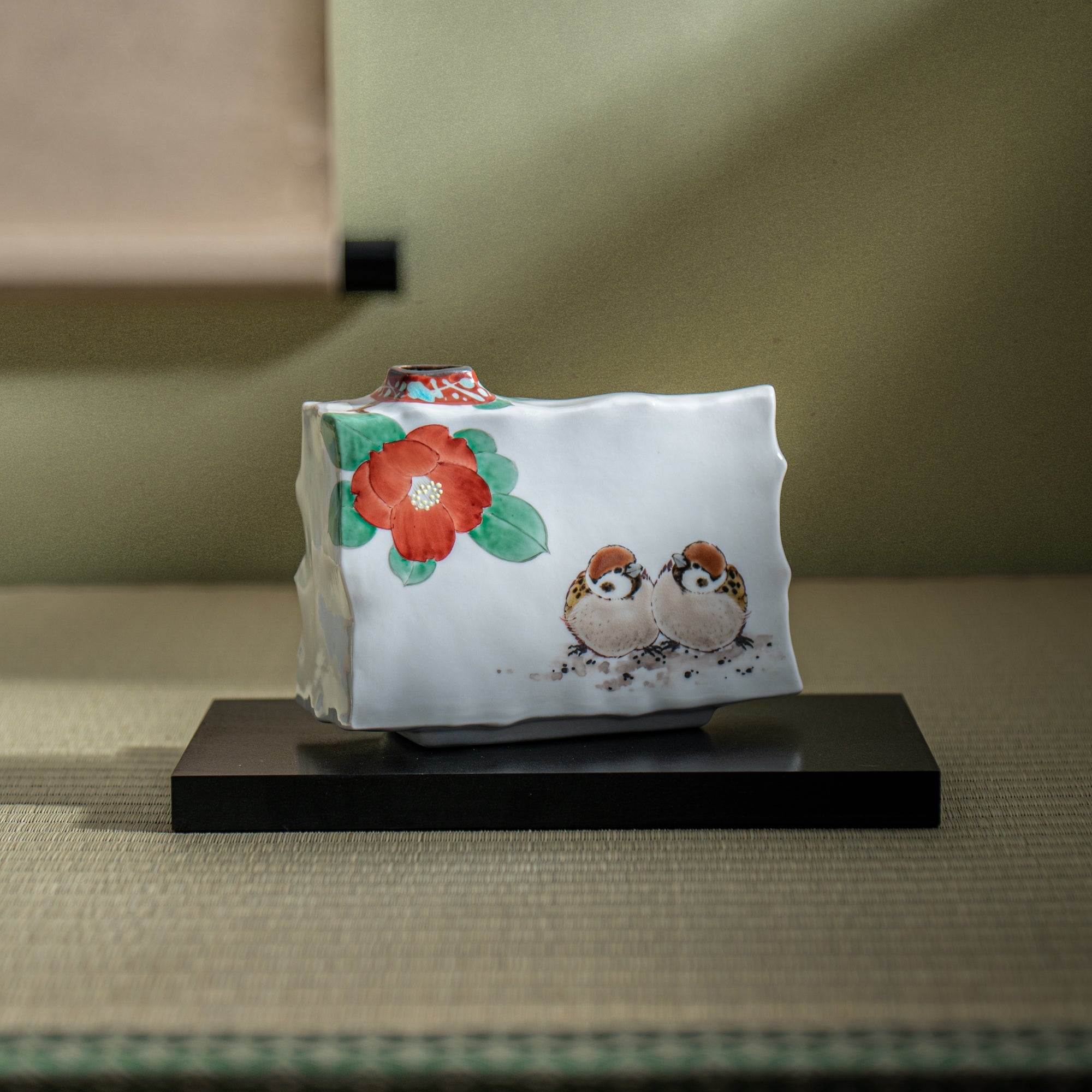
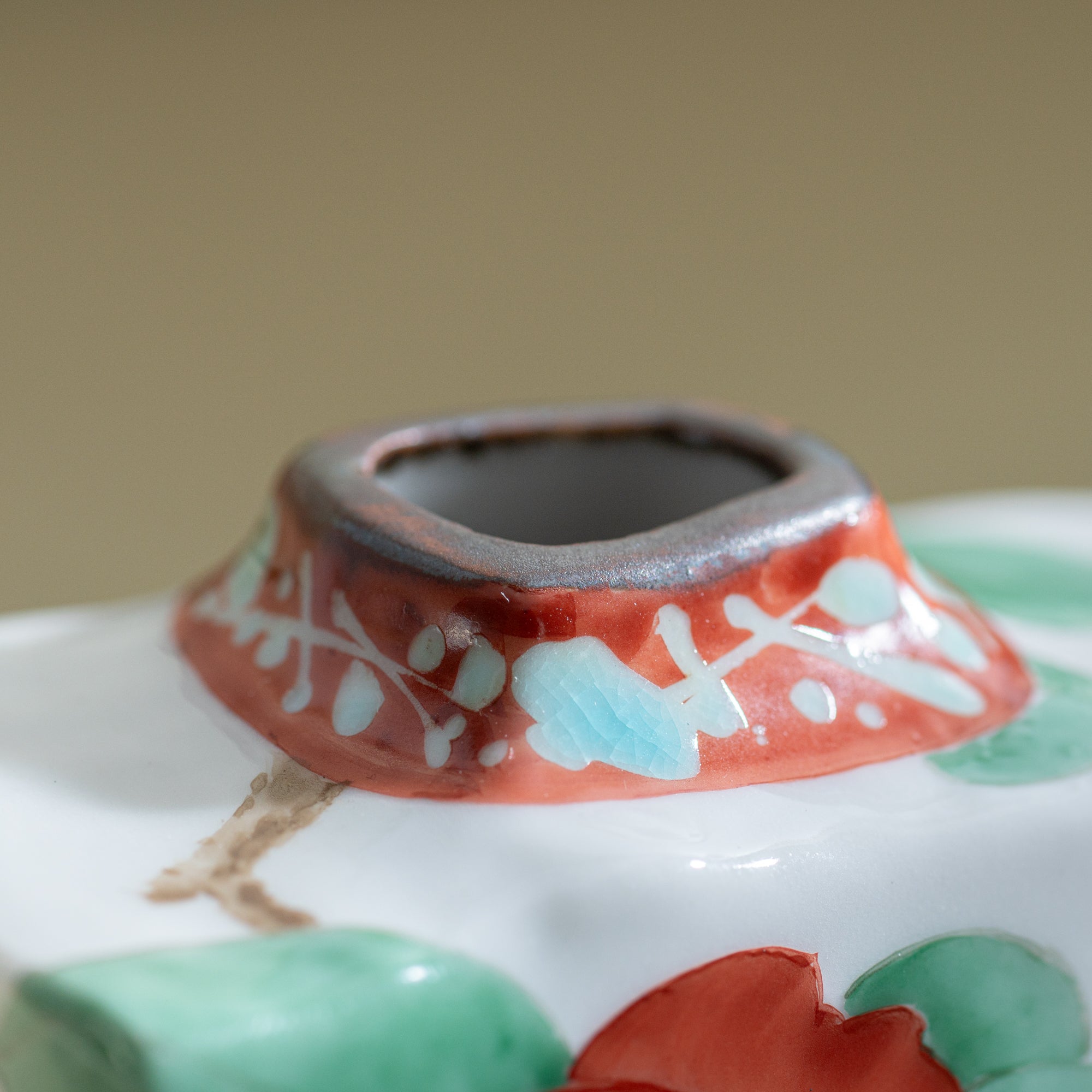
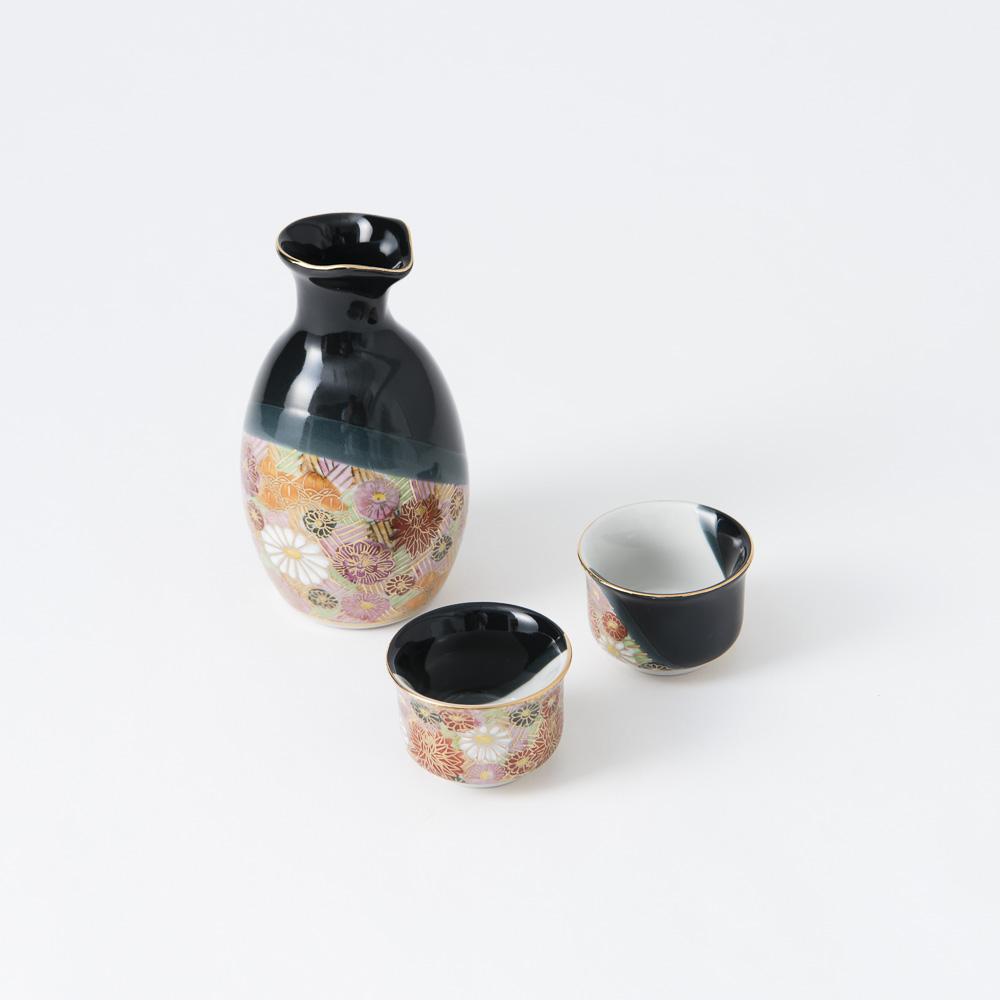
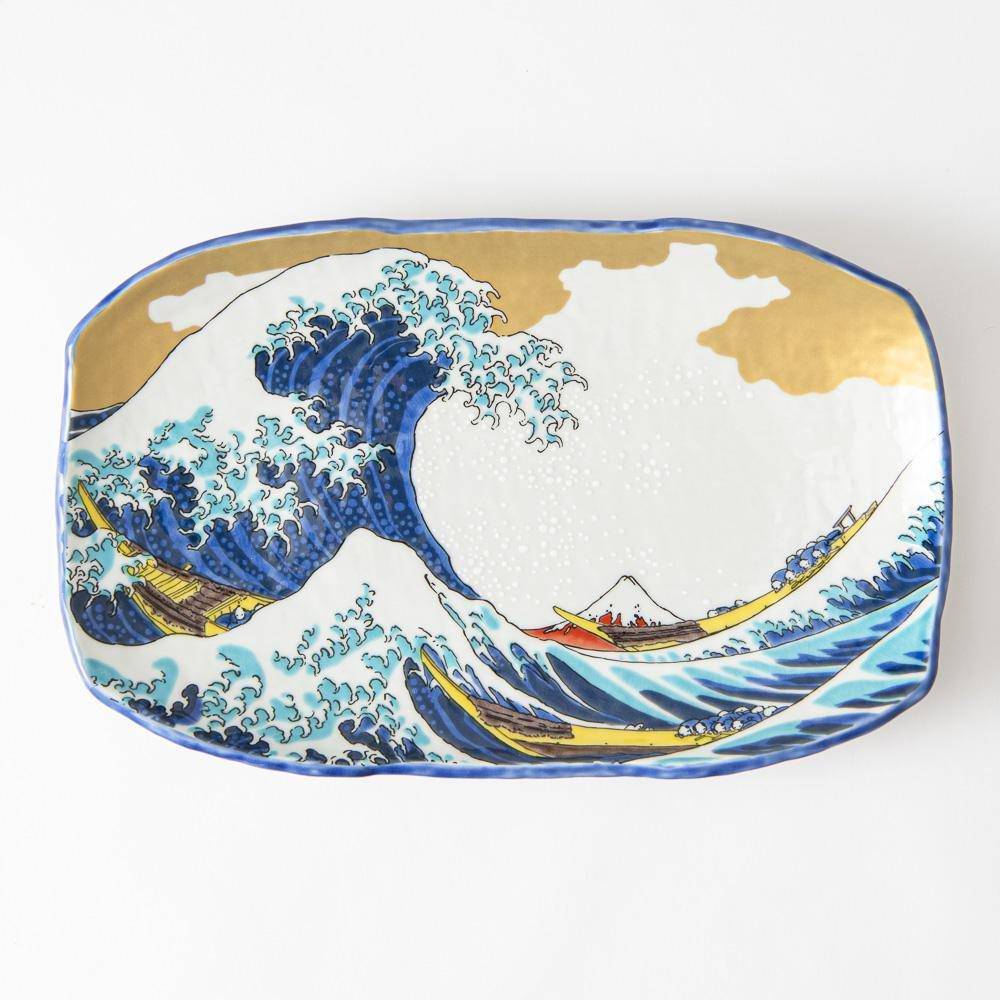
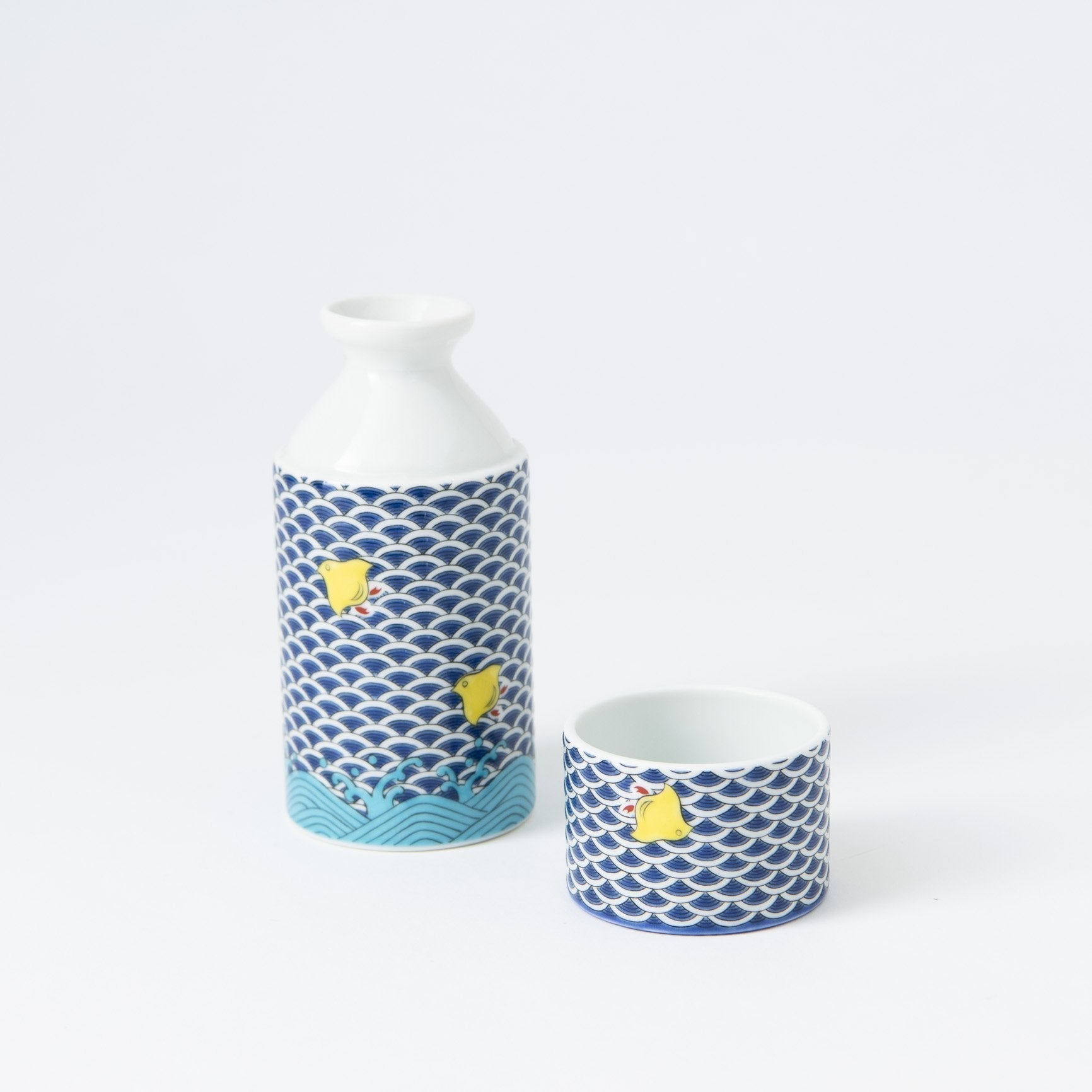
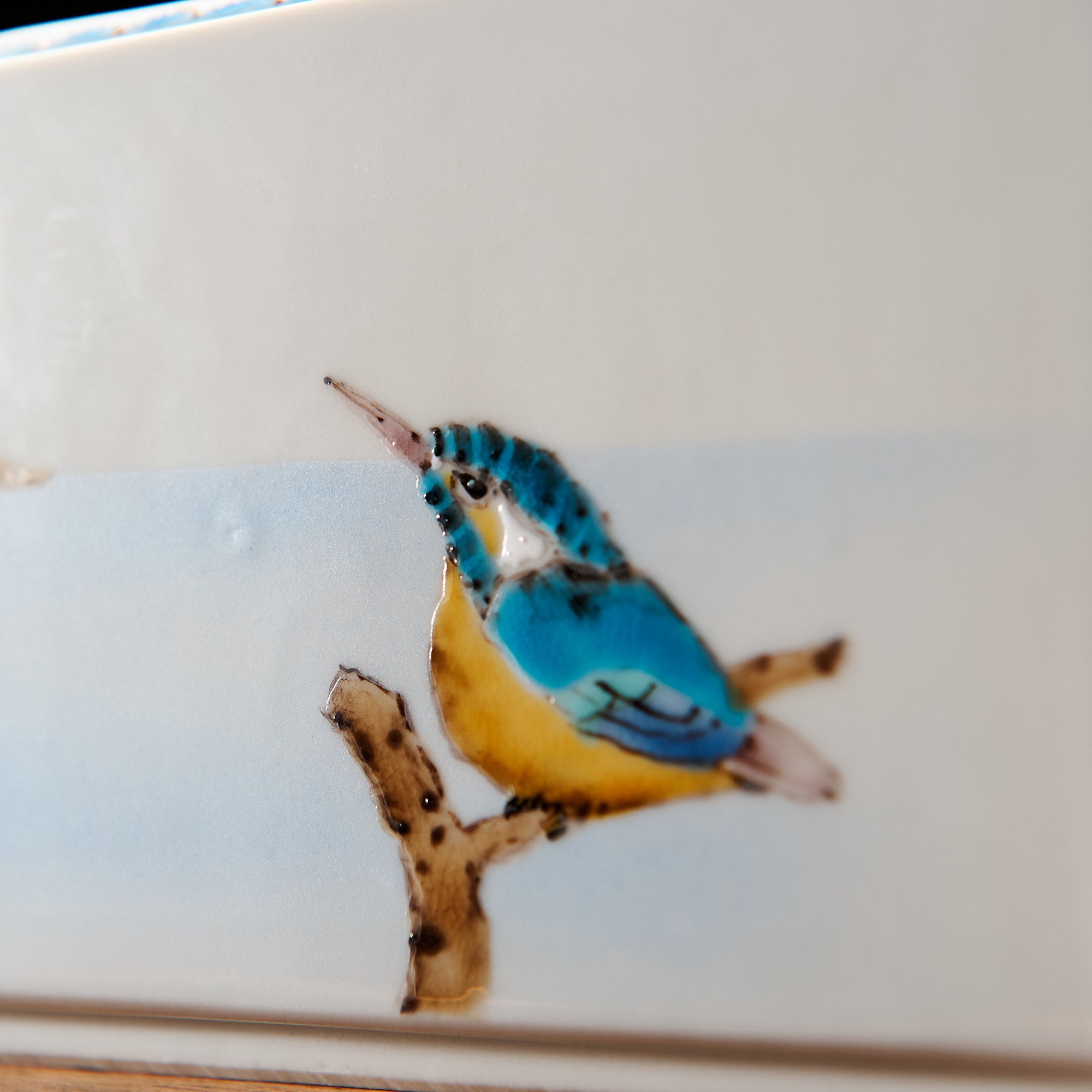
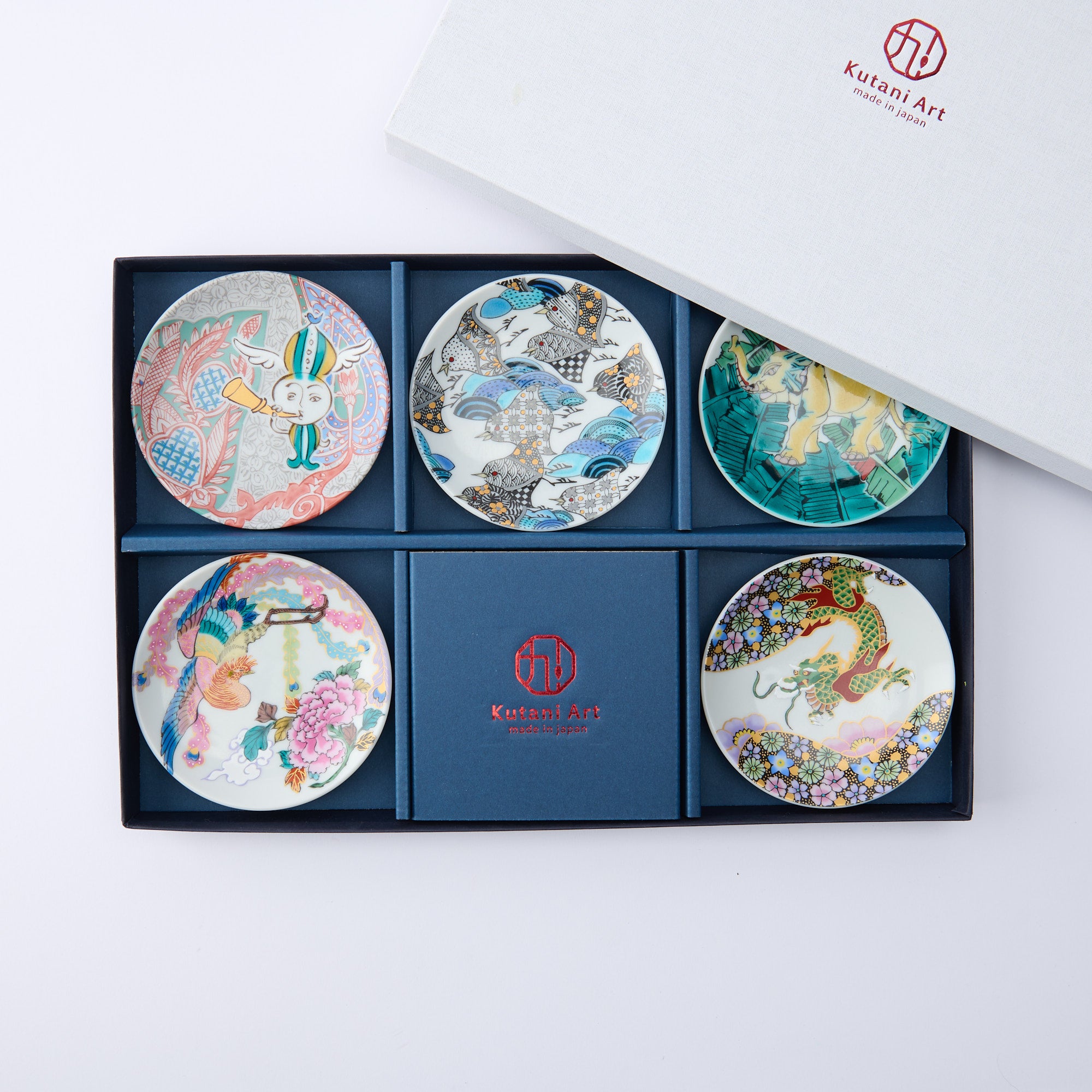
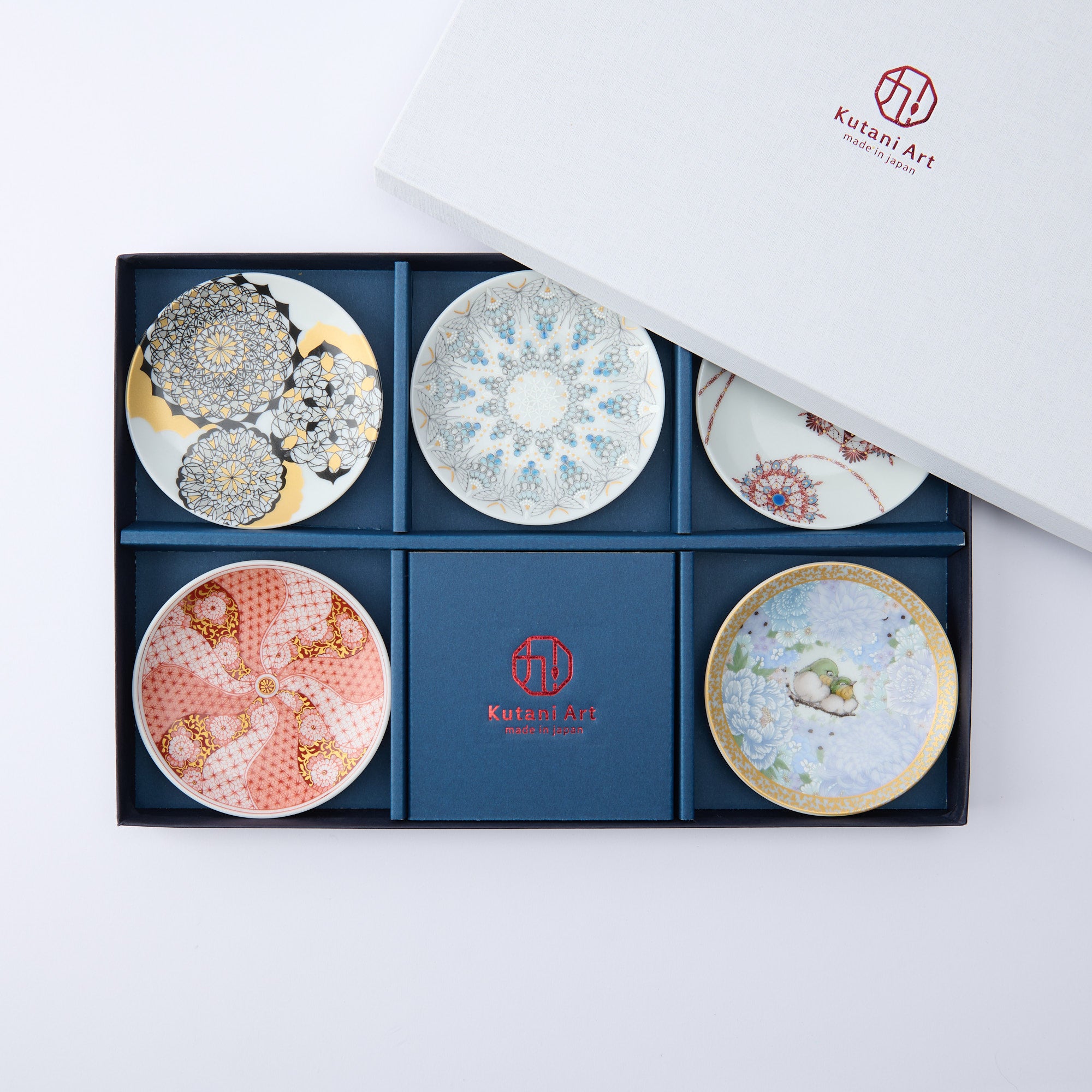
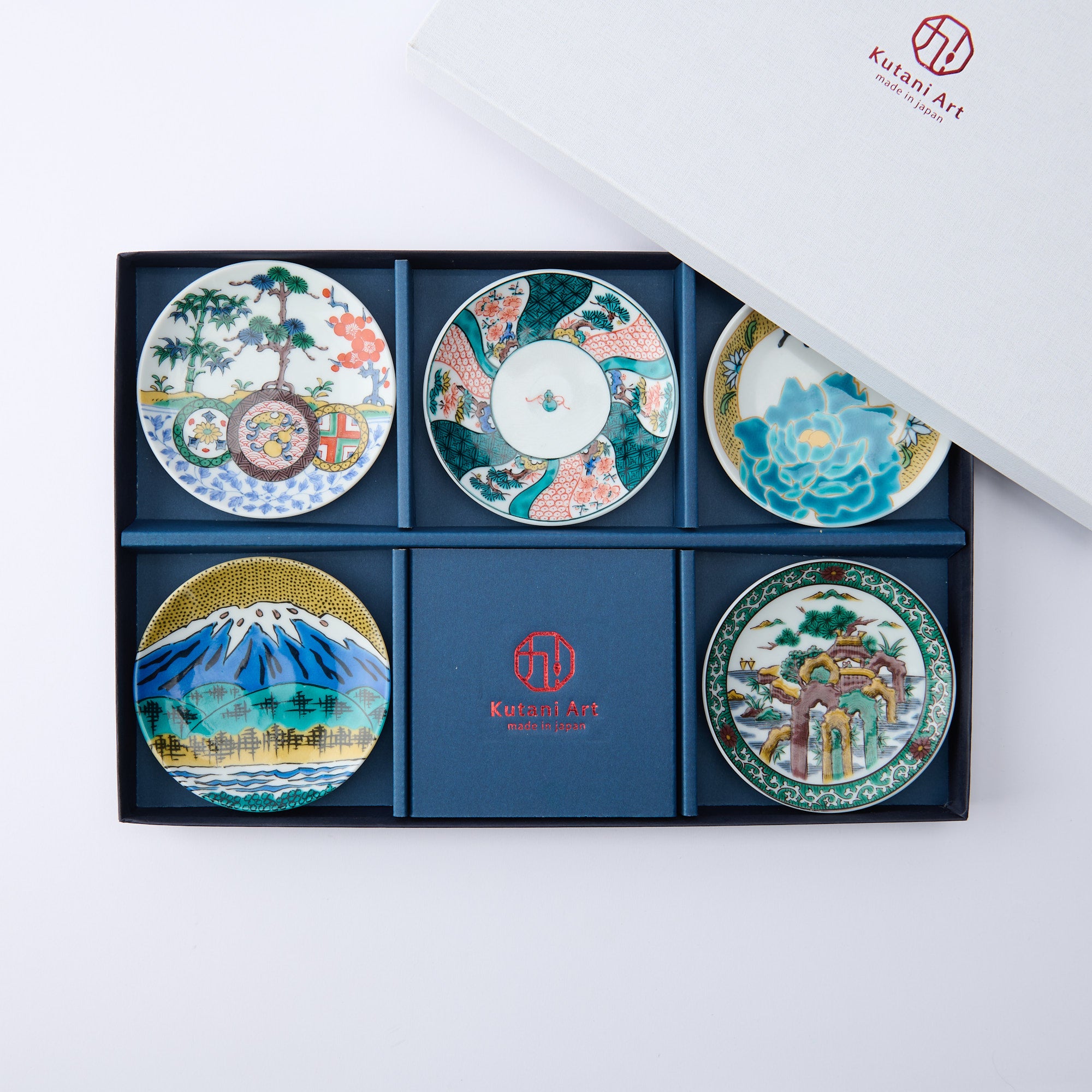
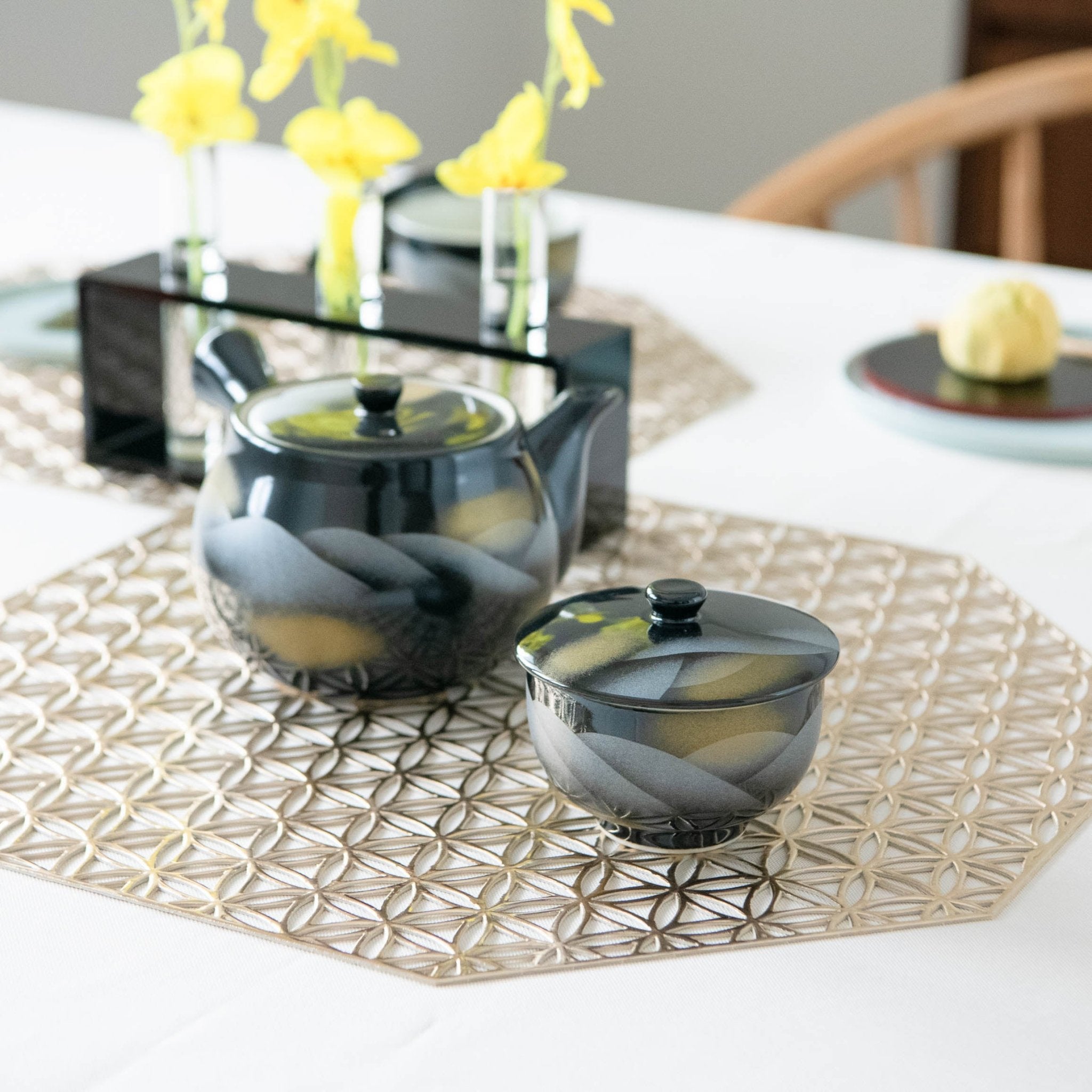
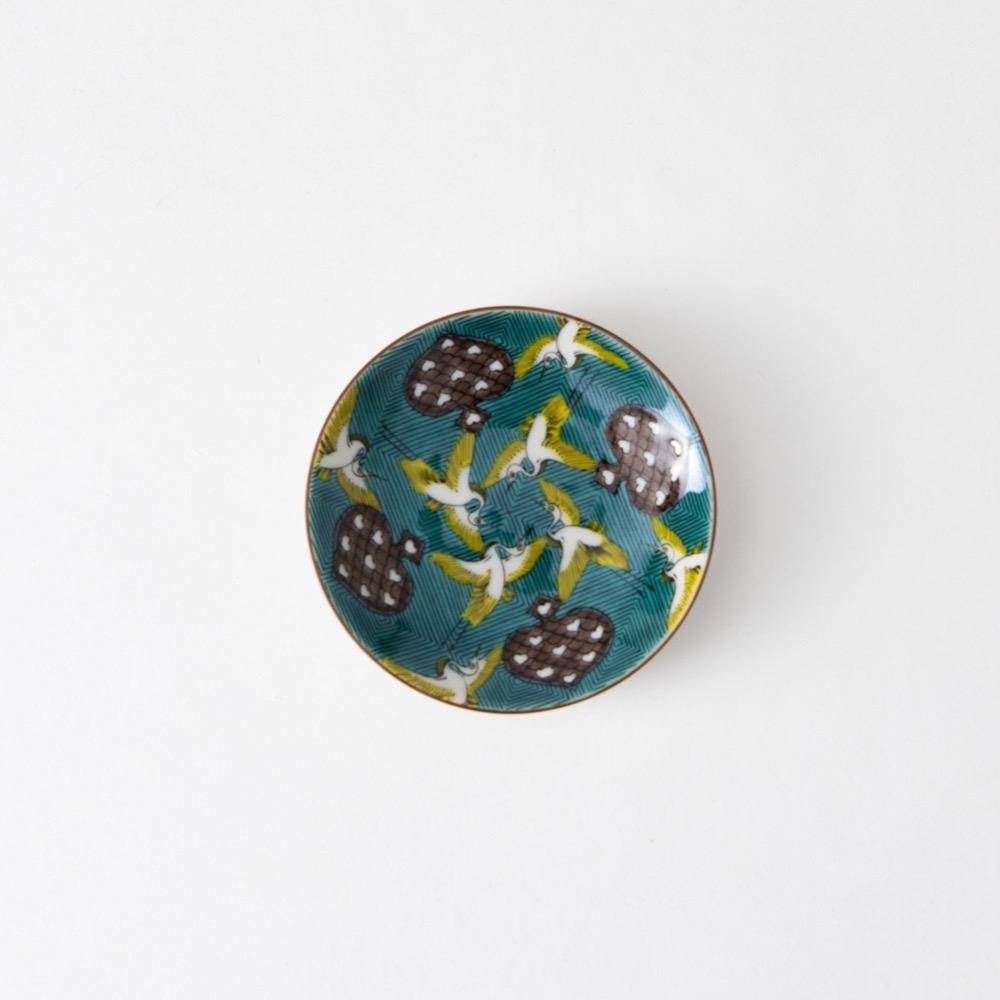
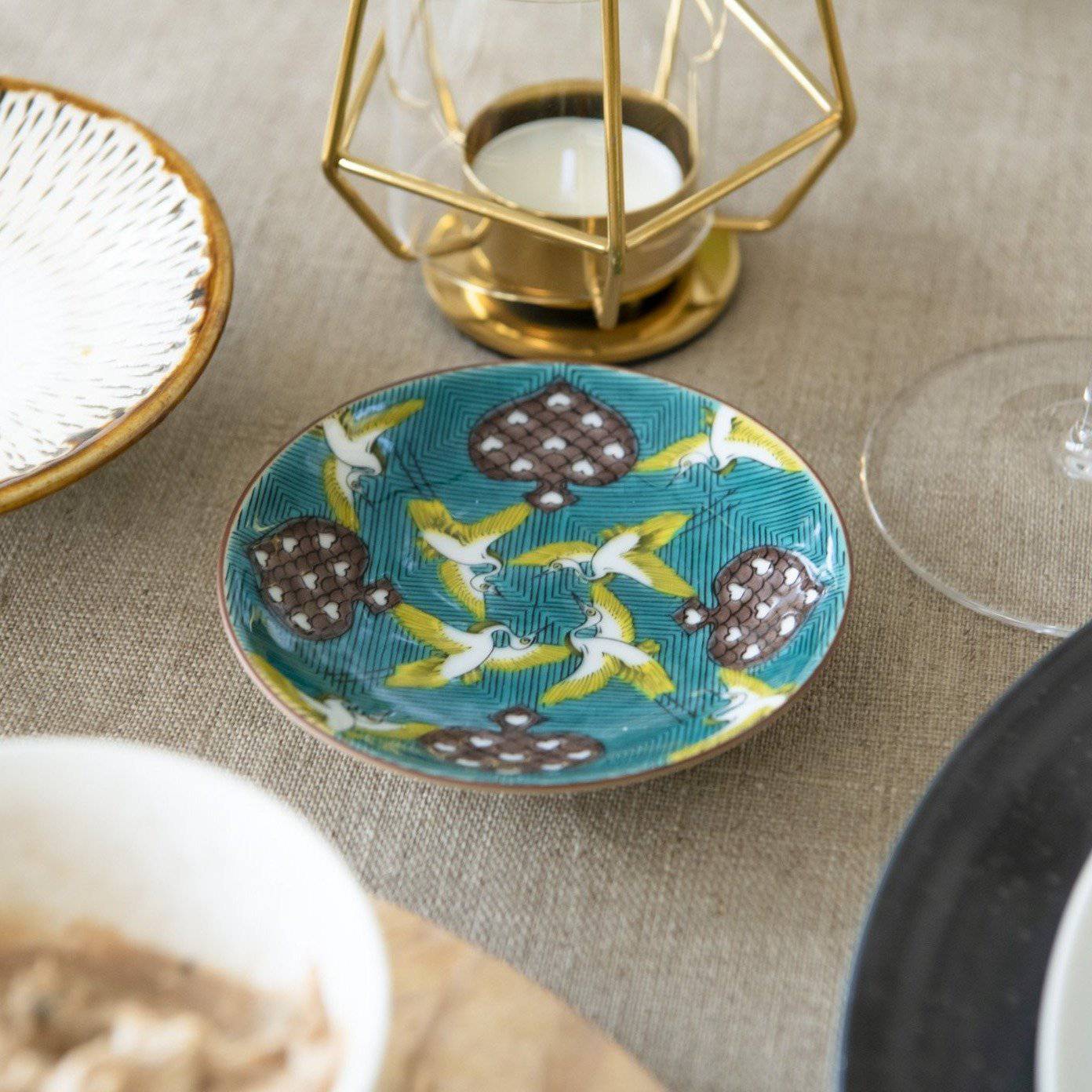
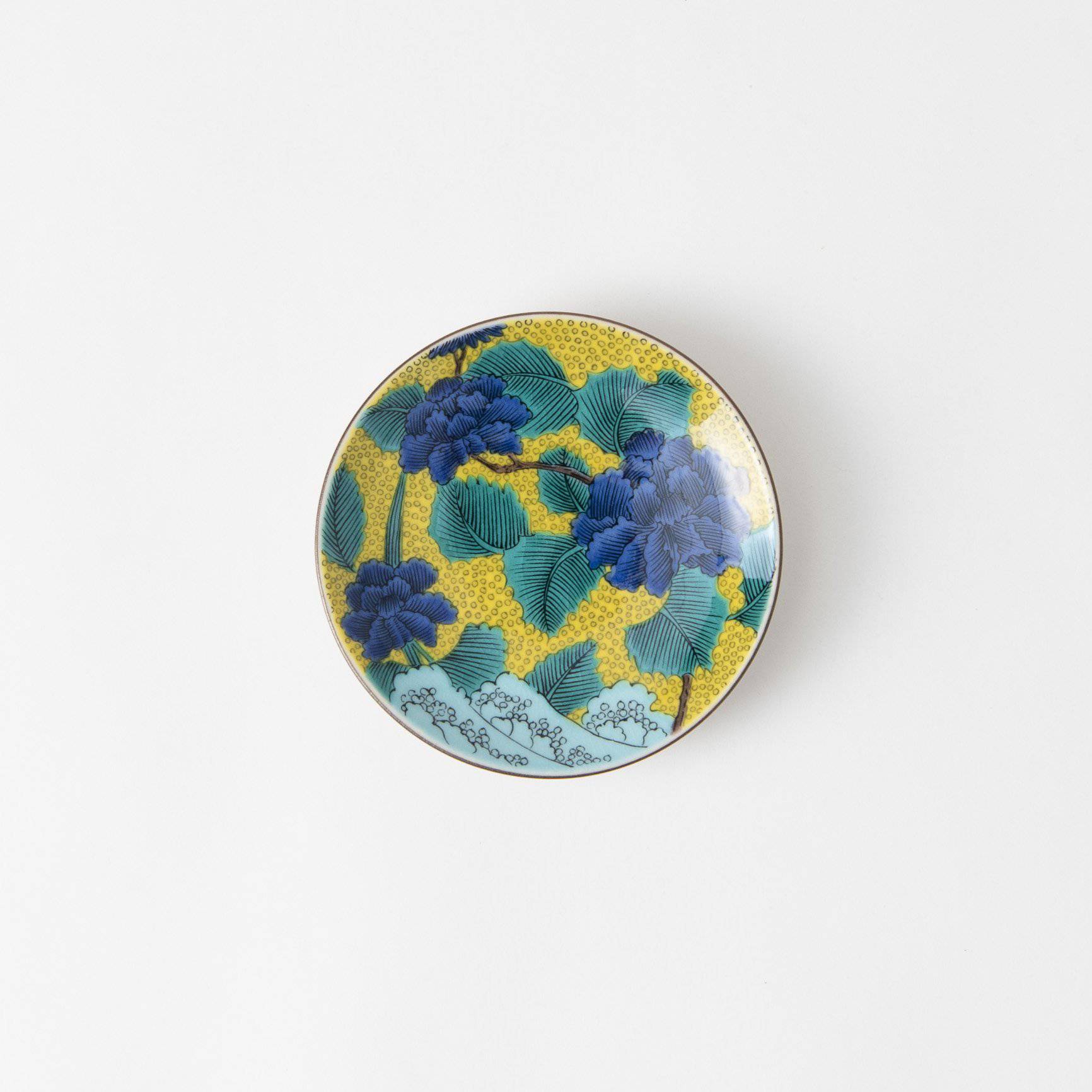
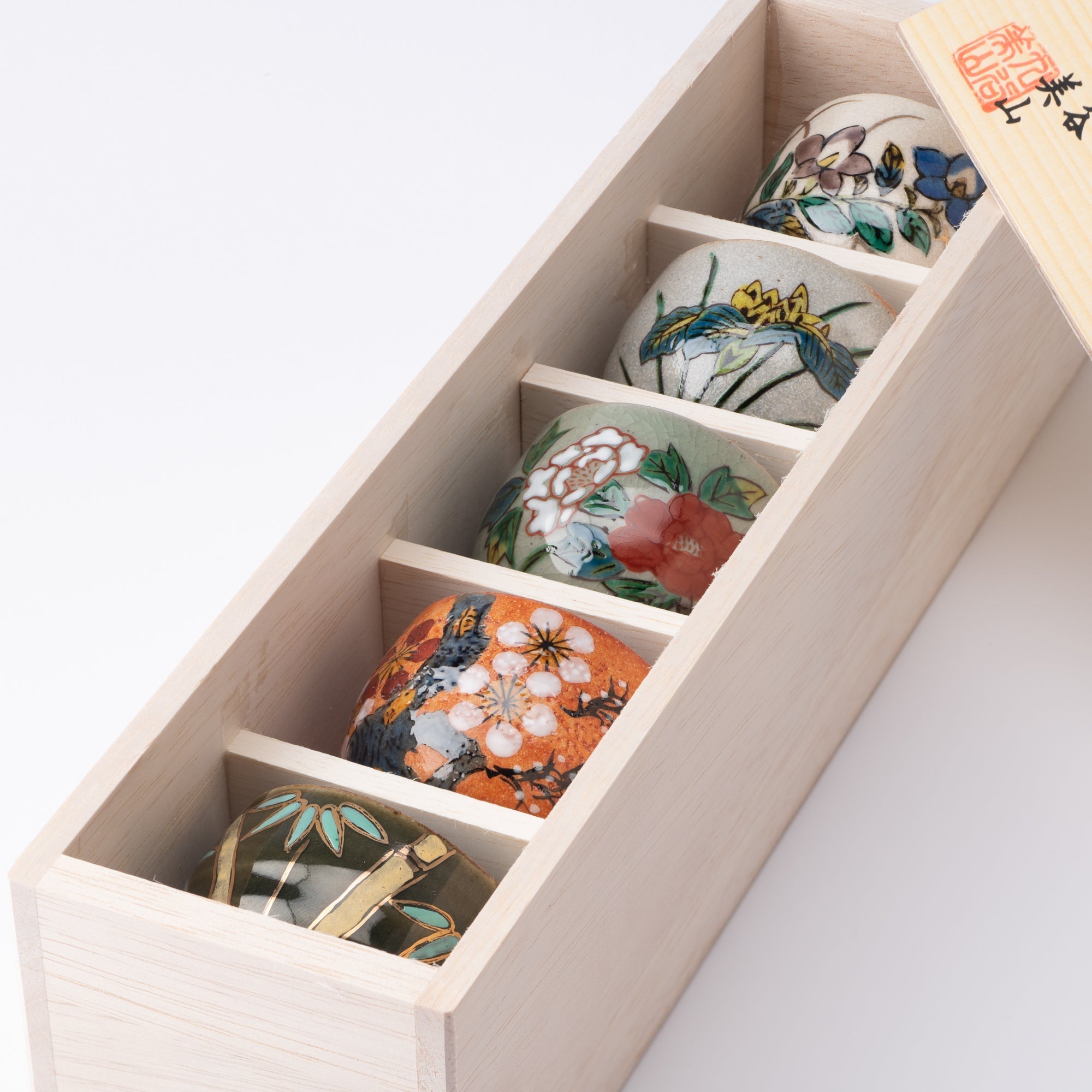
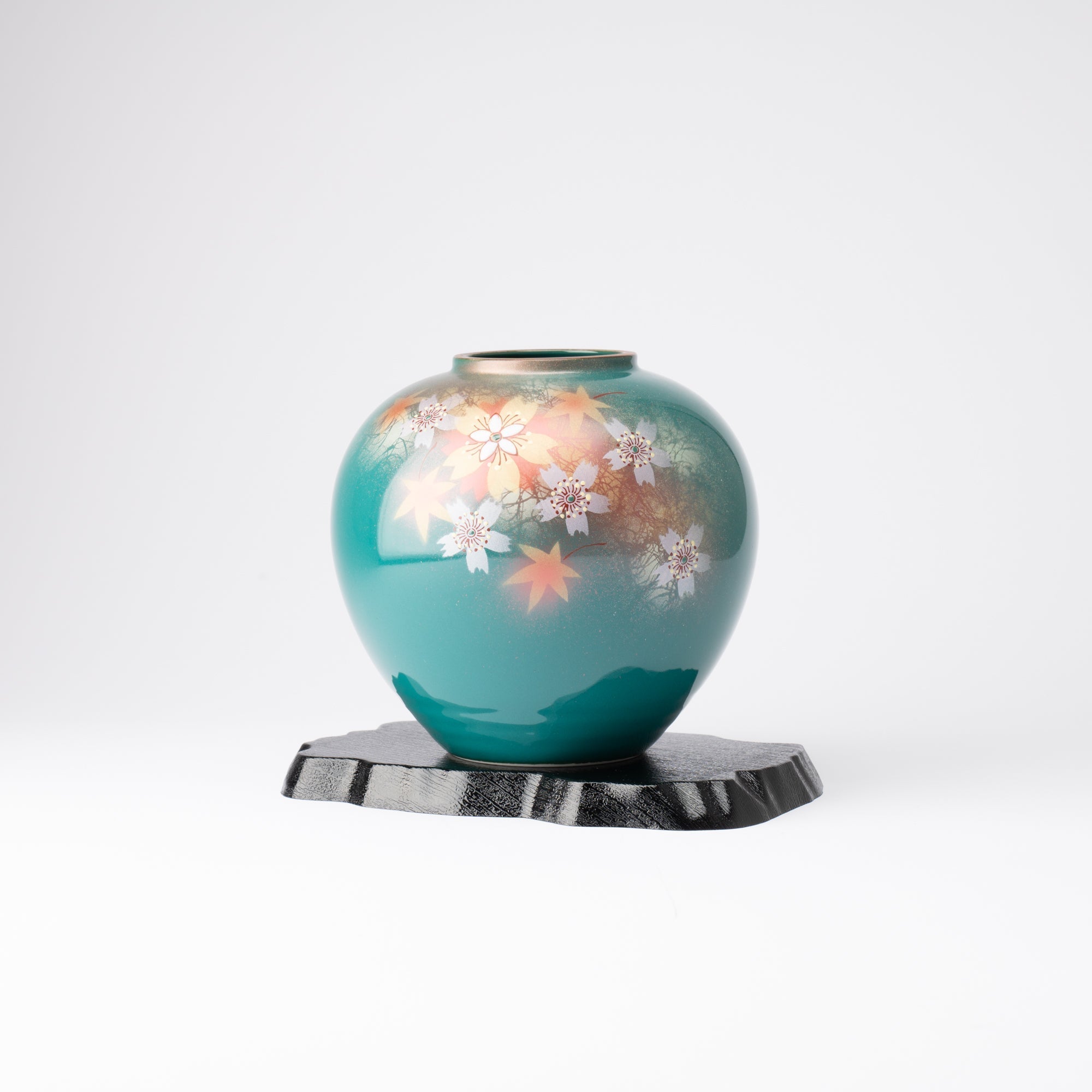
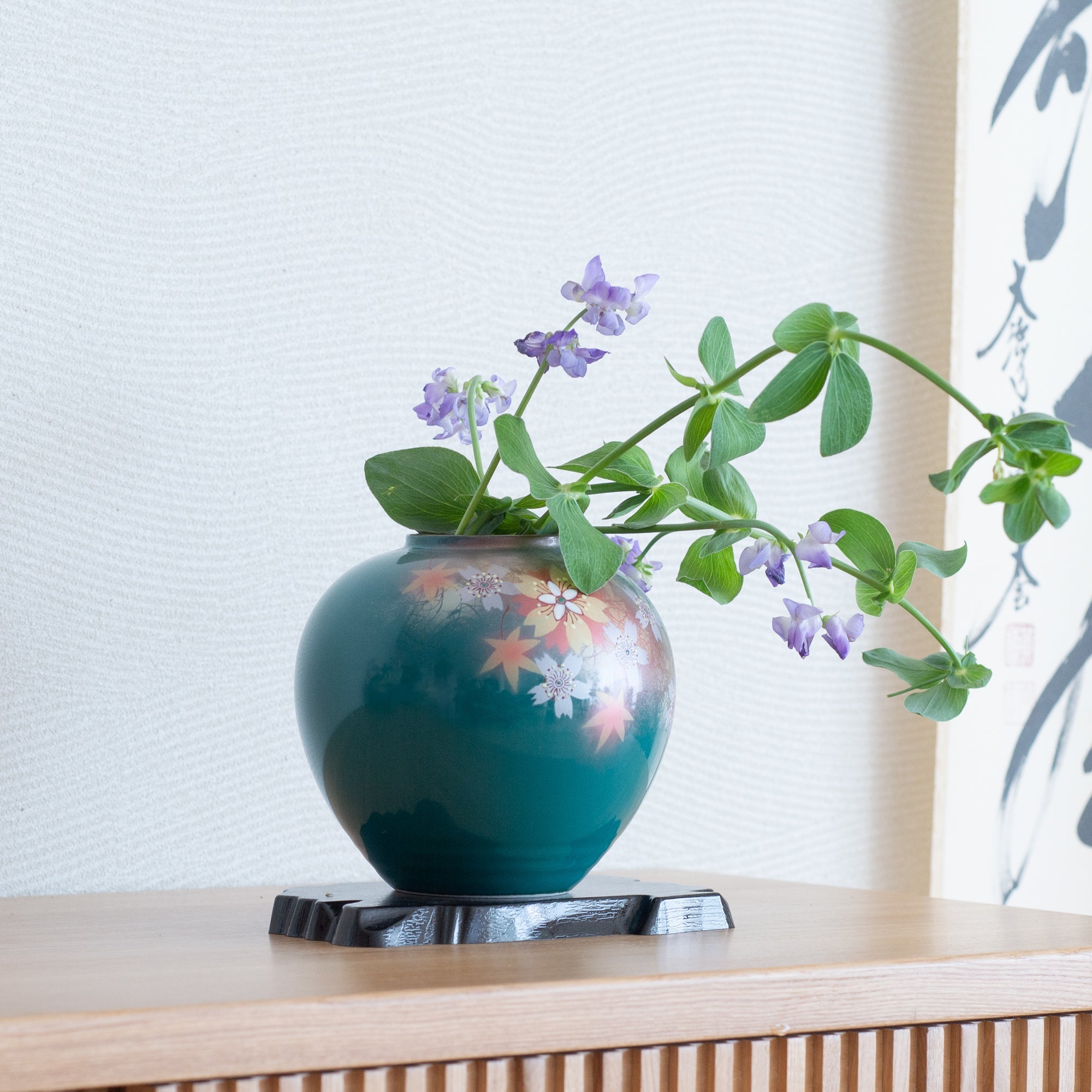
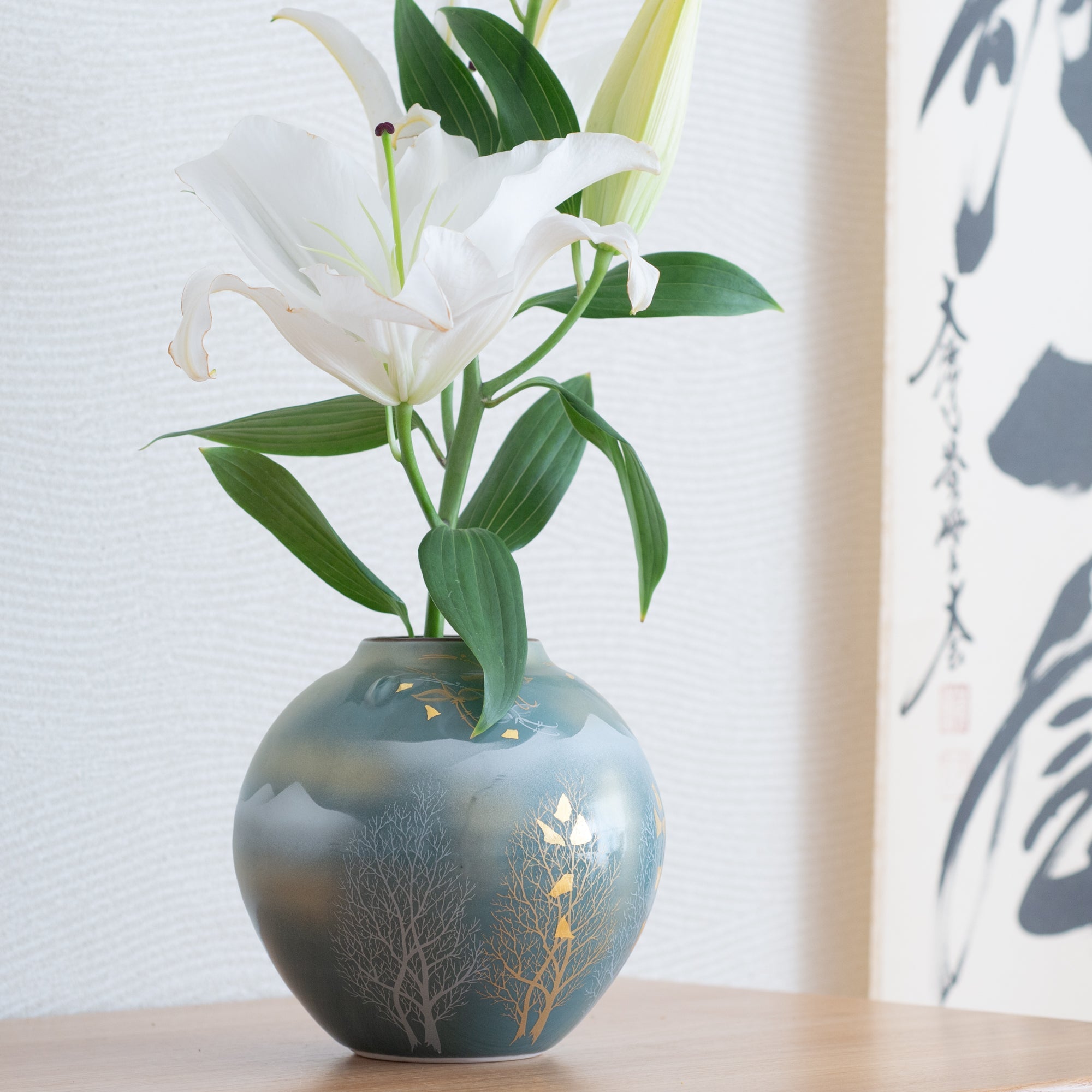
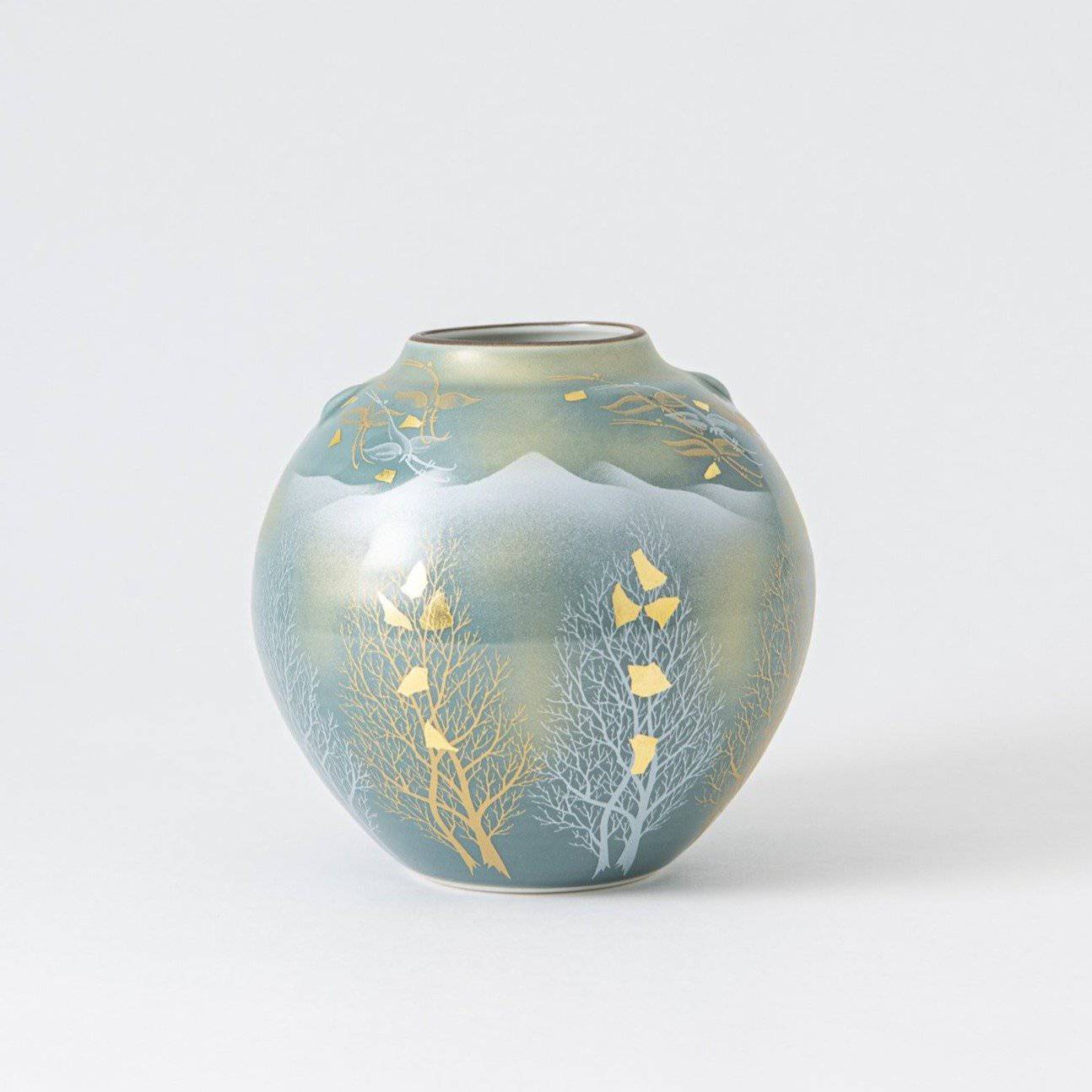
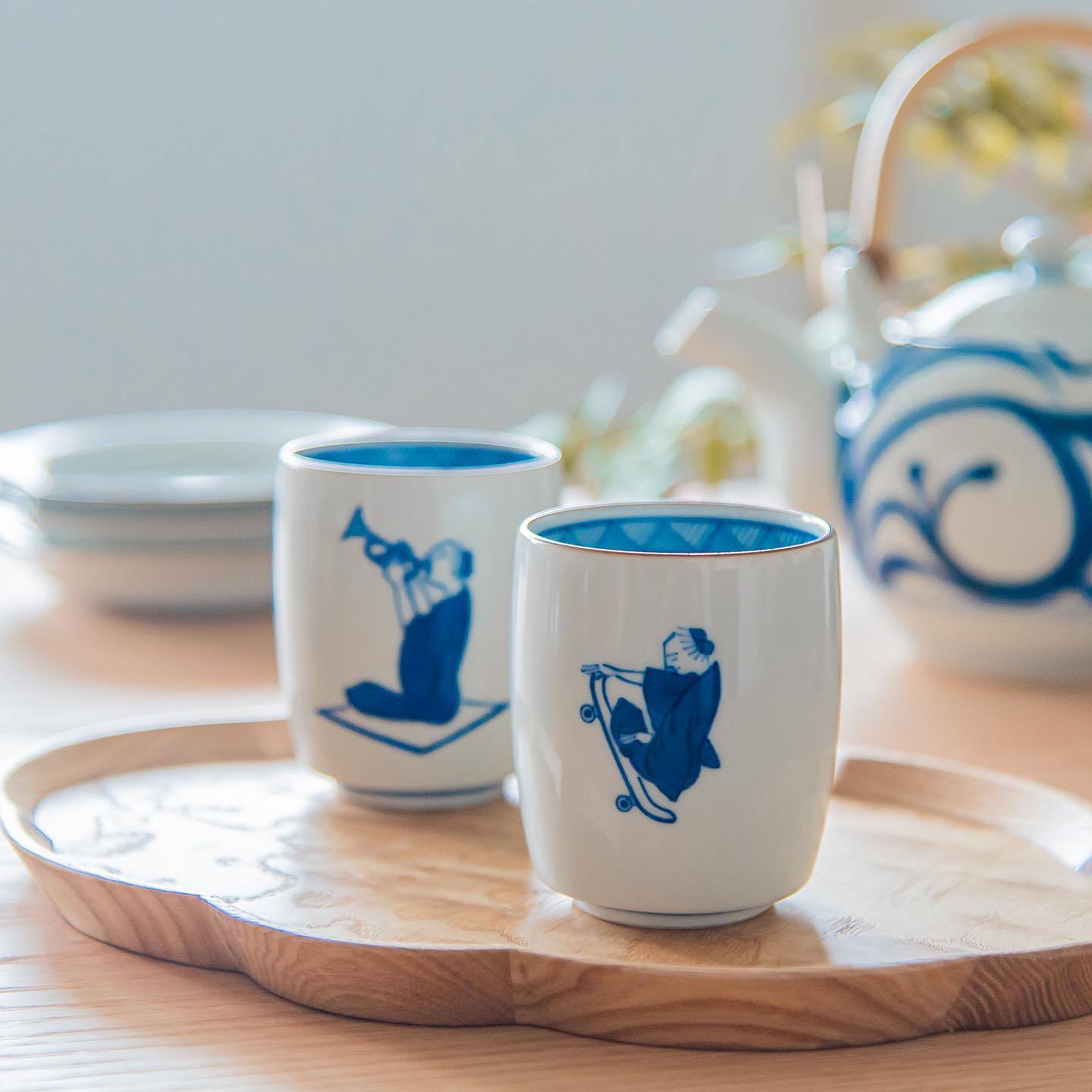
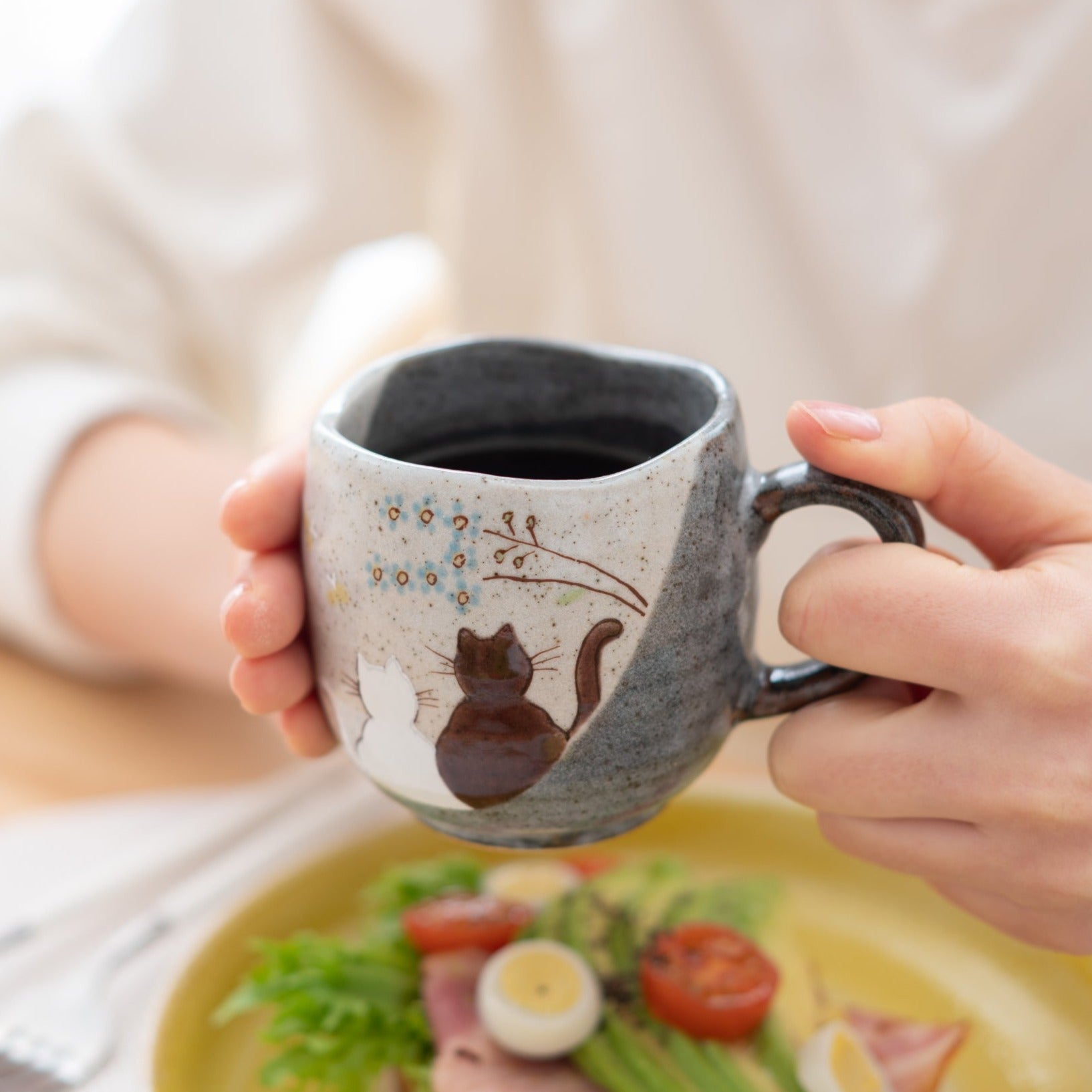
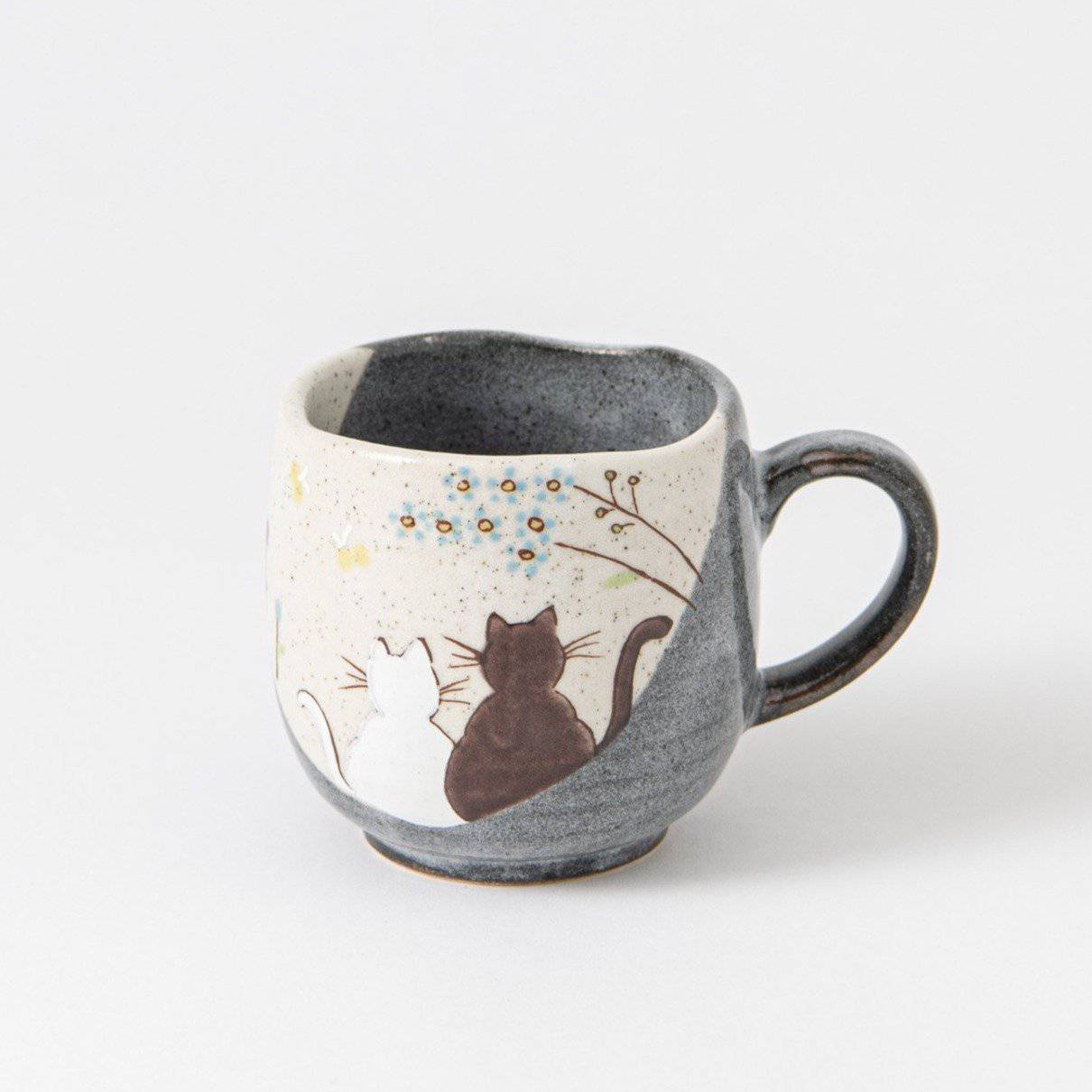
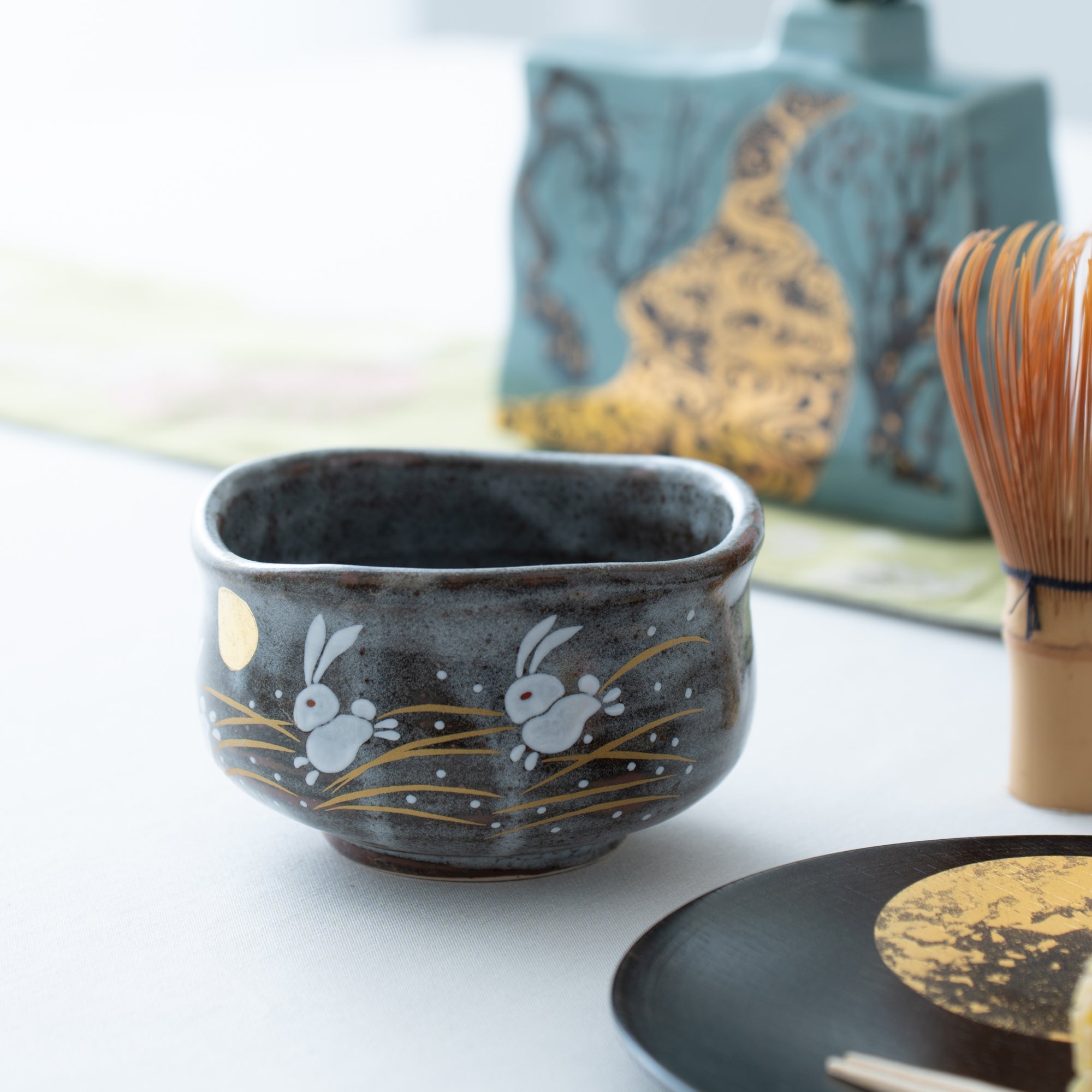
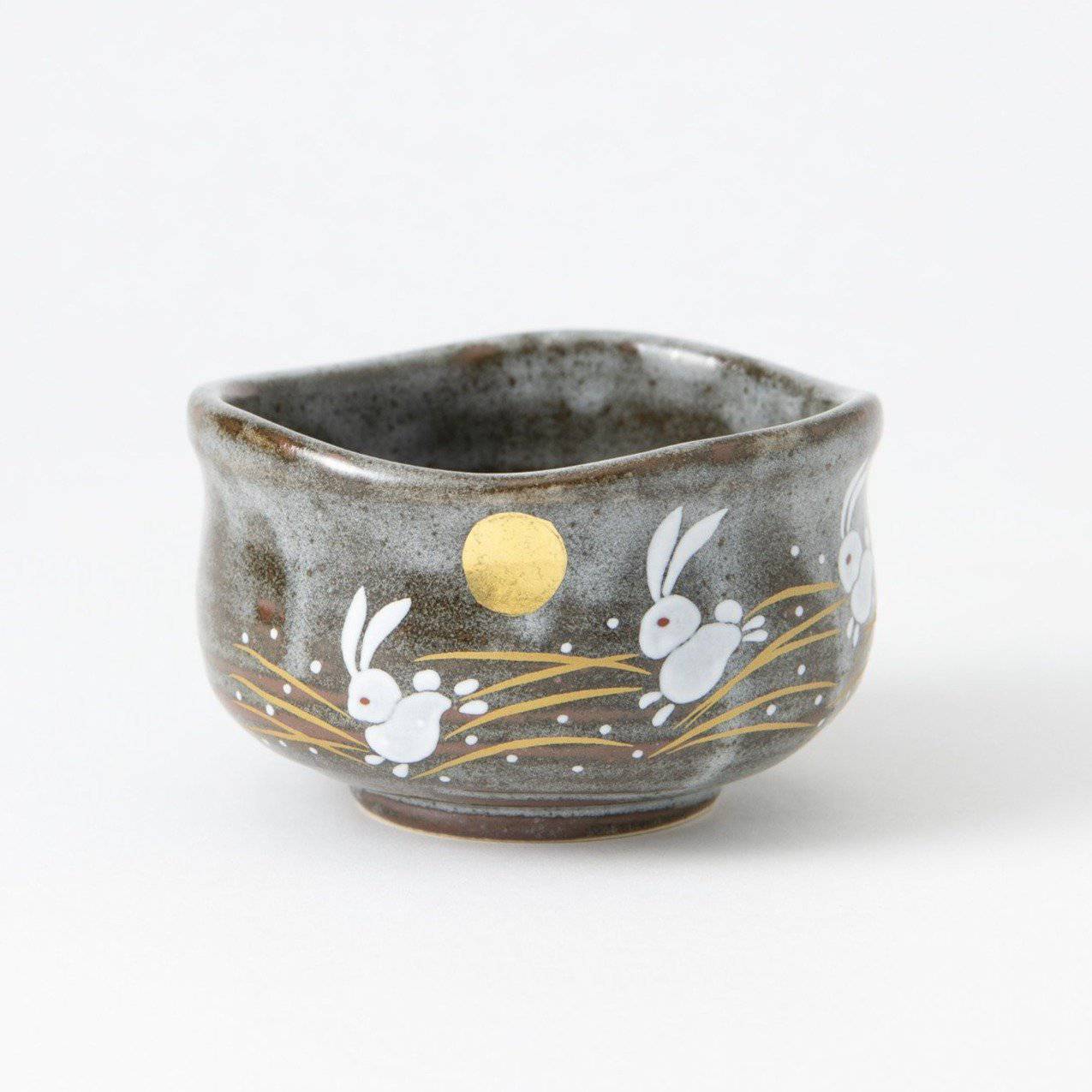
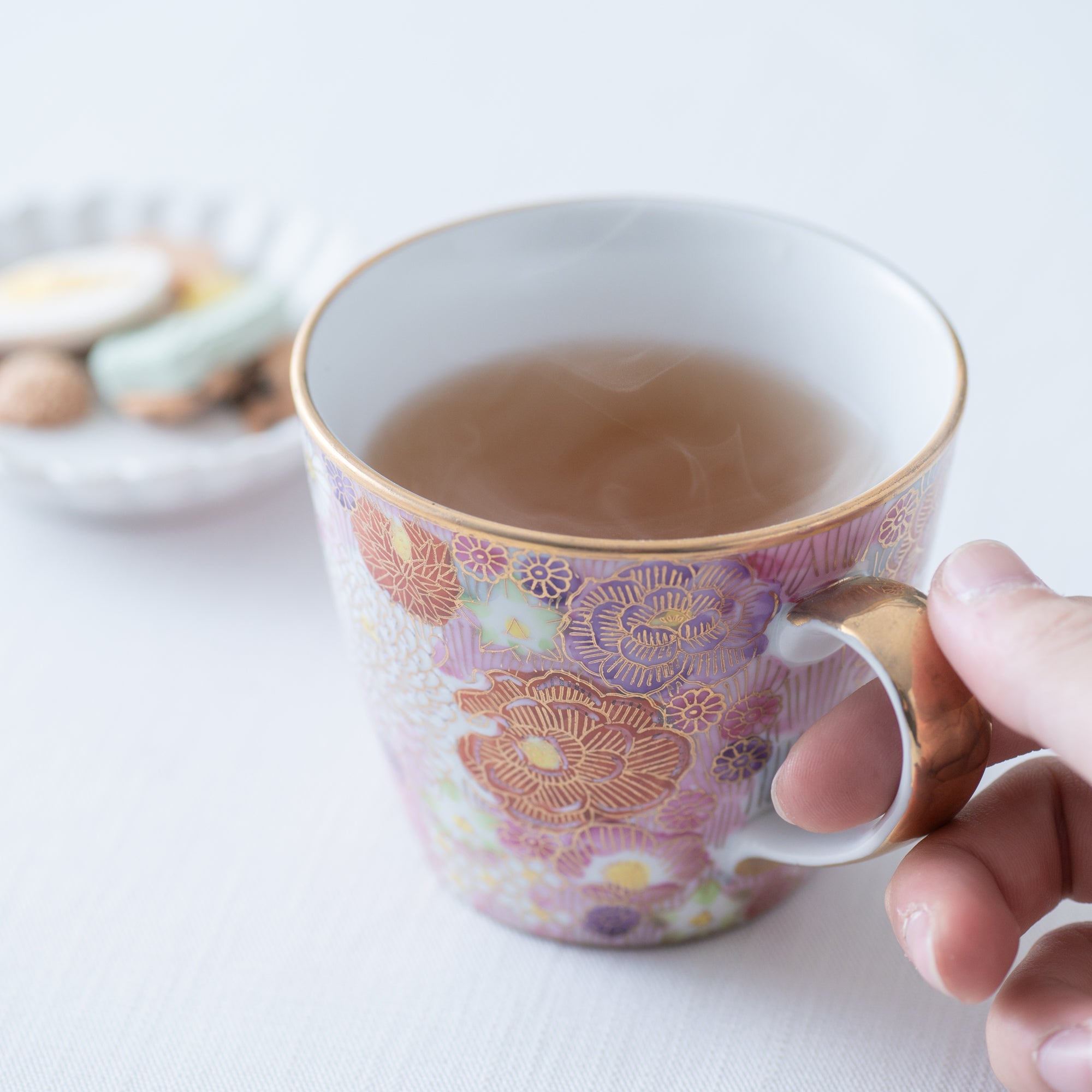
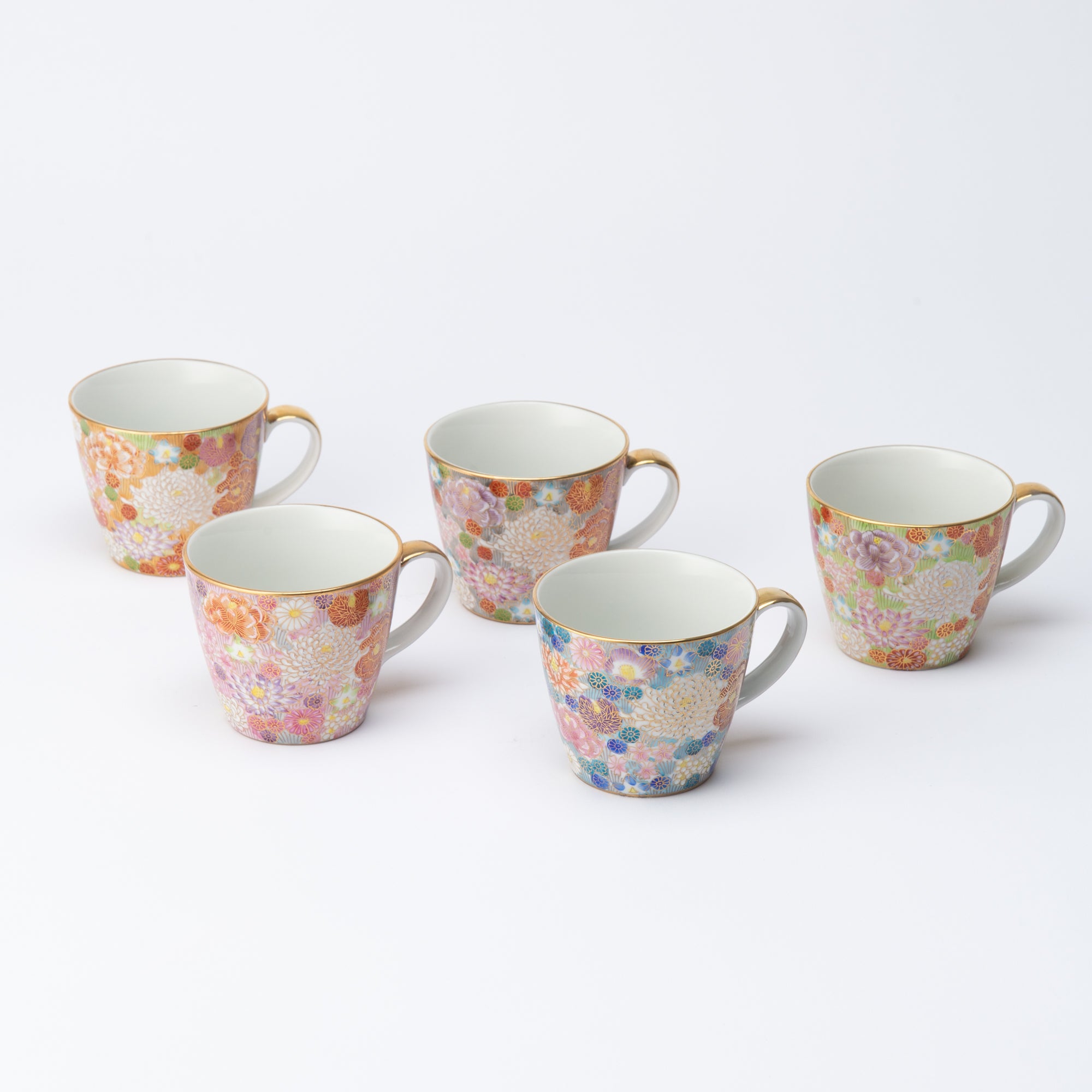
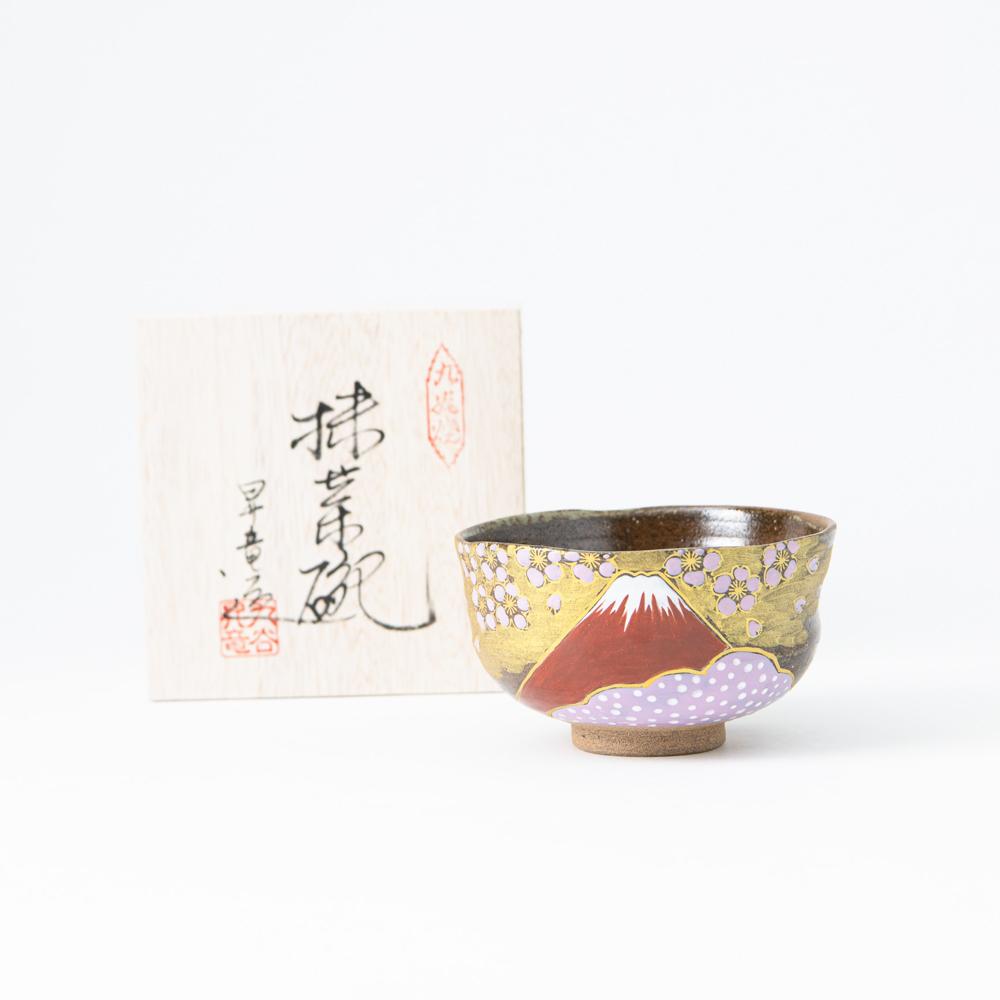
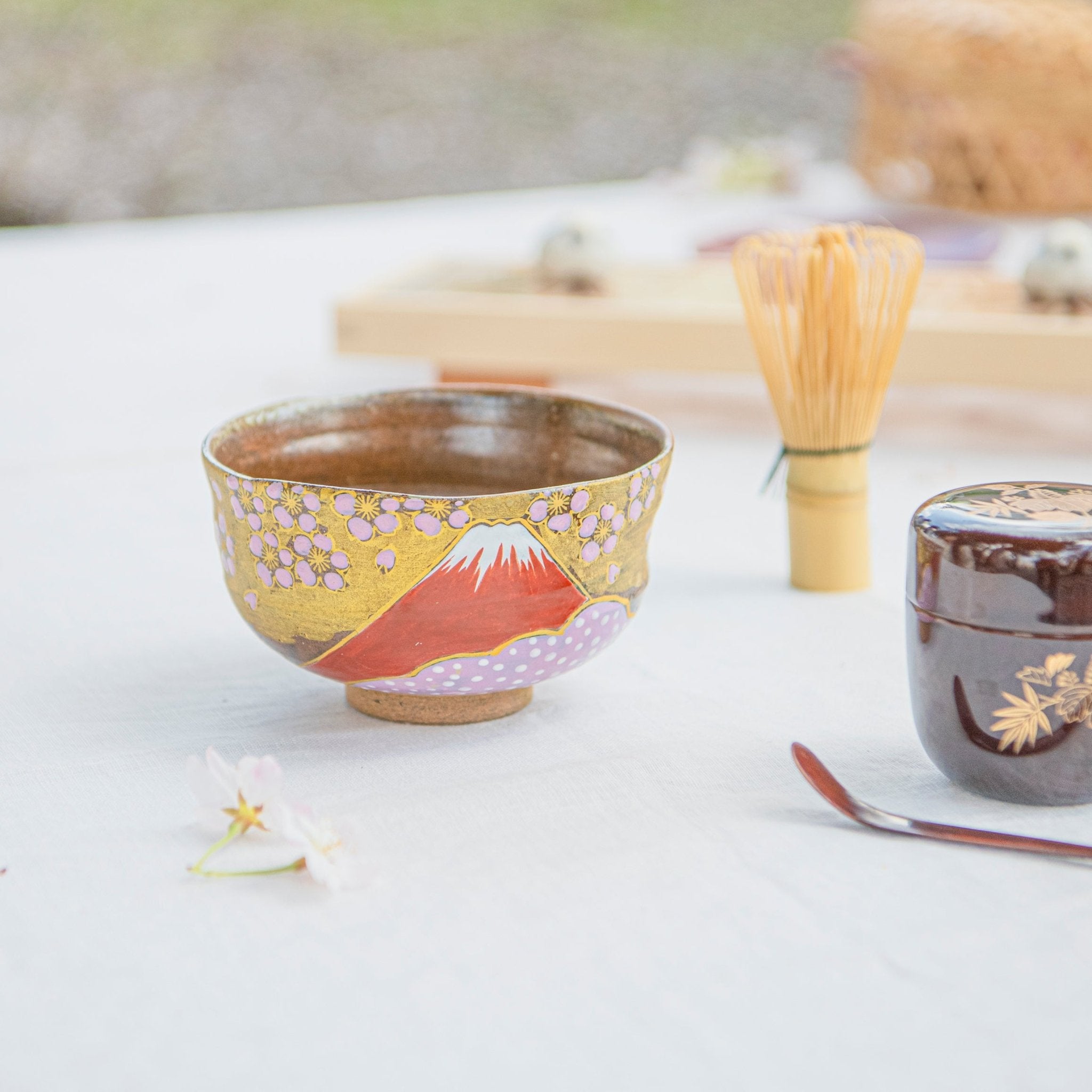
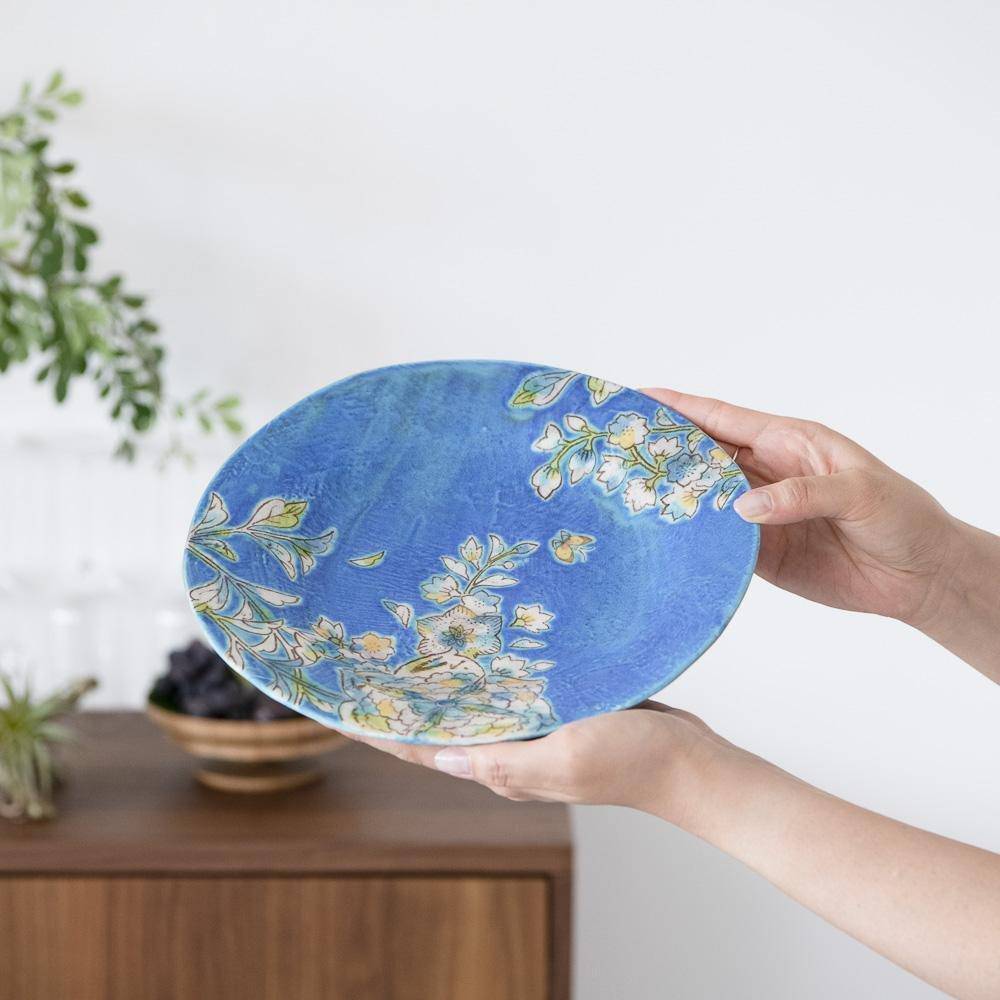
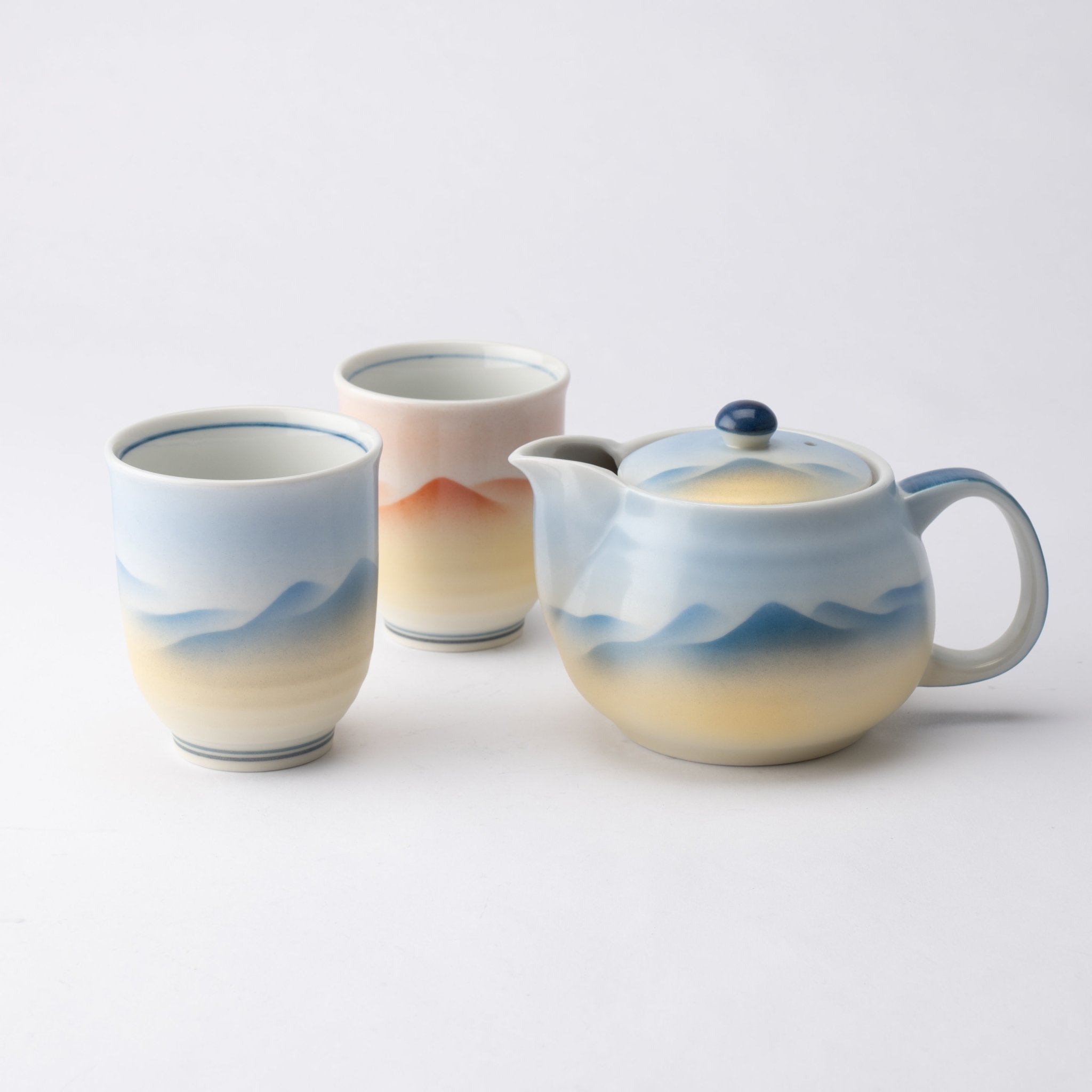
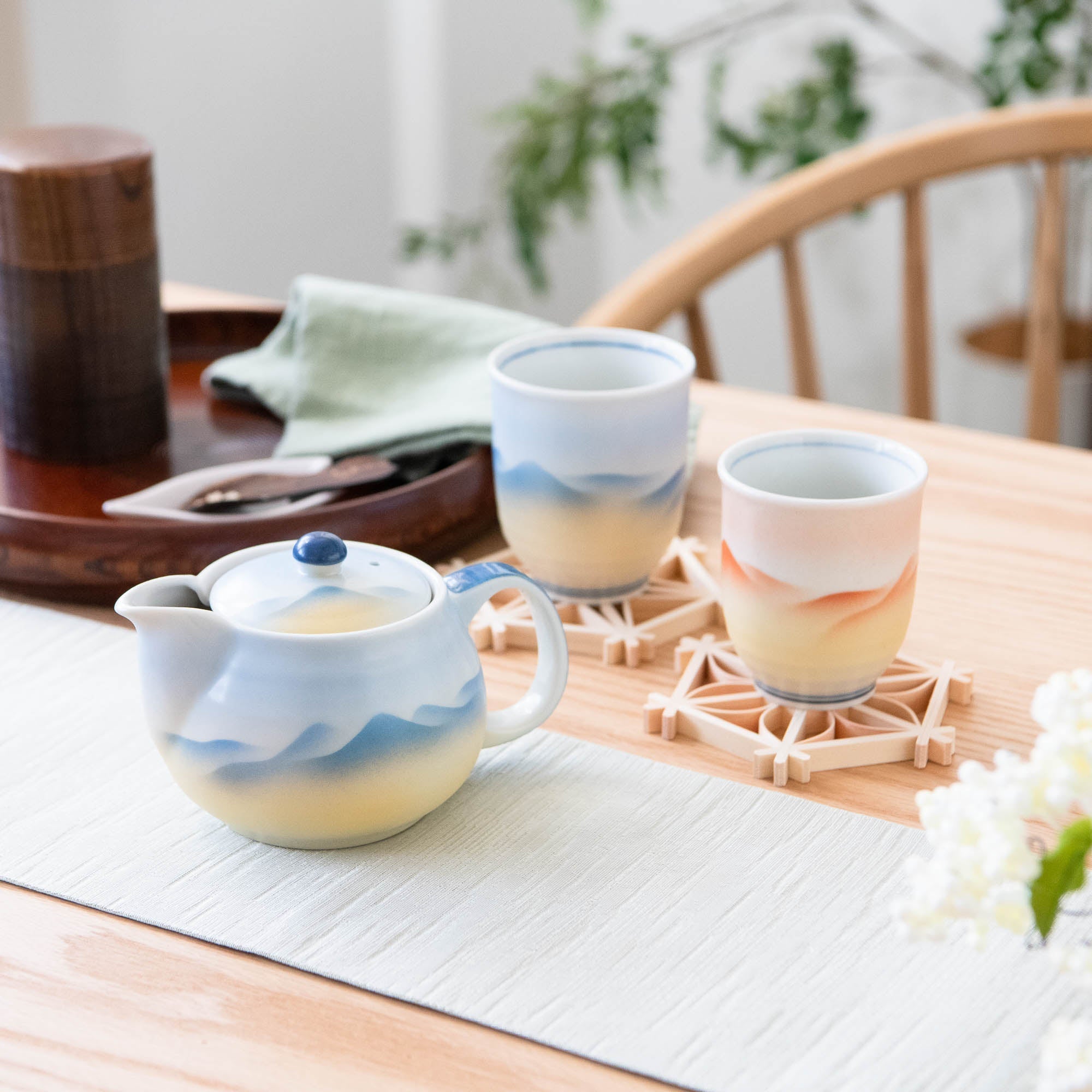
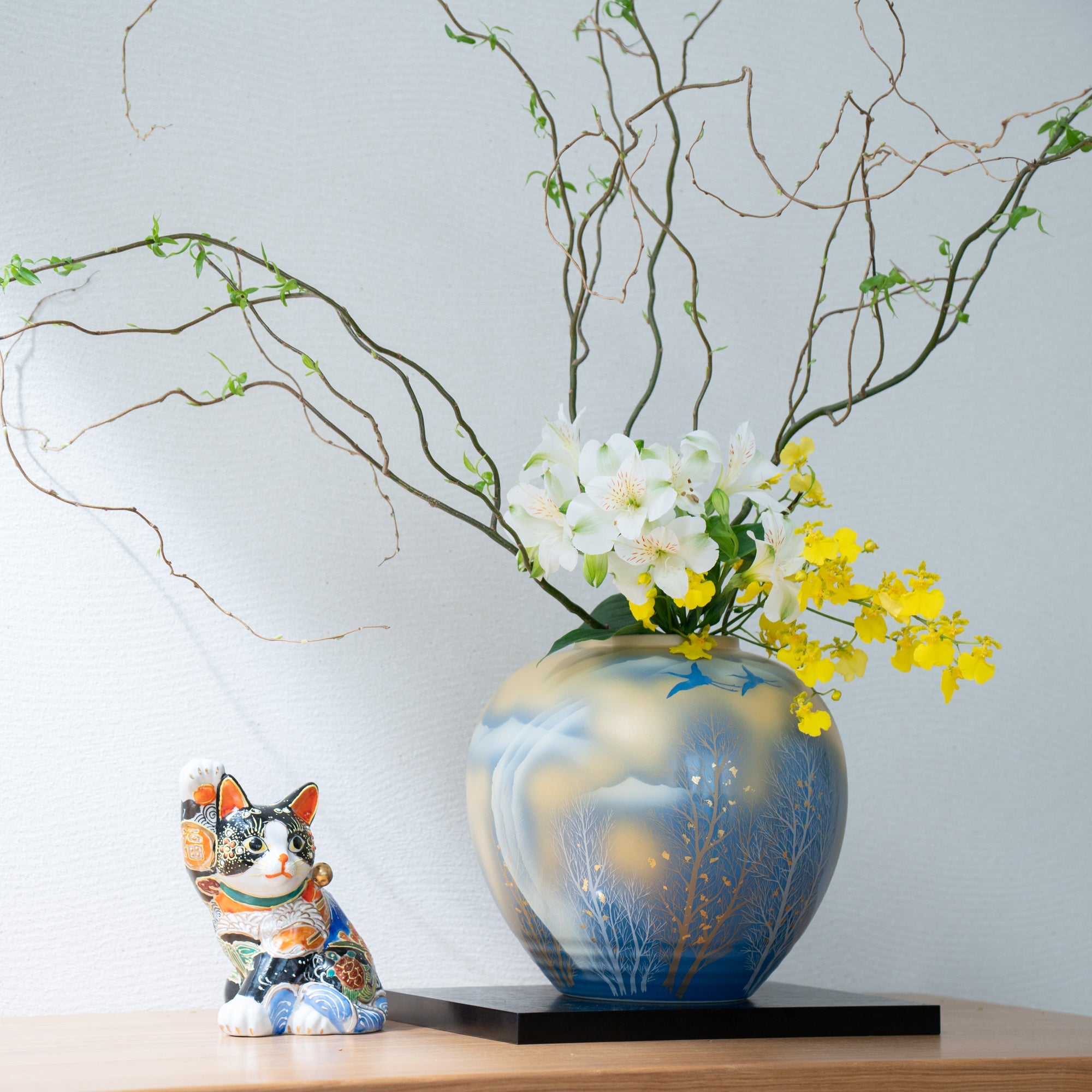
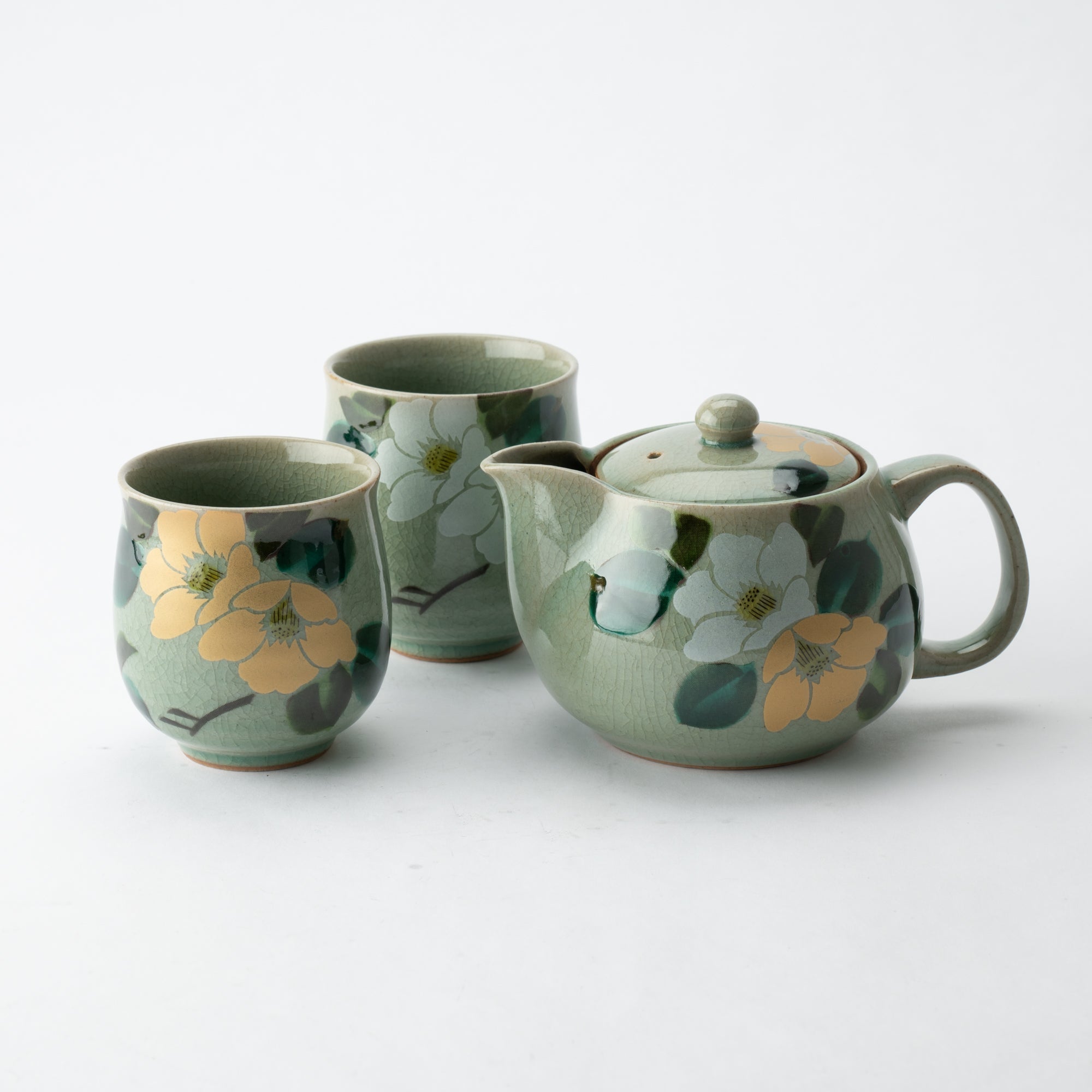
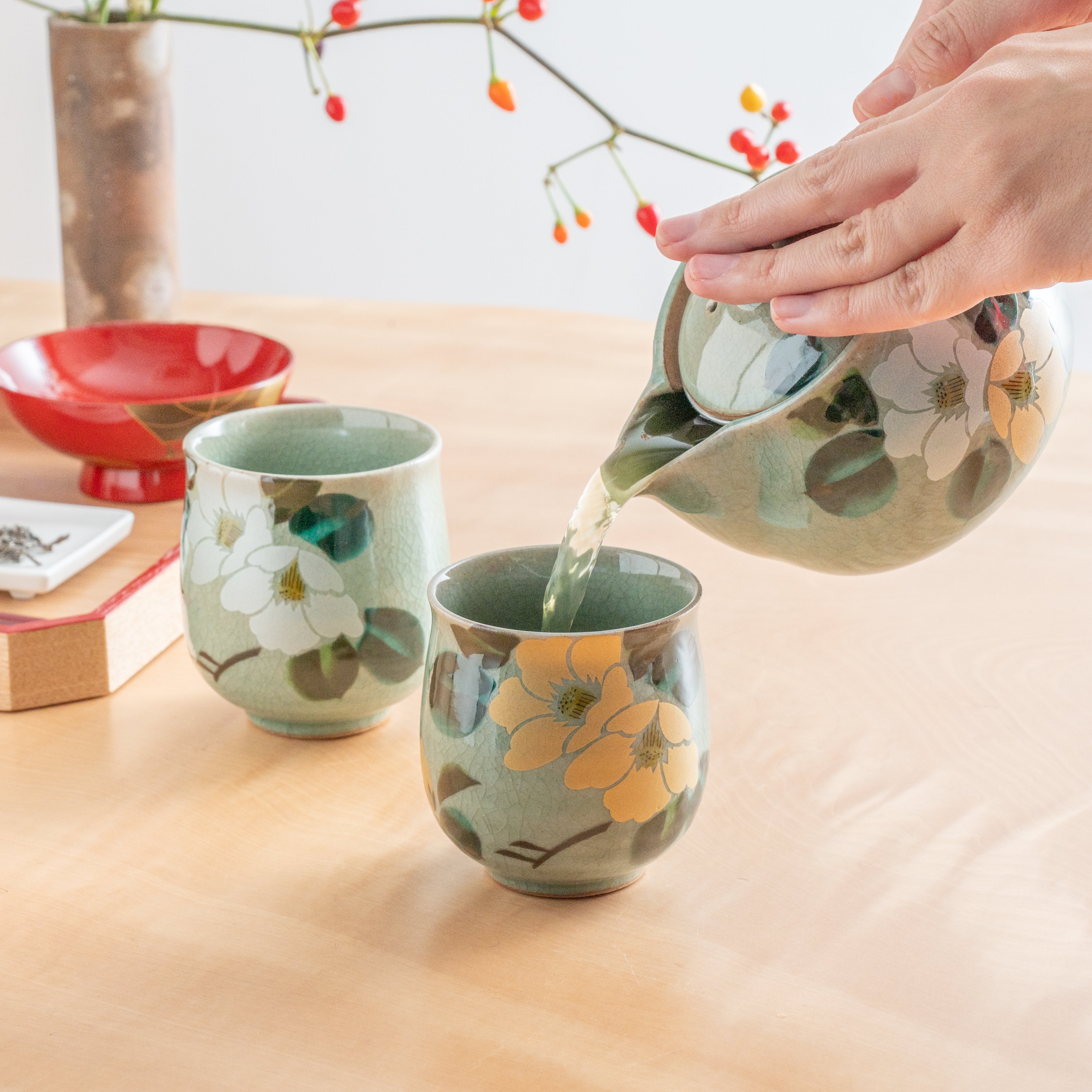
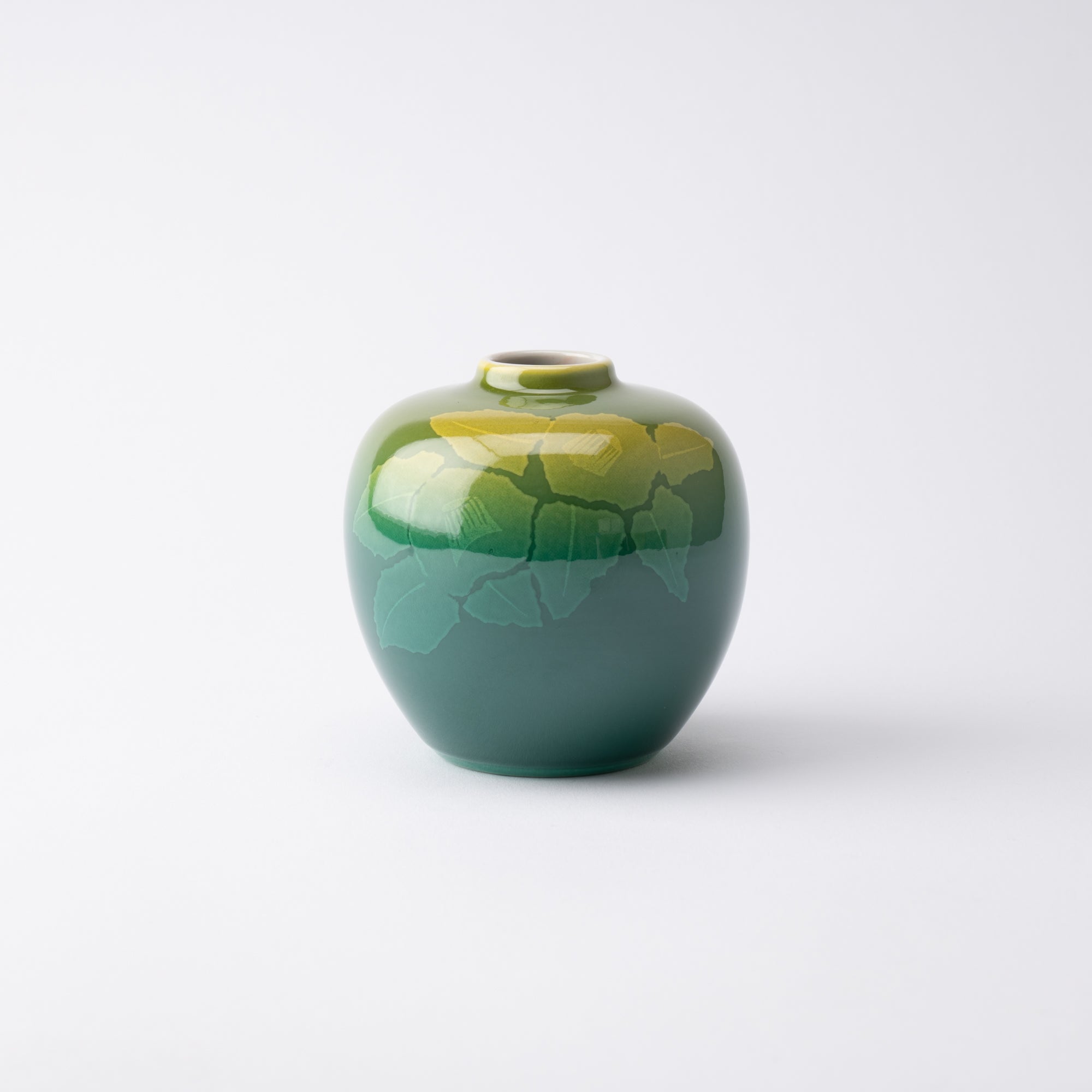
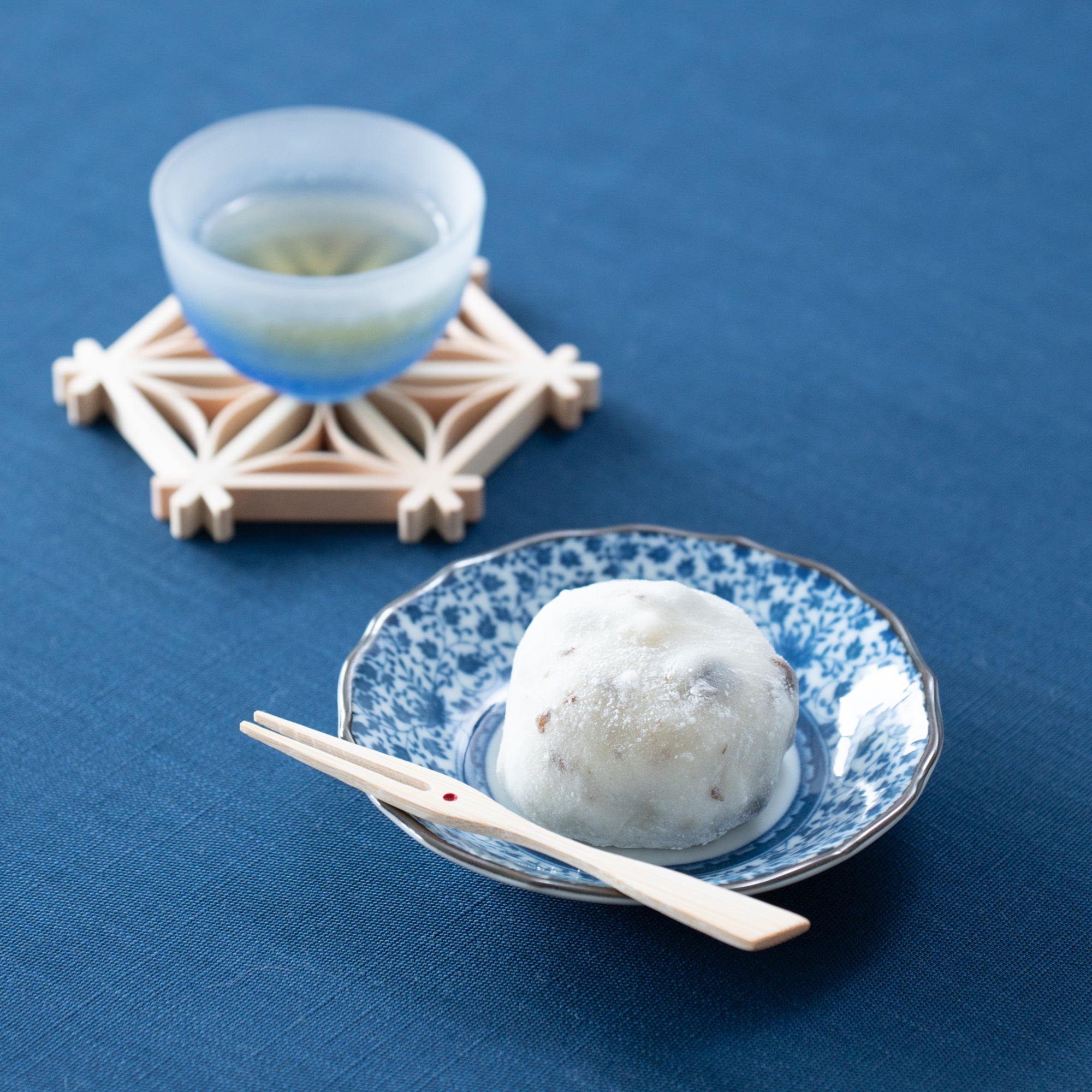
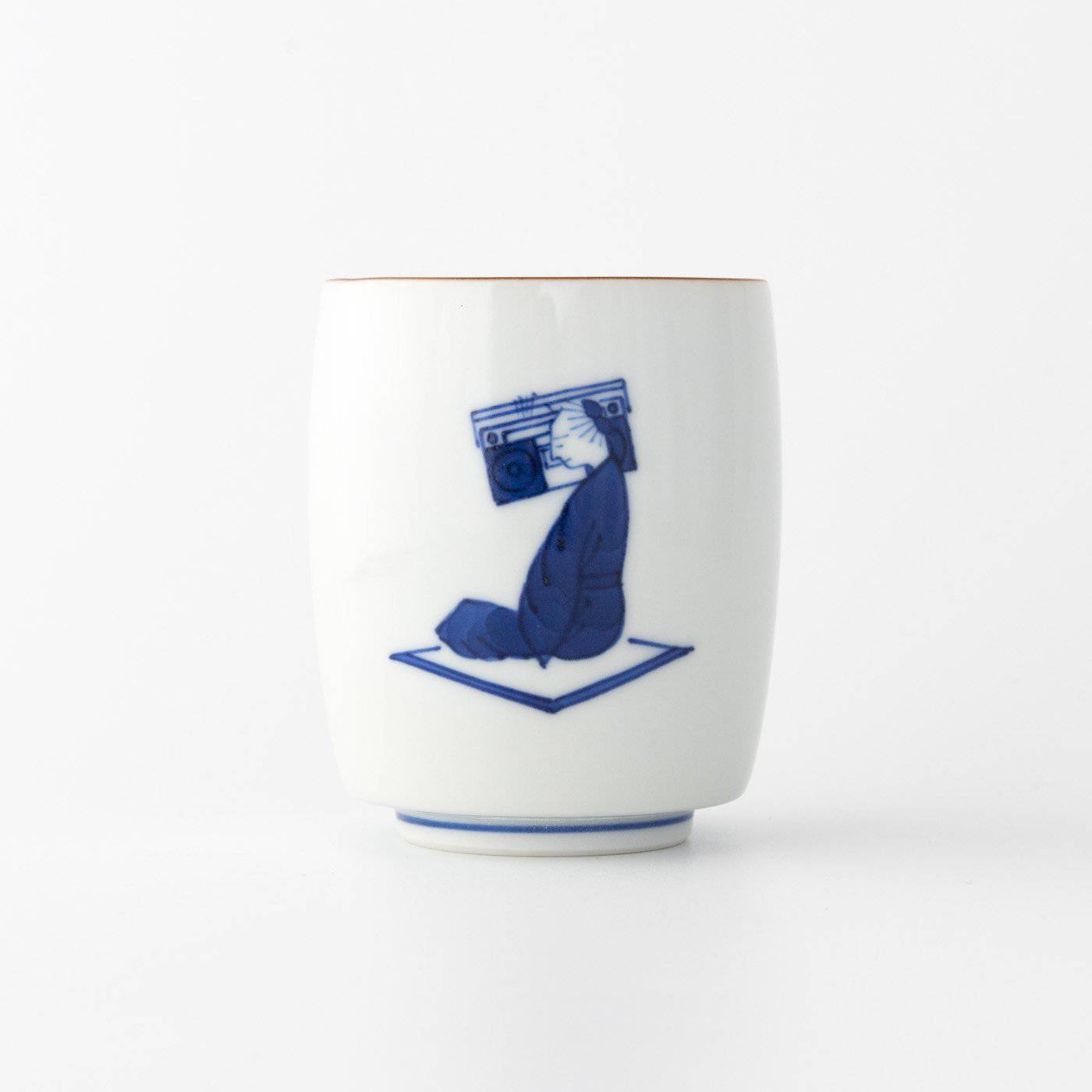
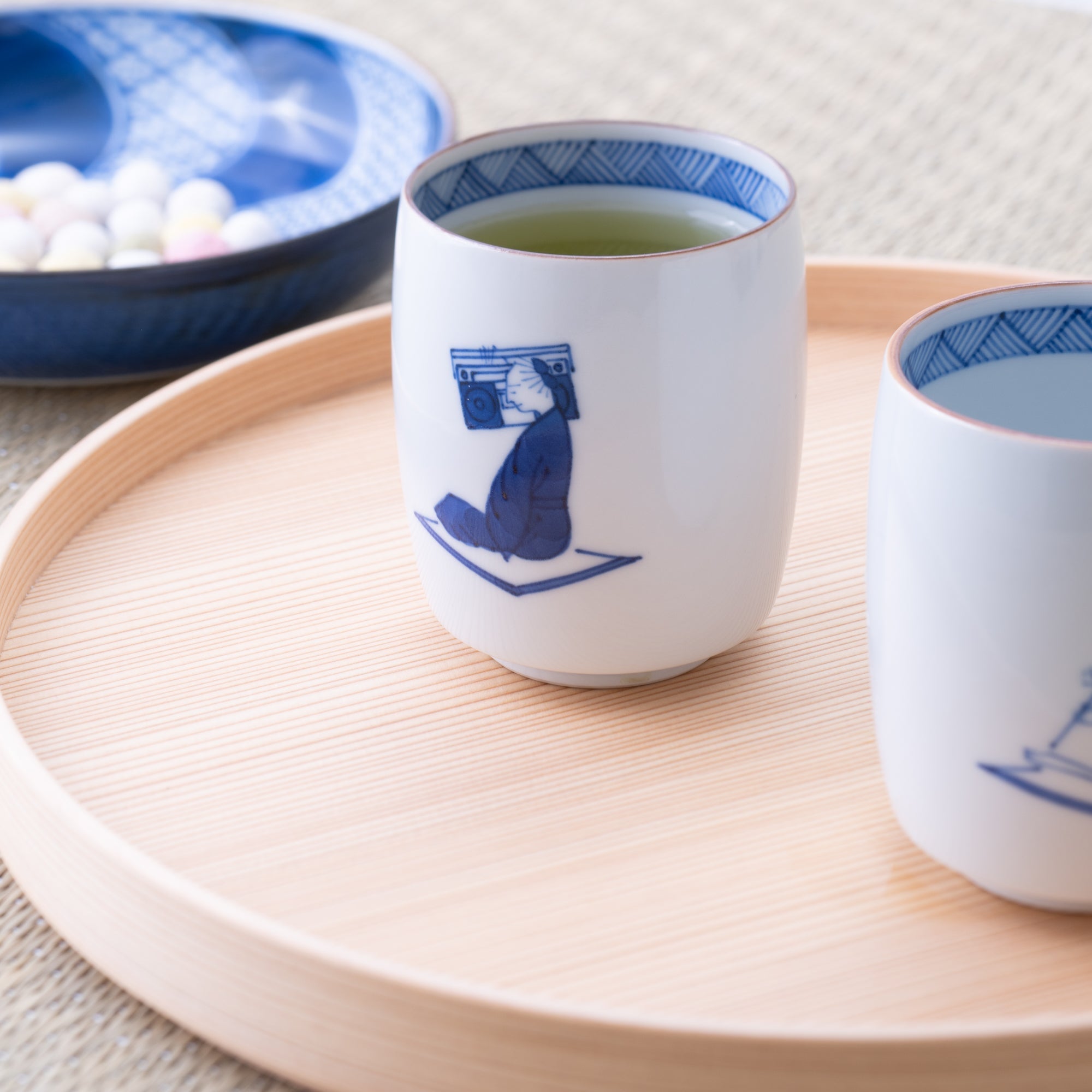
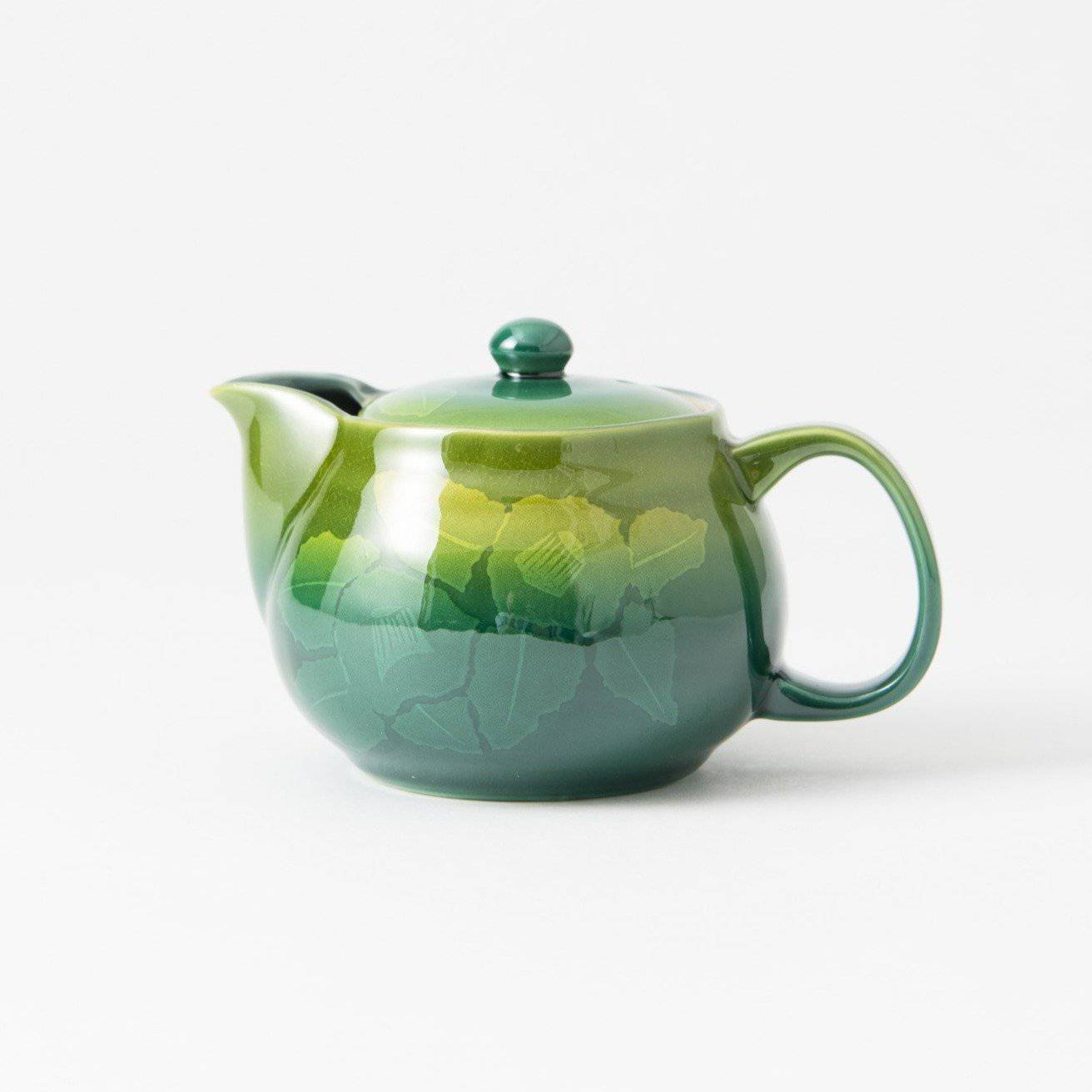
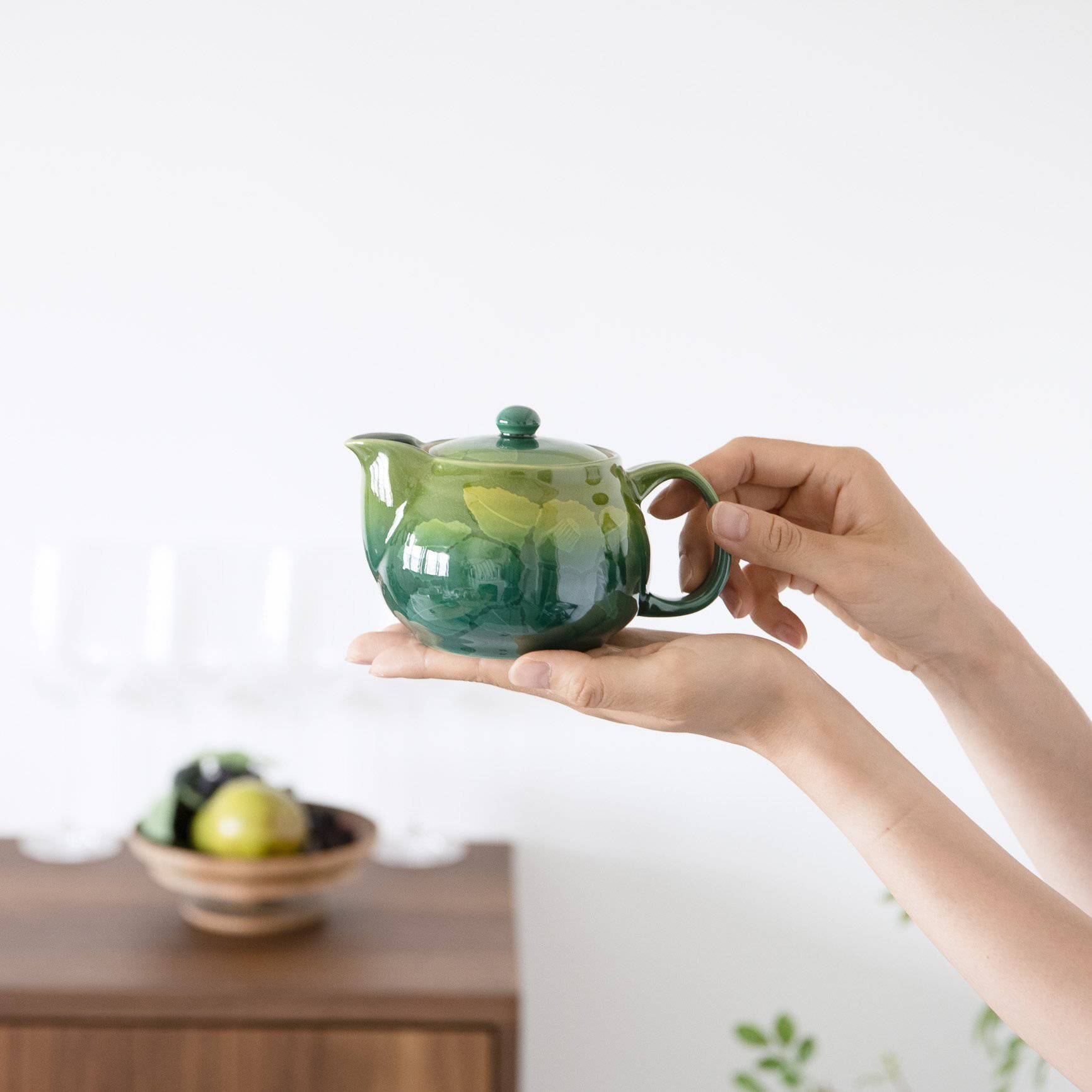
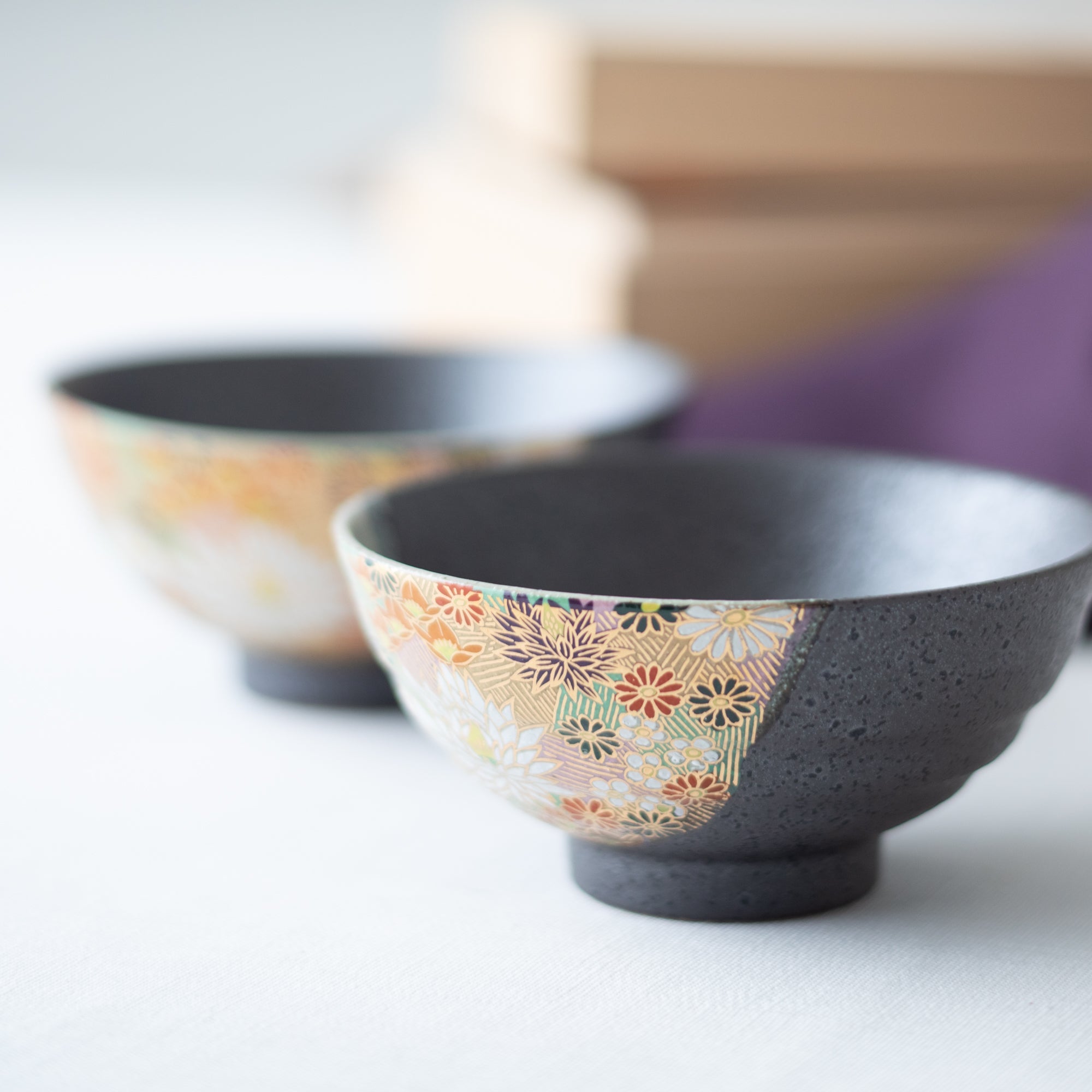
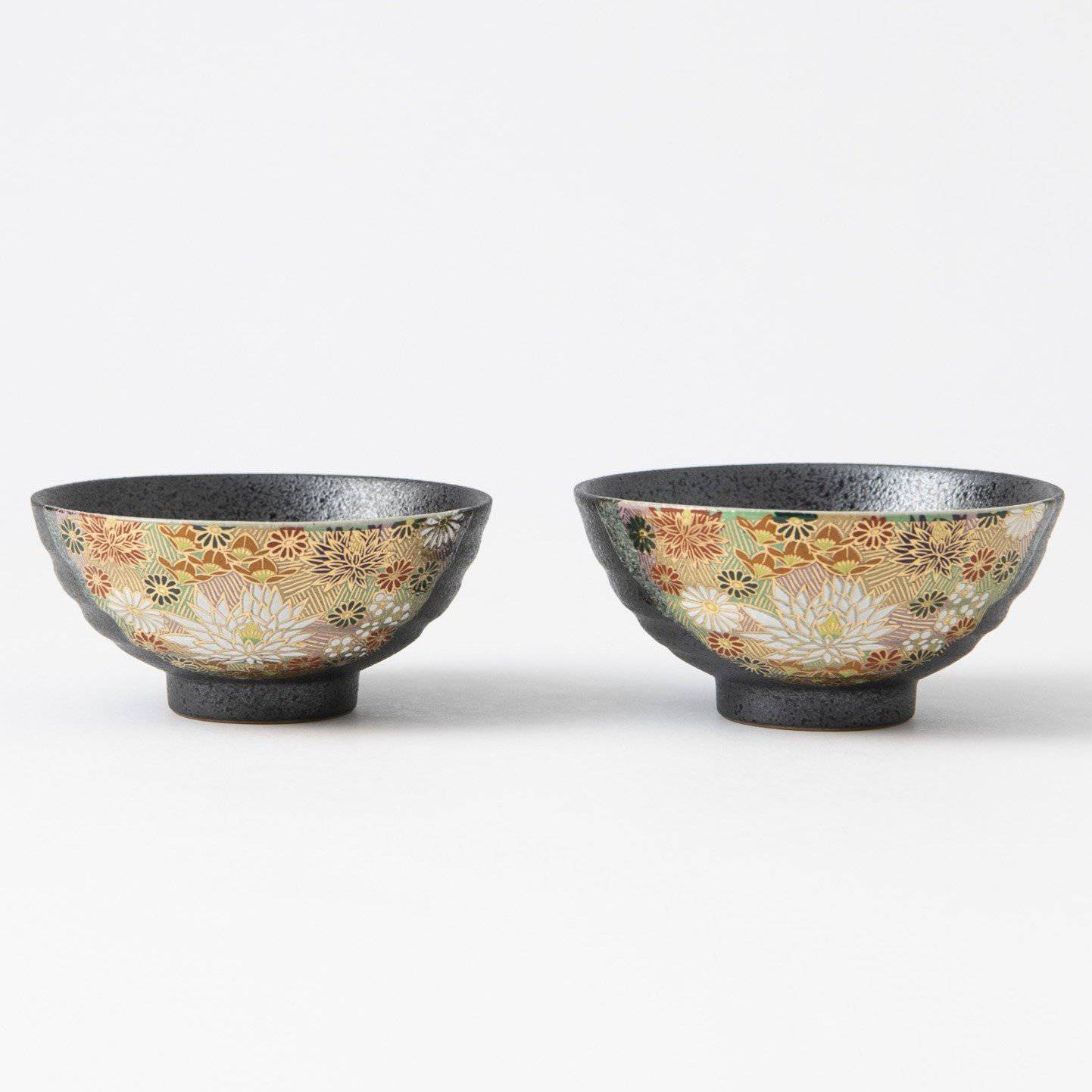
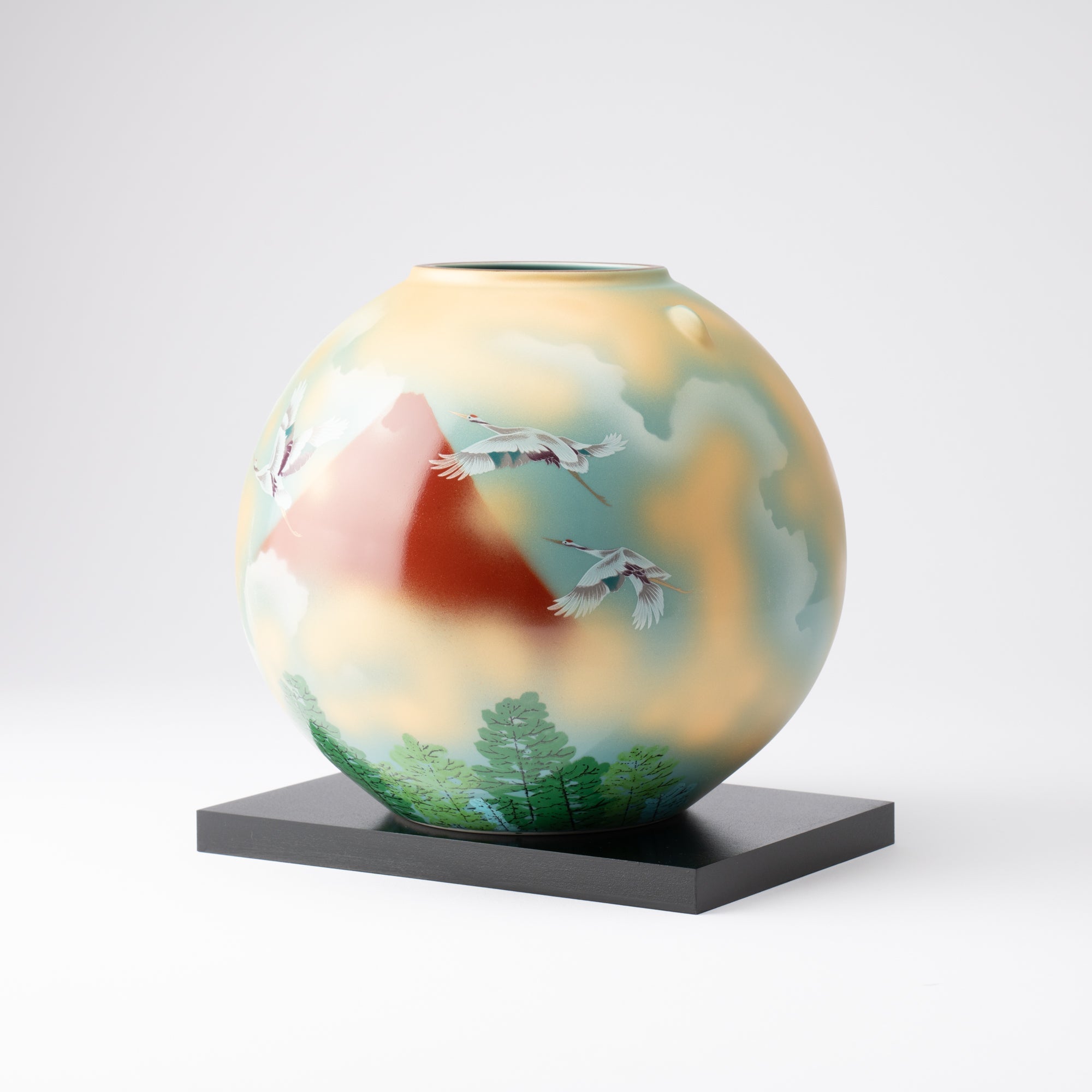
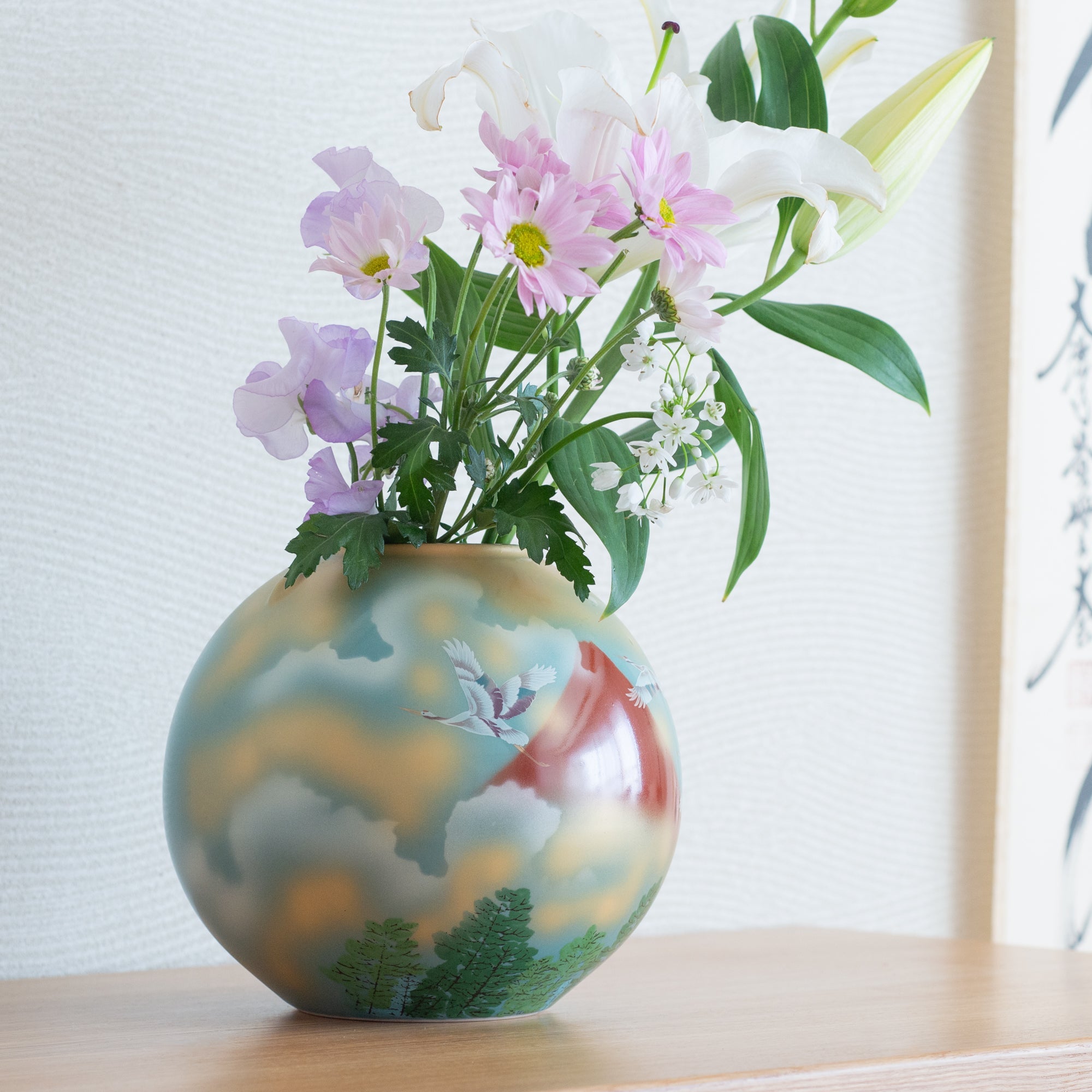
Kutani ware is a pottery produced in the Kaga region of Ishikawa Prefecture, with a history spanning over 350 years. It is characterized by the heavy brilliance of the five colors of navy blue, red, purple, green, and yellow that are applied to the bold and daring lines. Its long history has evolved through the tireless efforts and enthusiasm of people who have sought innovation while maintaining tradition.
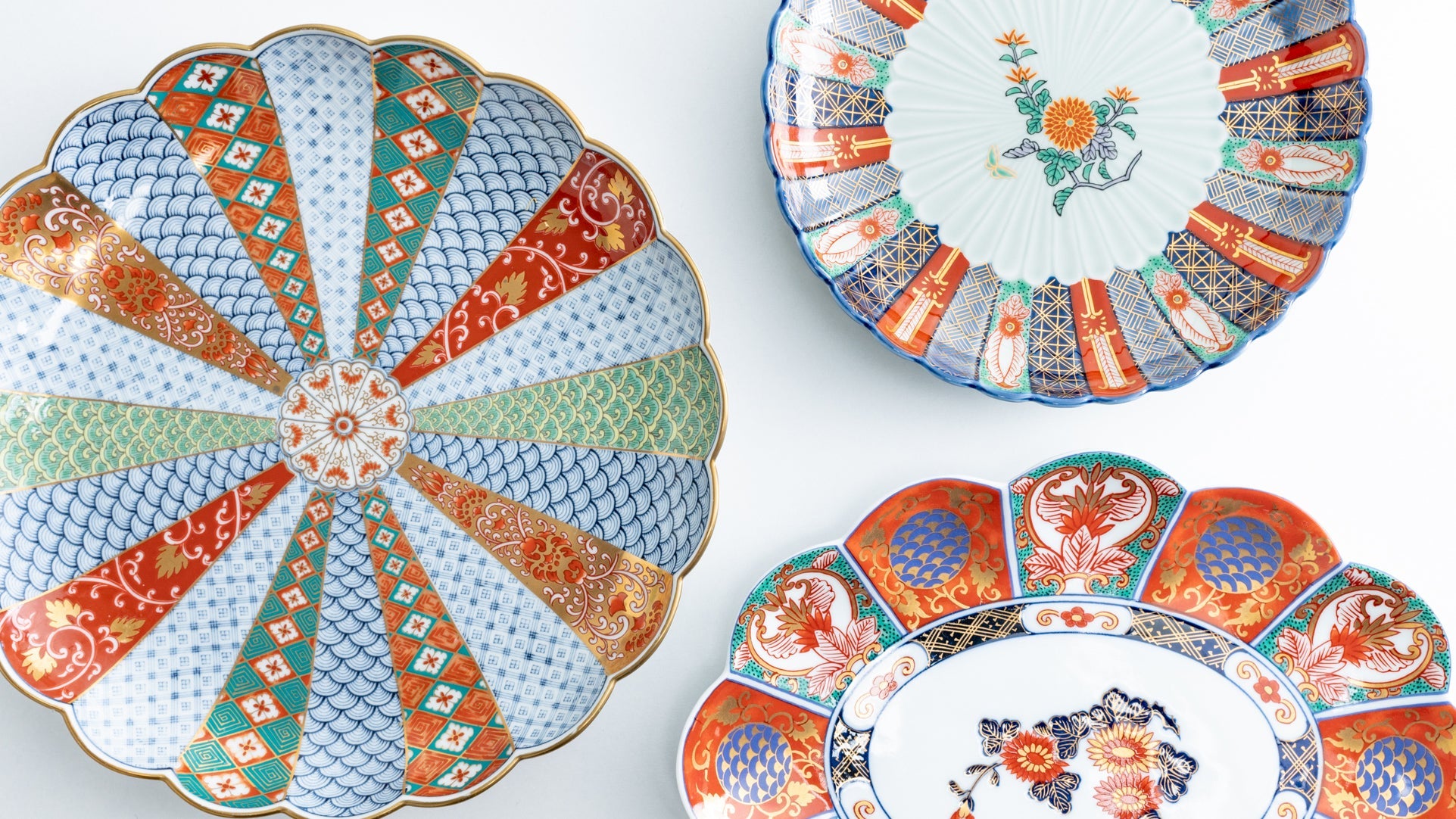
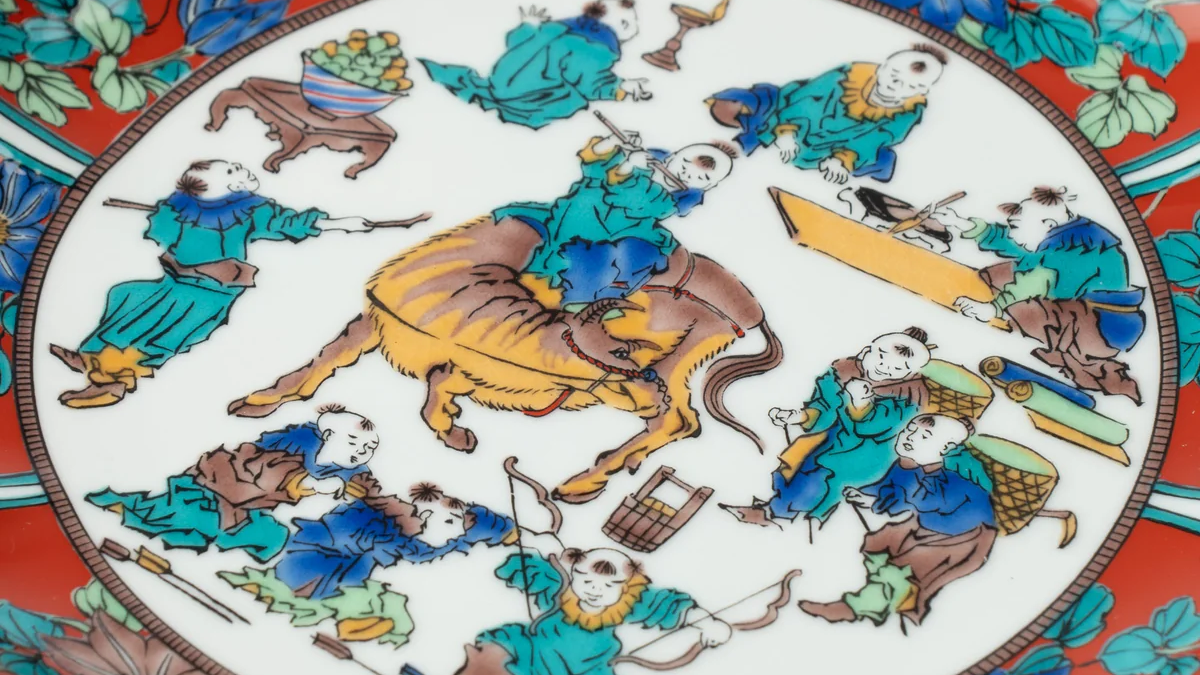
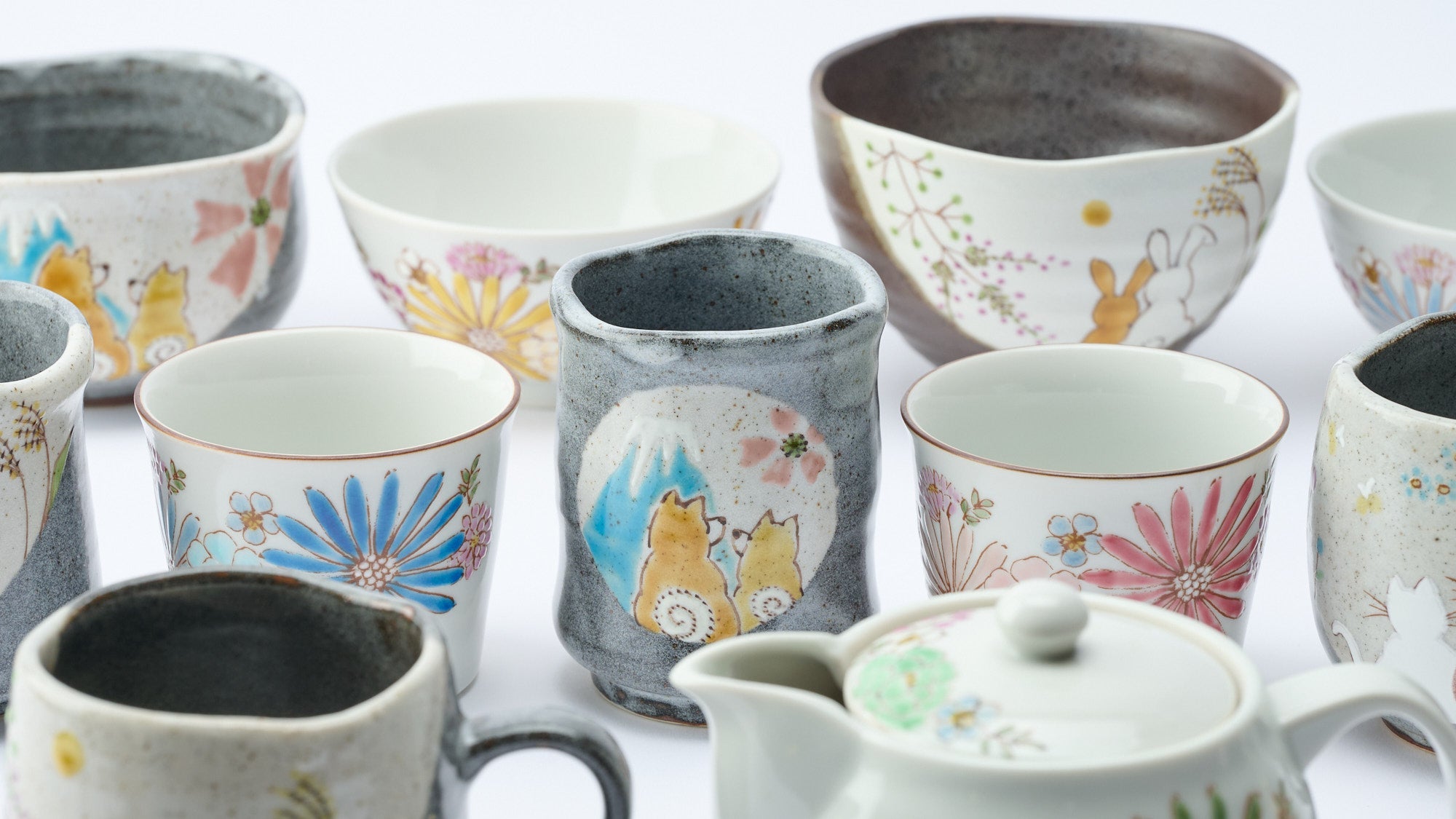
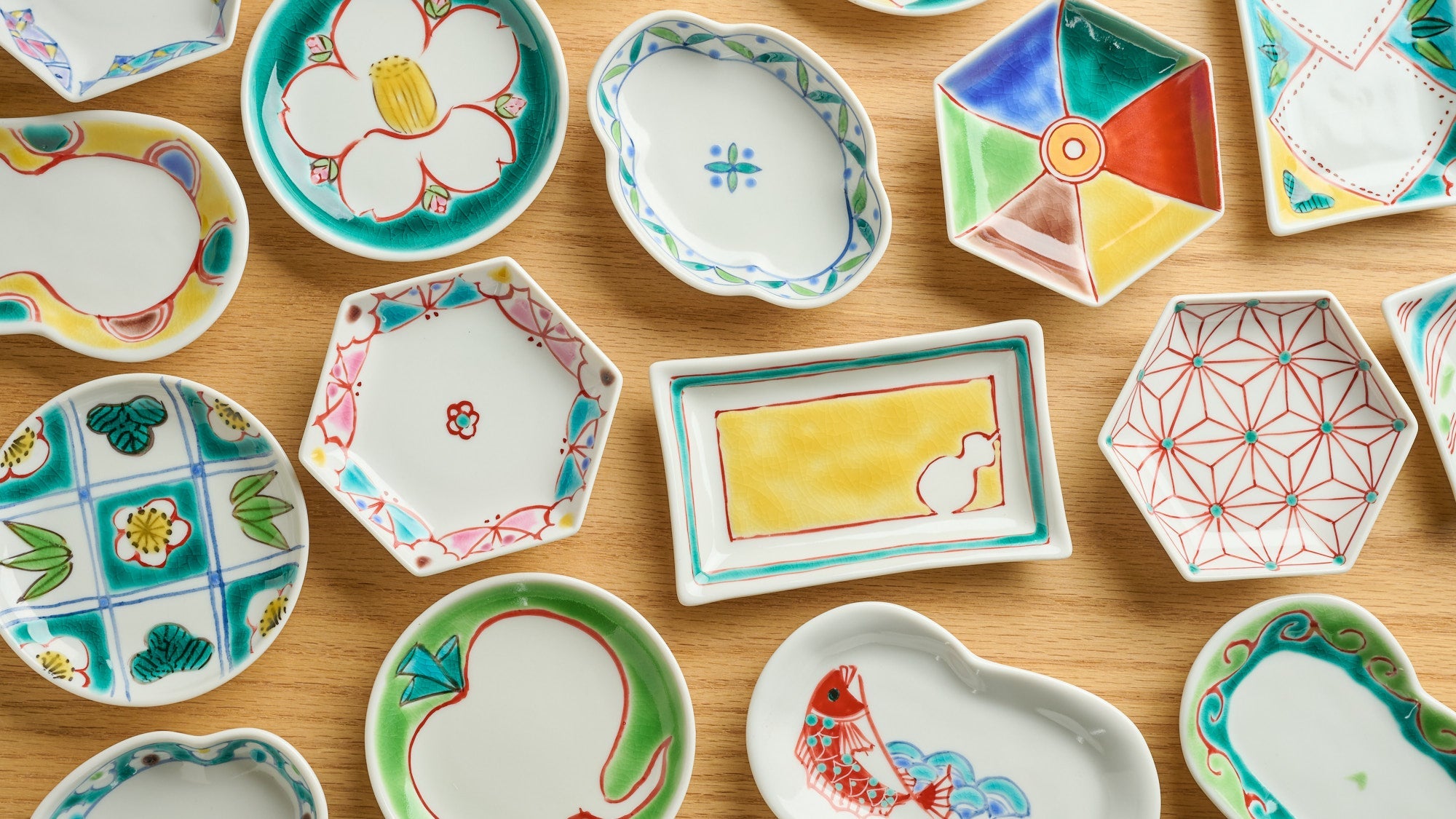
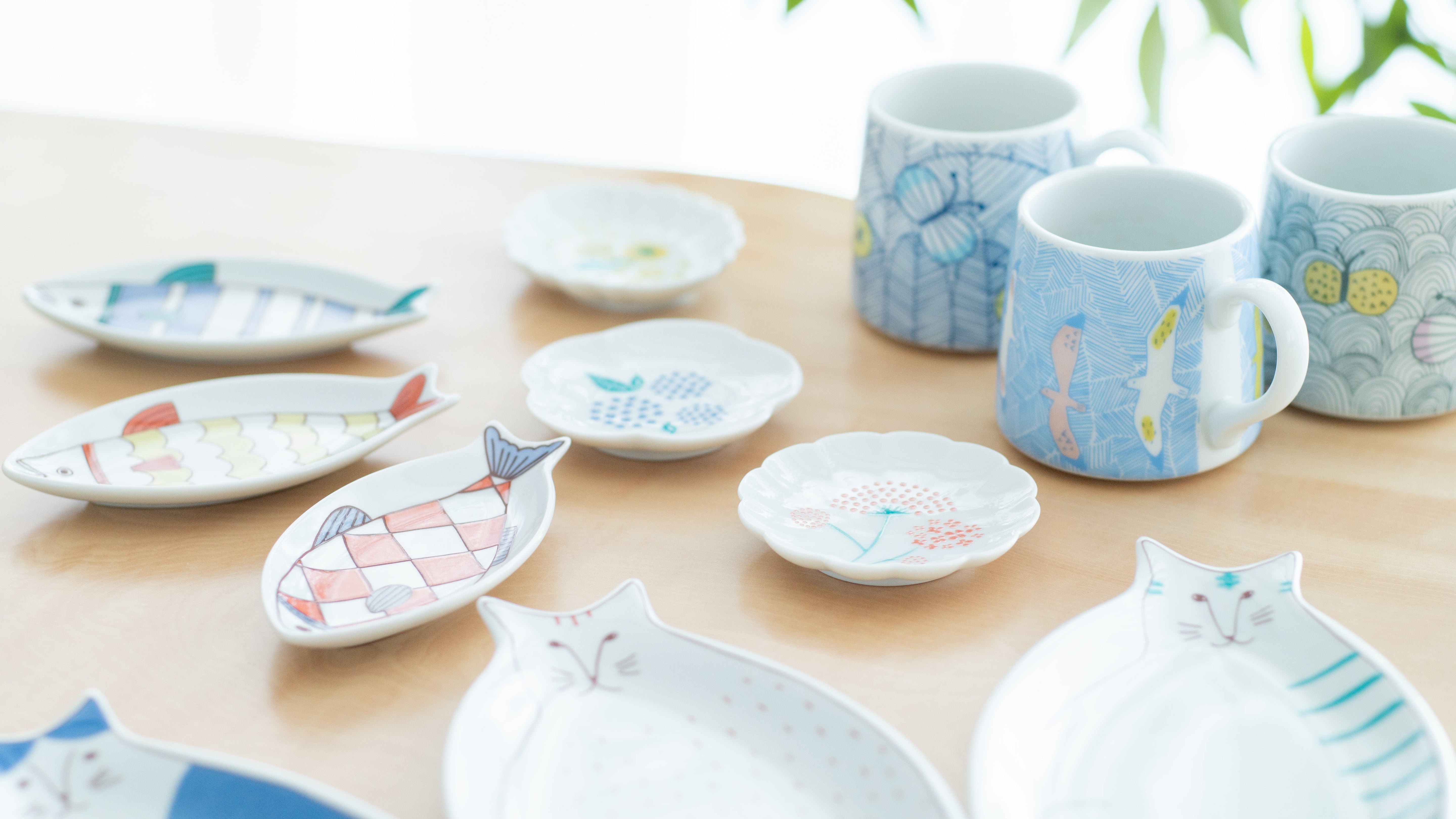
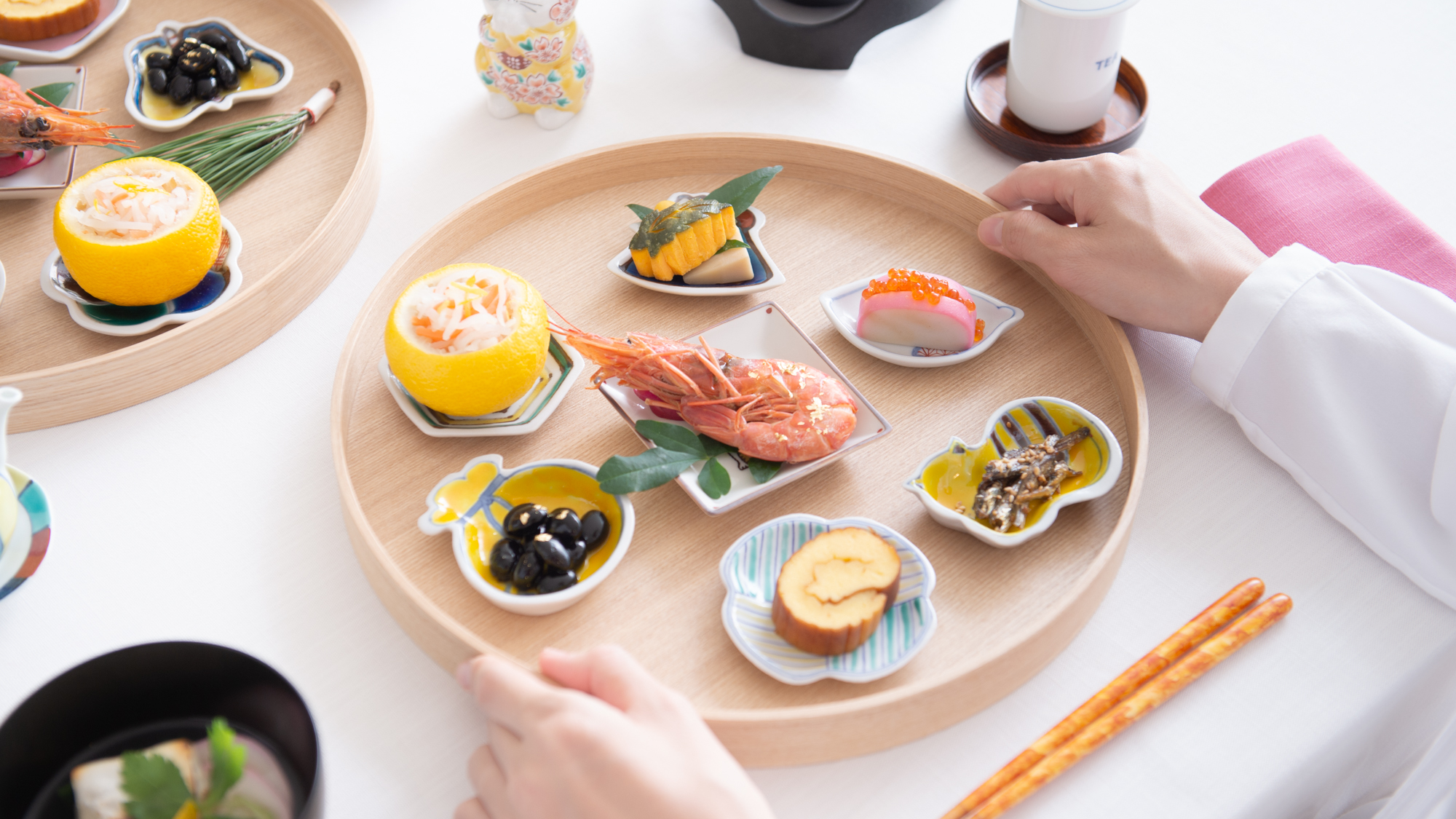
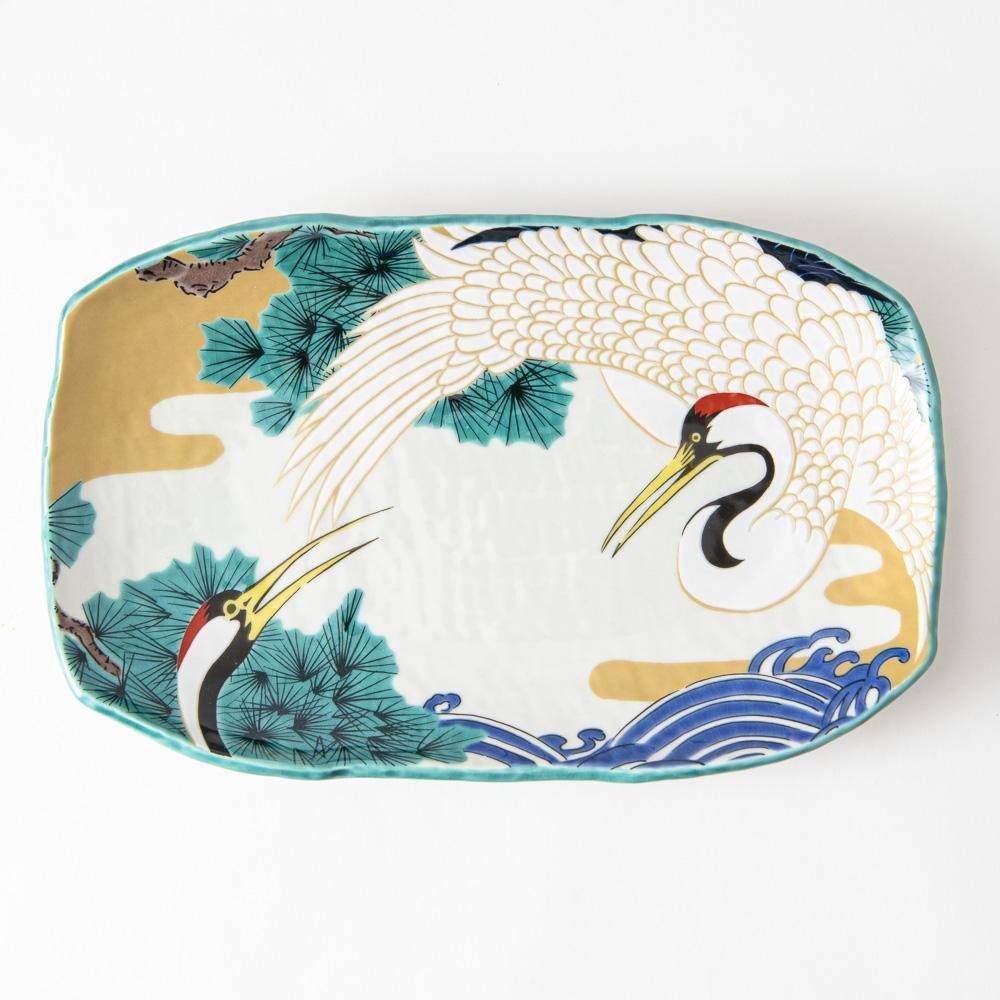
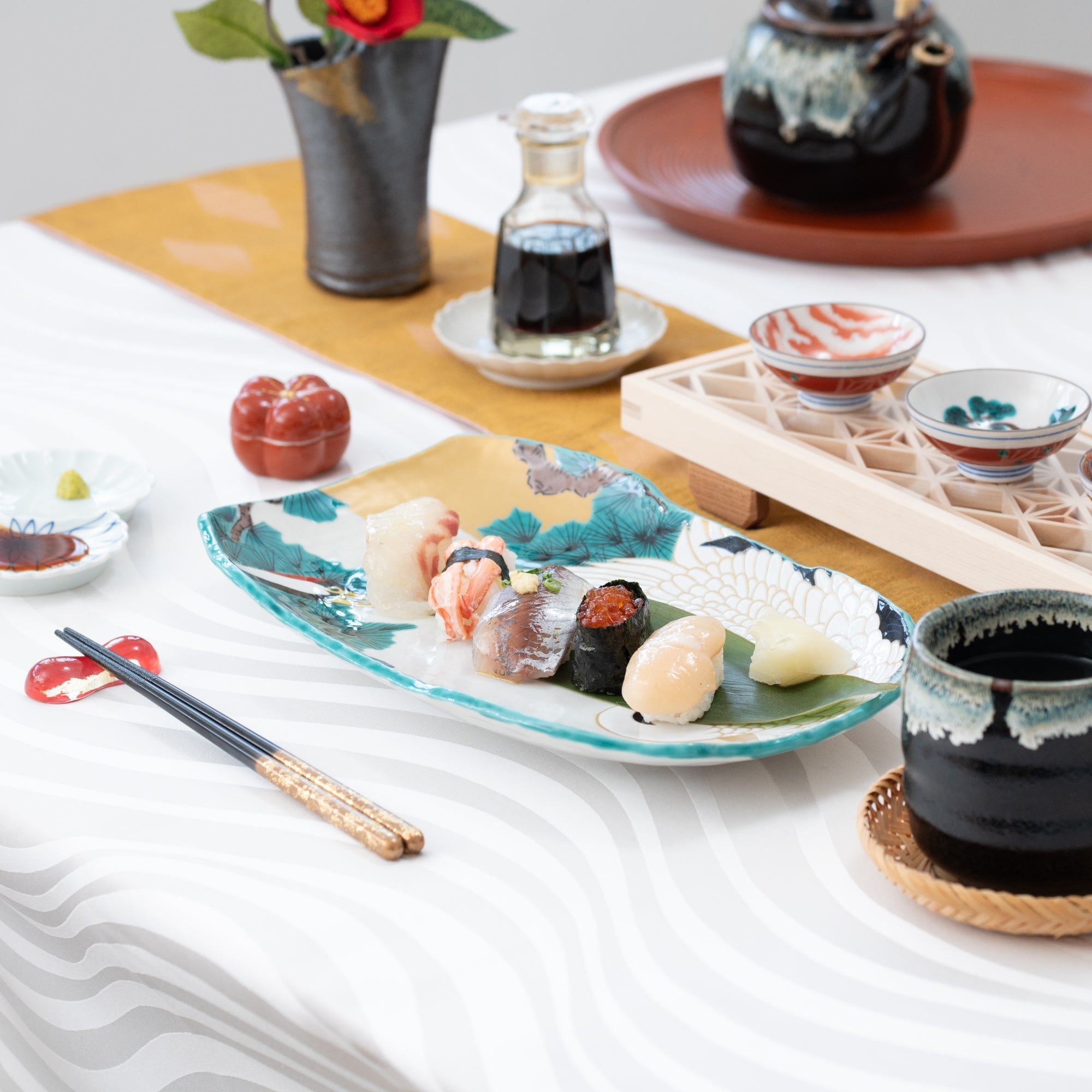
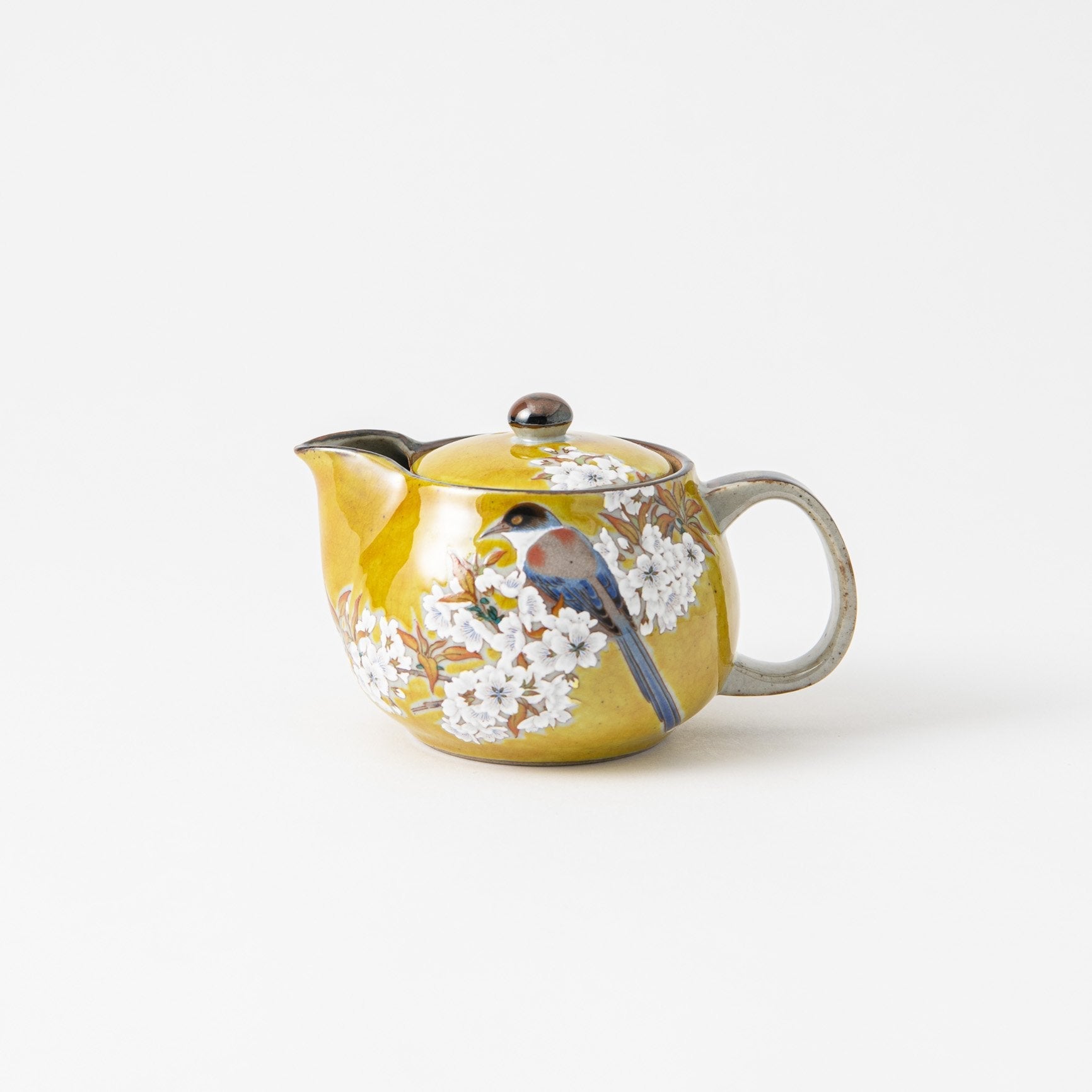
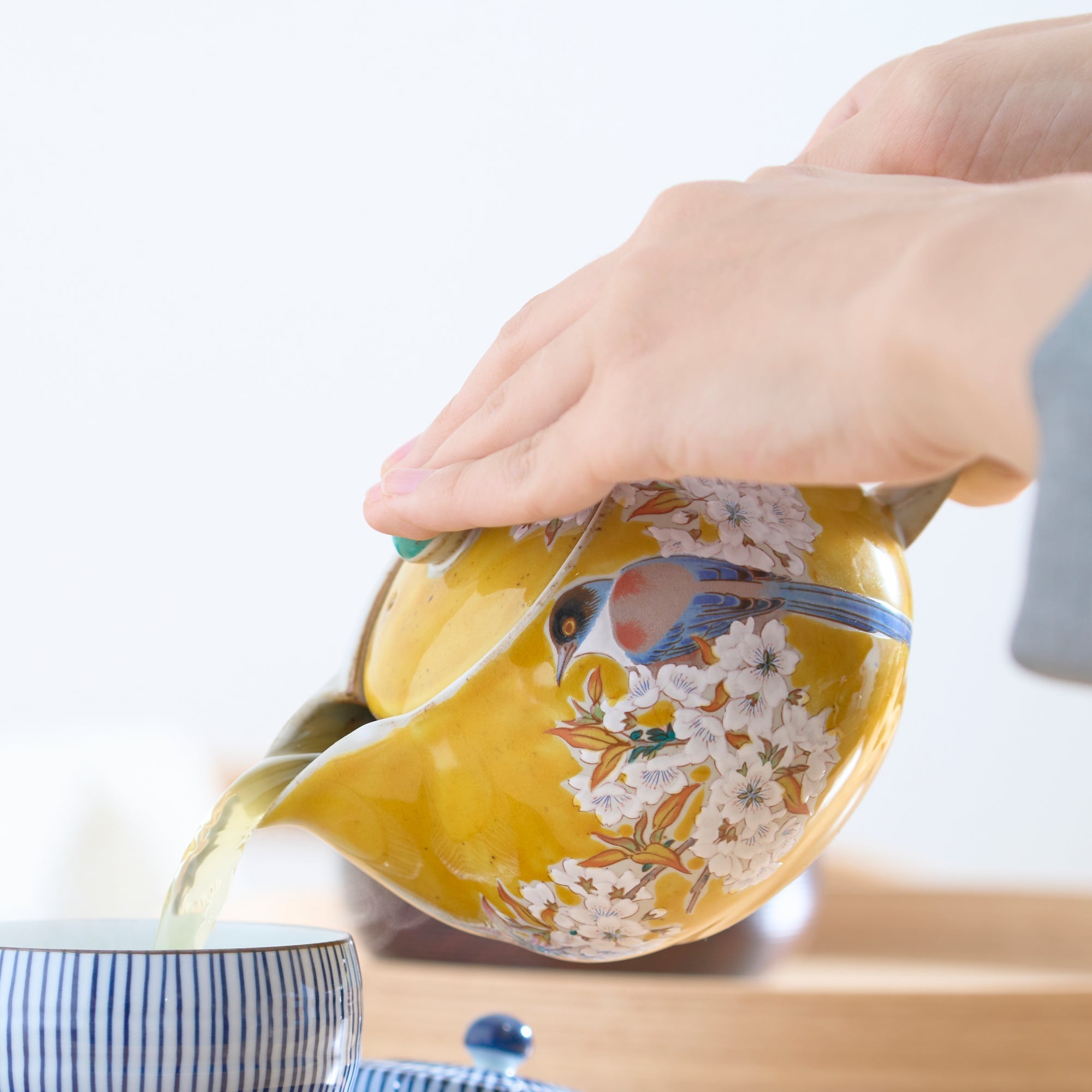
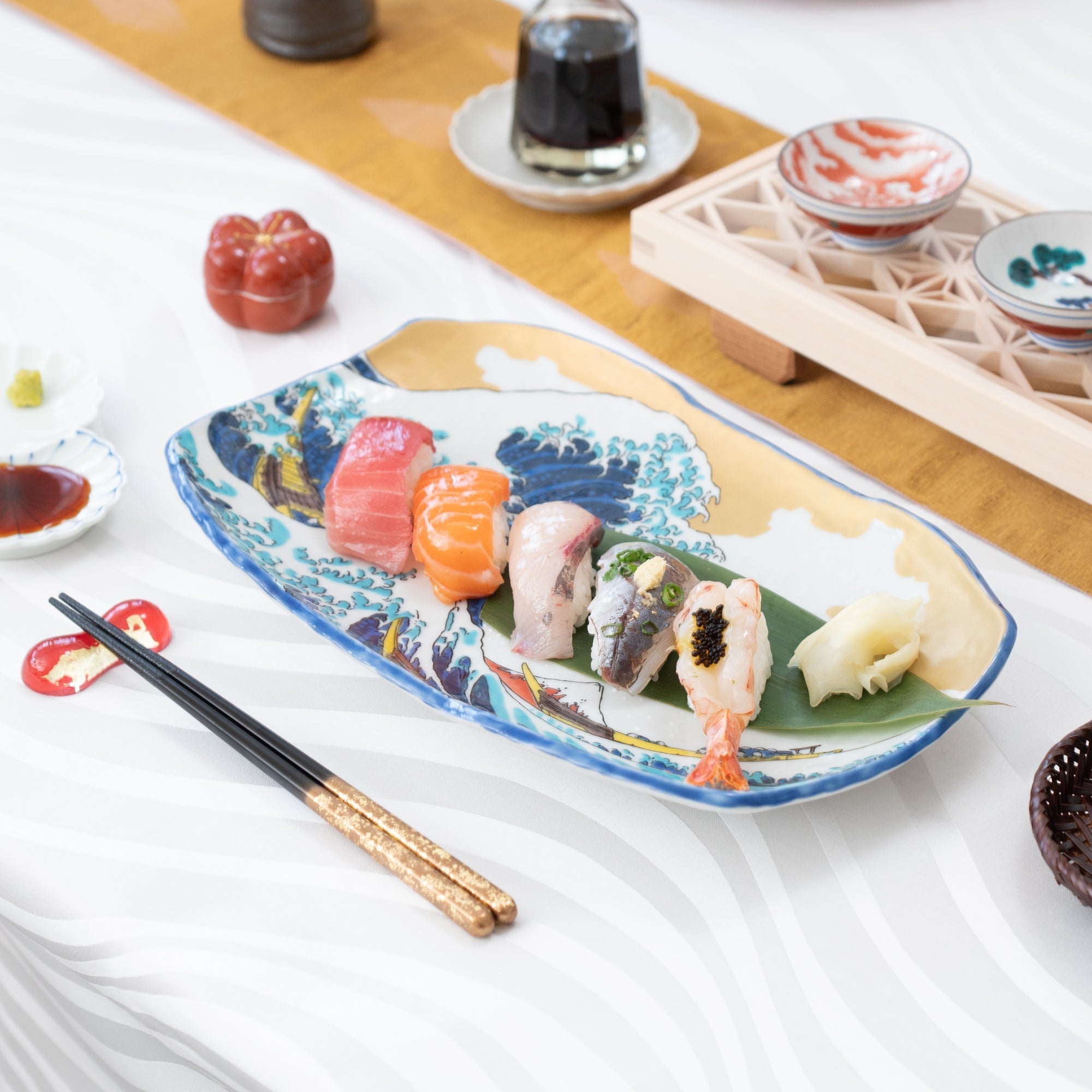
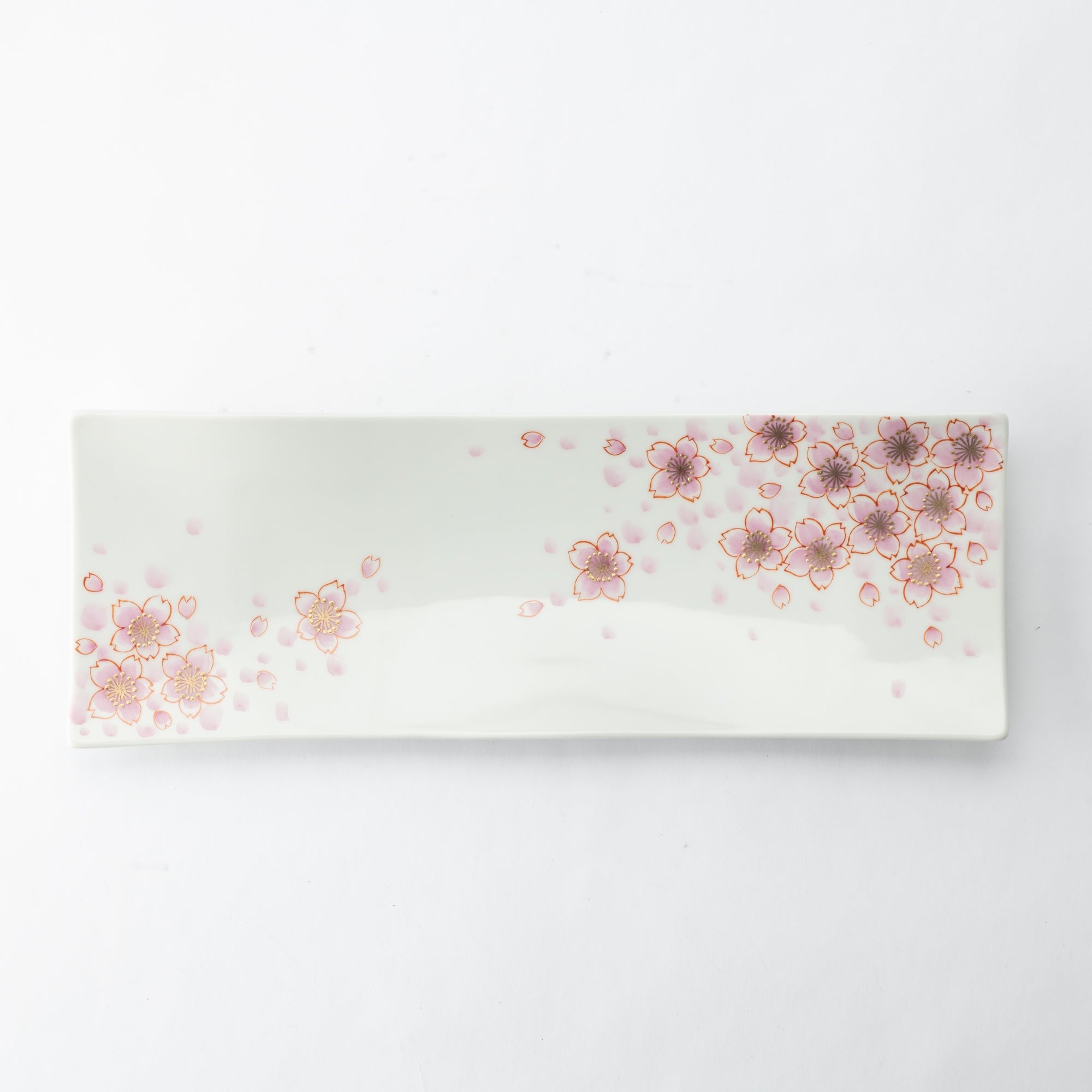
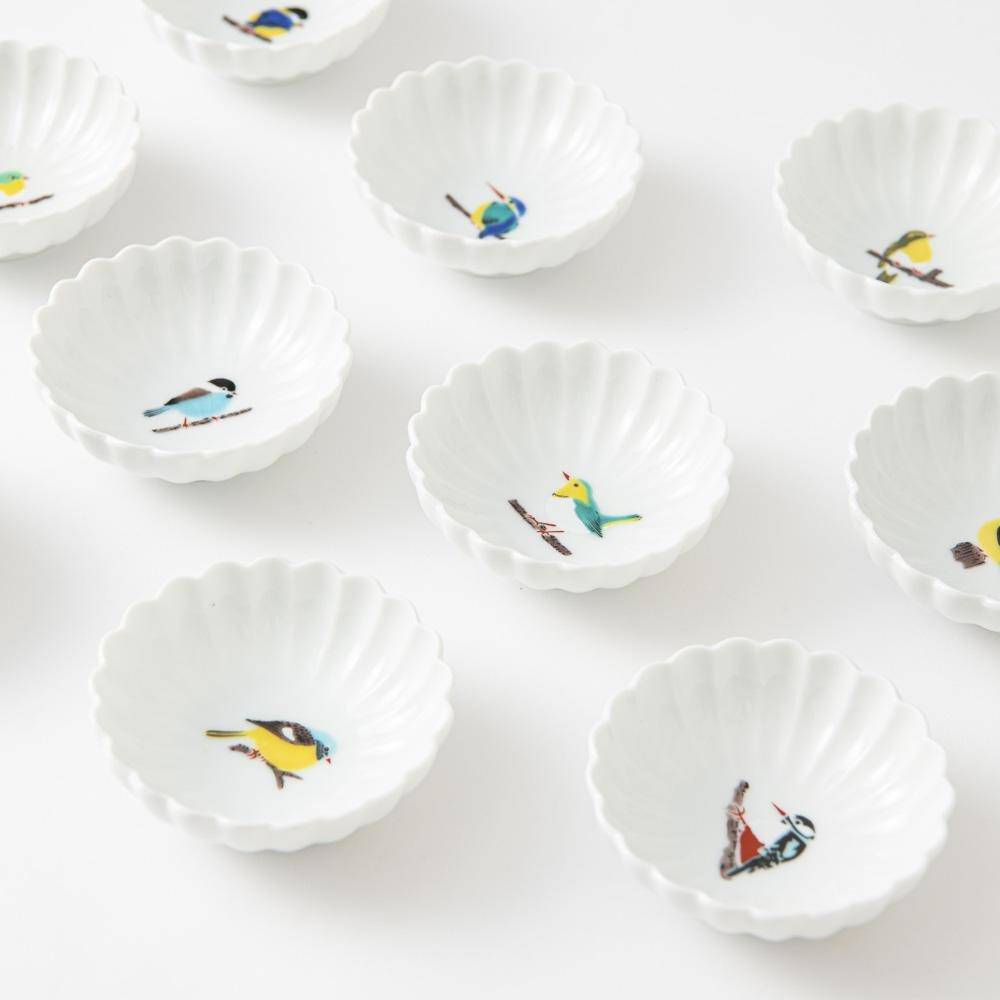
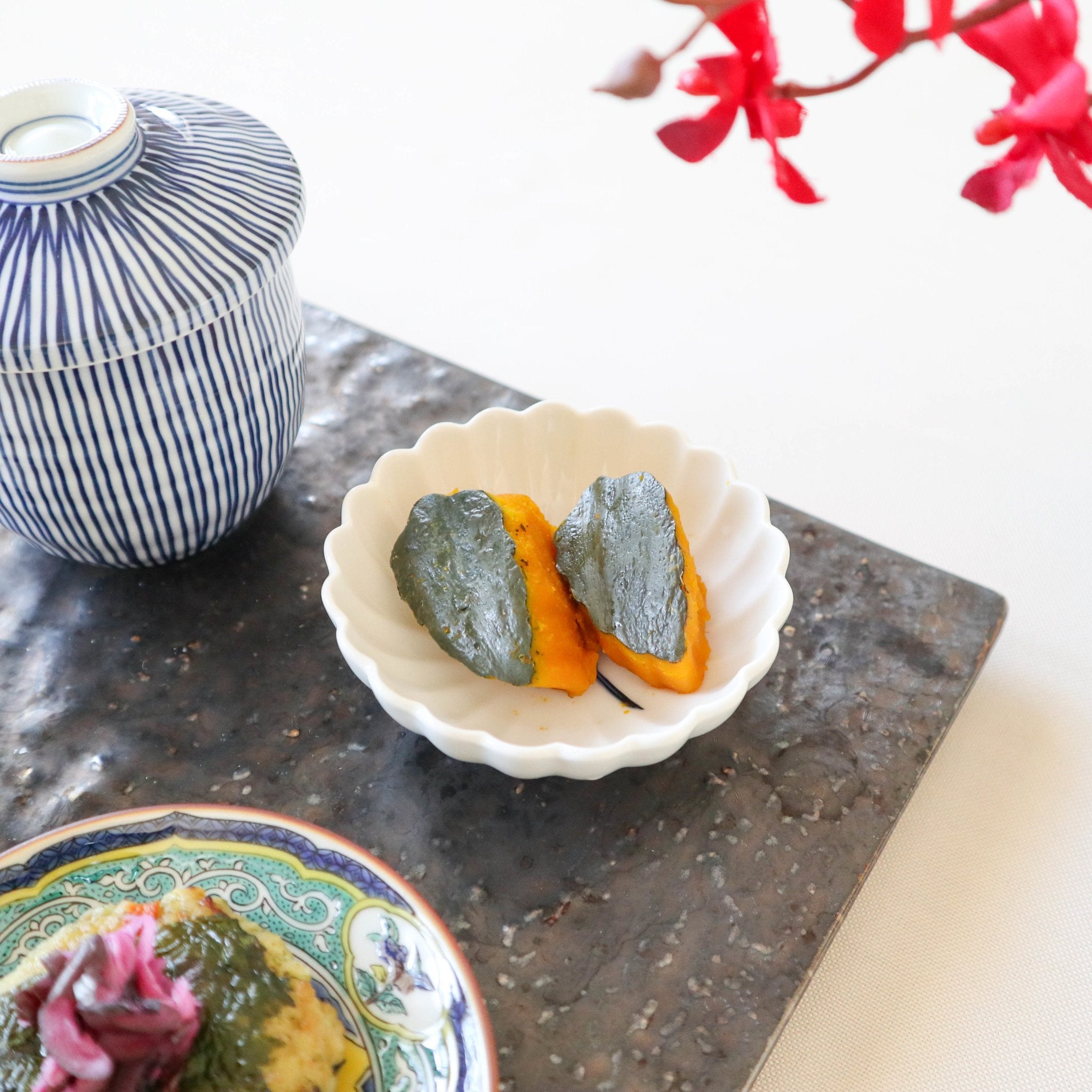
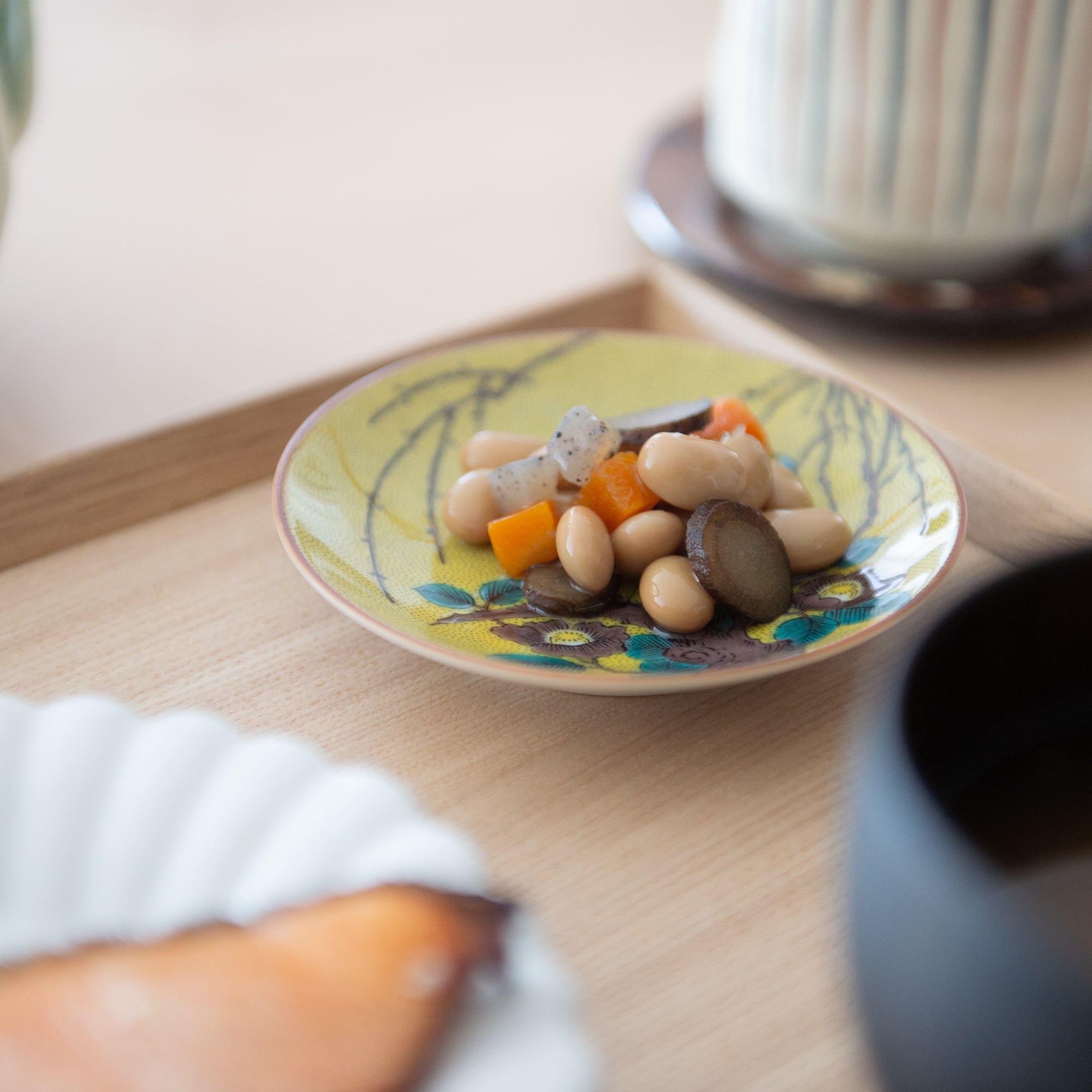
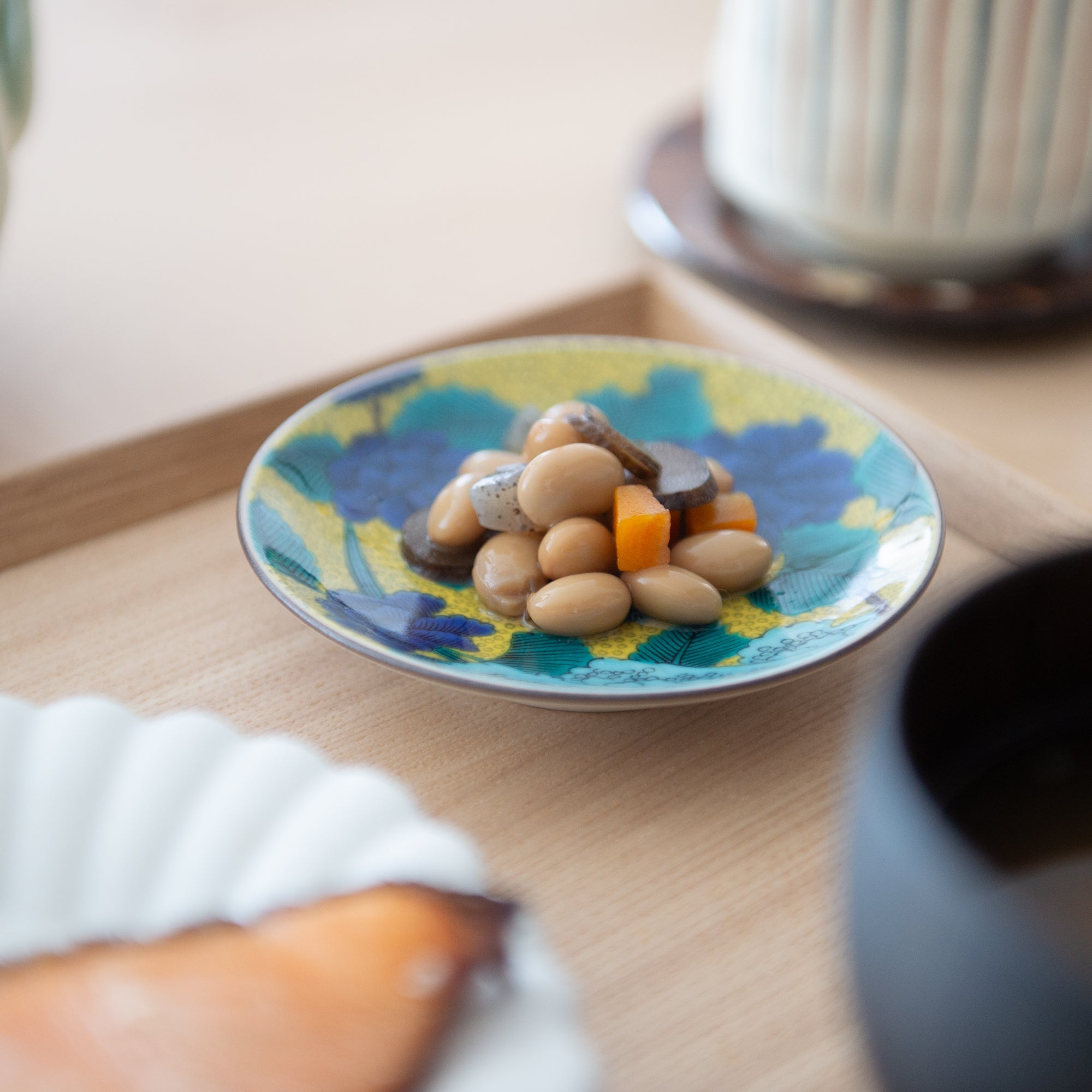
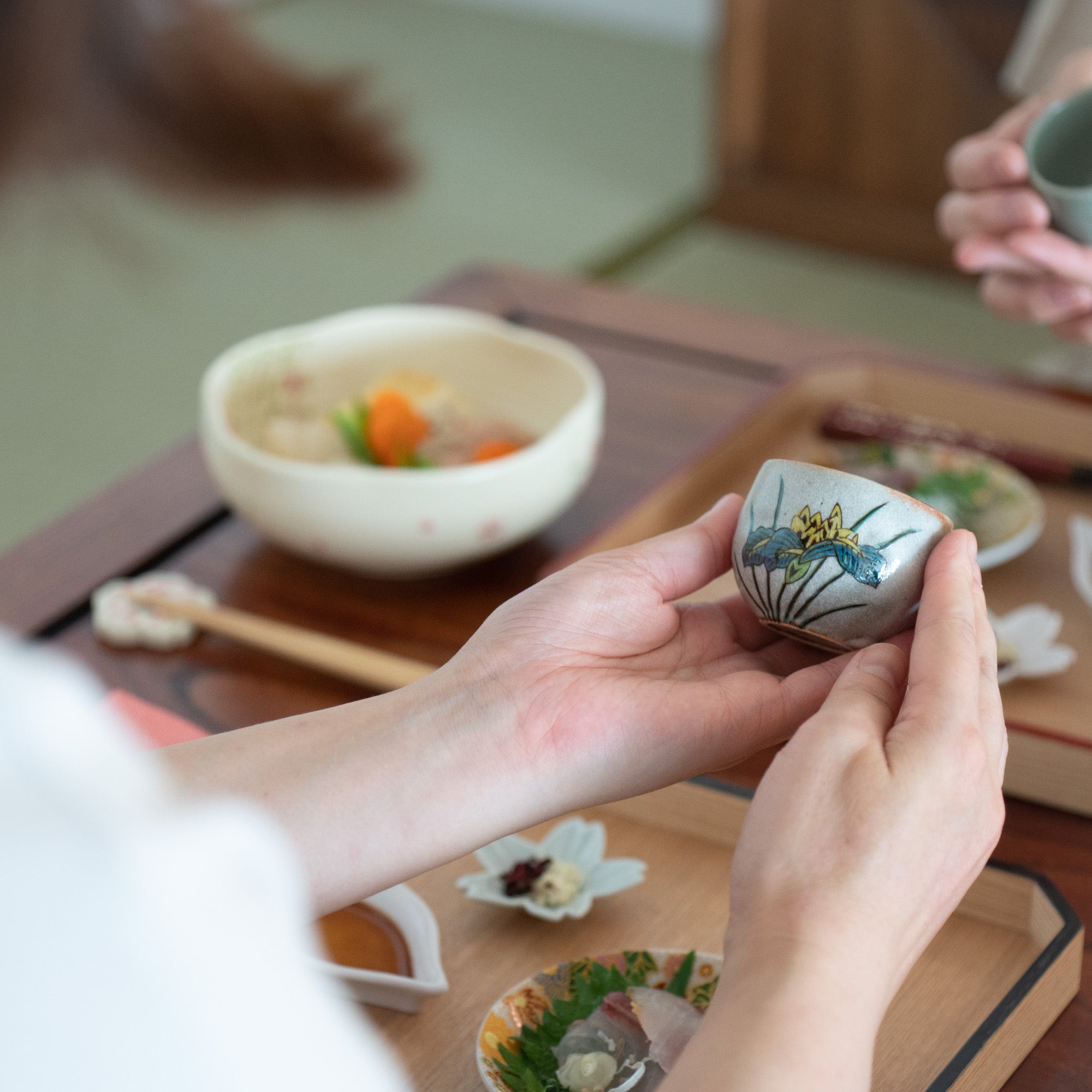
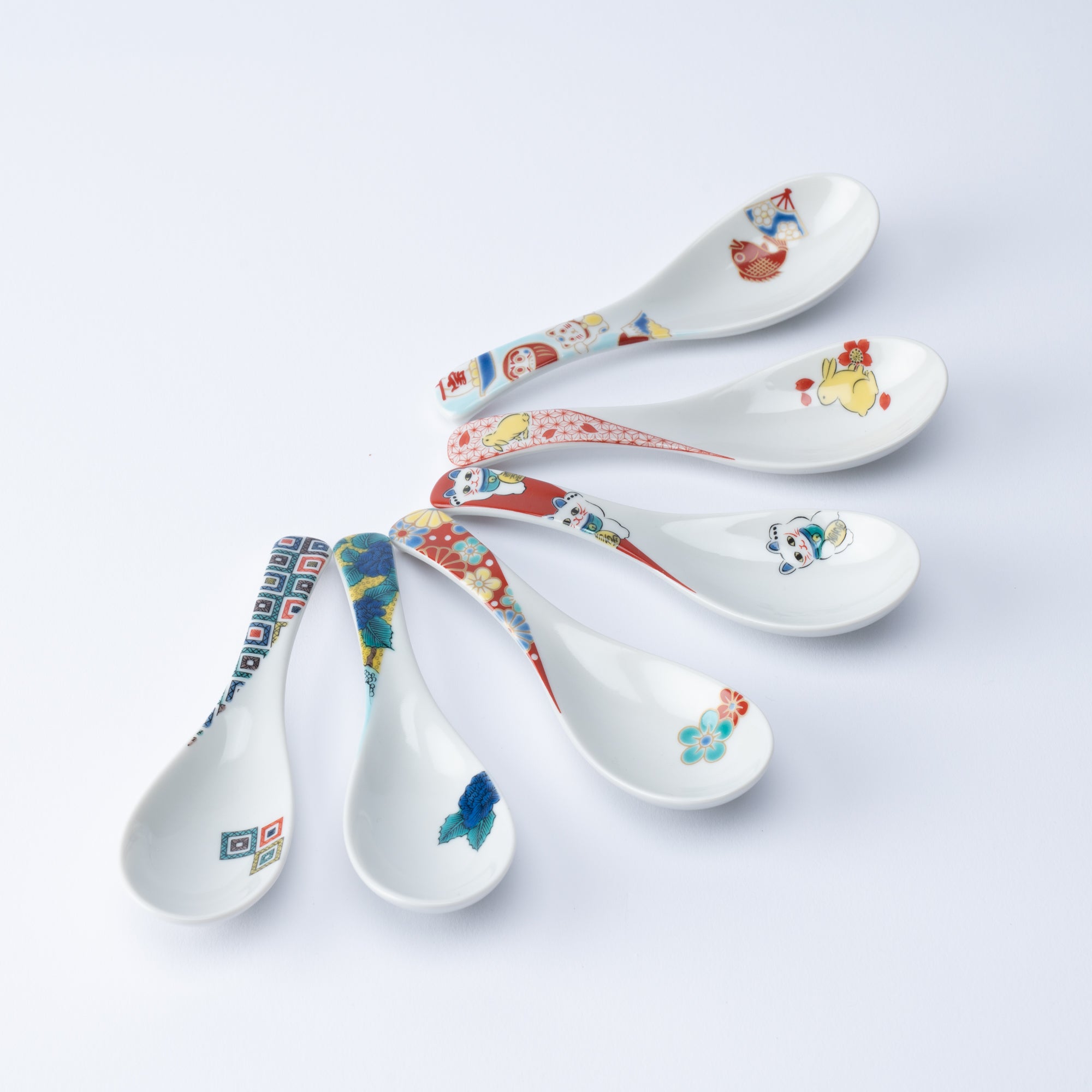
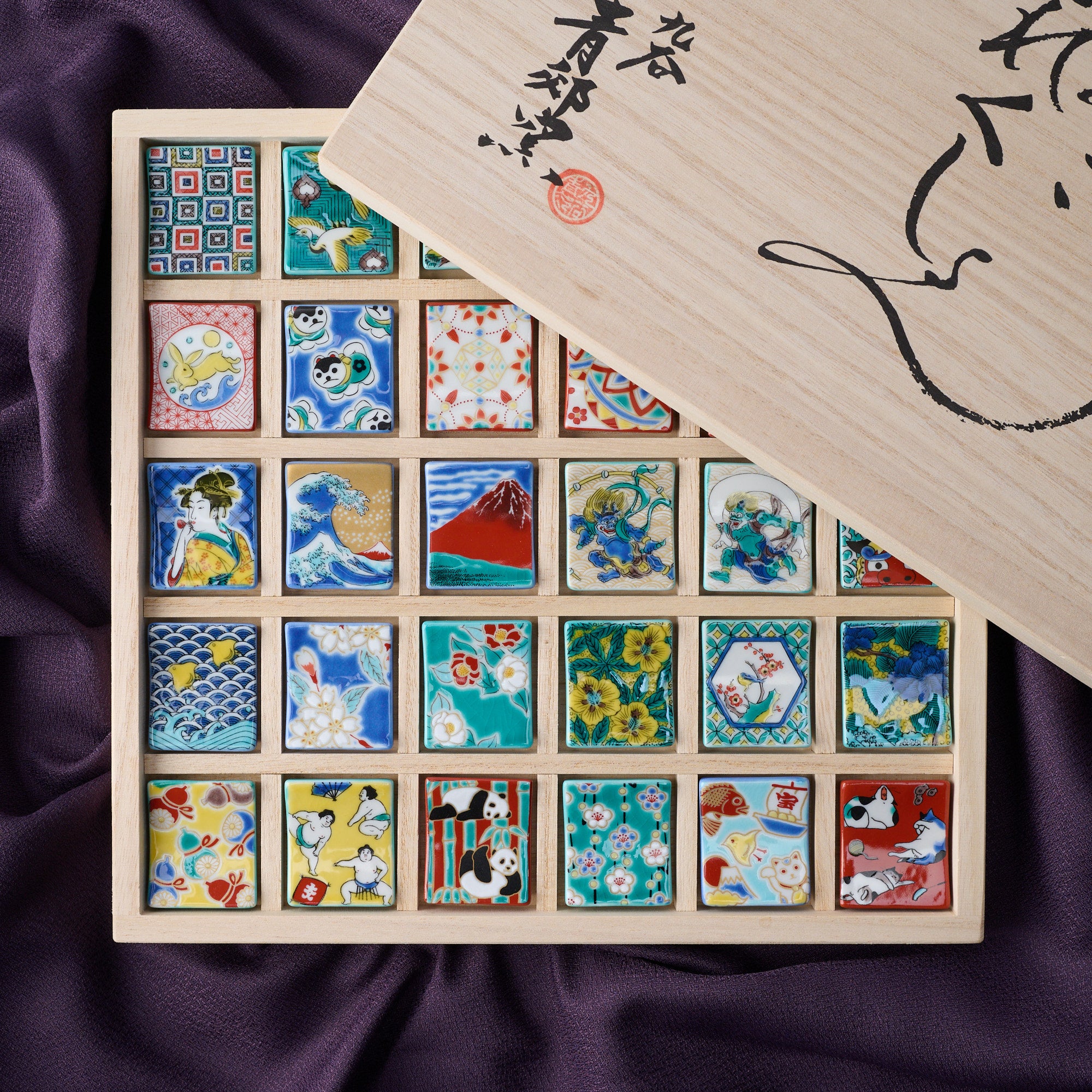
Kutani ware is a type of Japanese ceramic that includes both porcelain and stoneware produced in the southern region of Ishikawa Prefecture. It is celebrated for its dynamic, painterly overglaze decoration, often featuring traditional Japanese motifs such as kacho (flowers and birds) and sansui (landscapes). These vivid and expressive designs are found not only on everyday tableware like plates and bowls but also on art pieces.
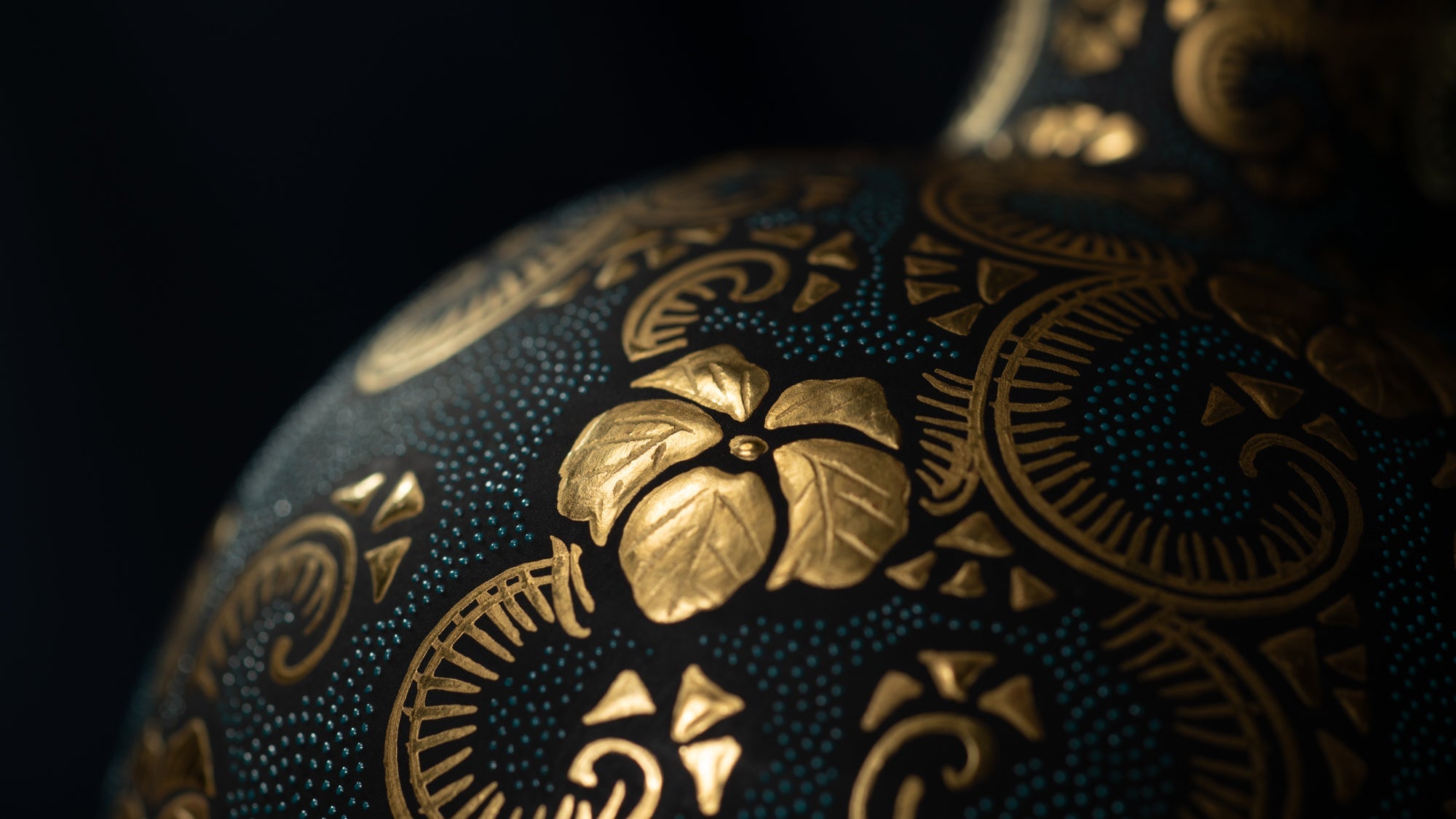
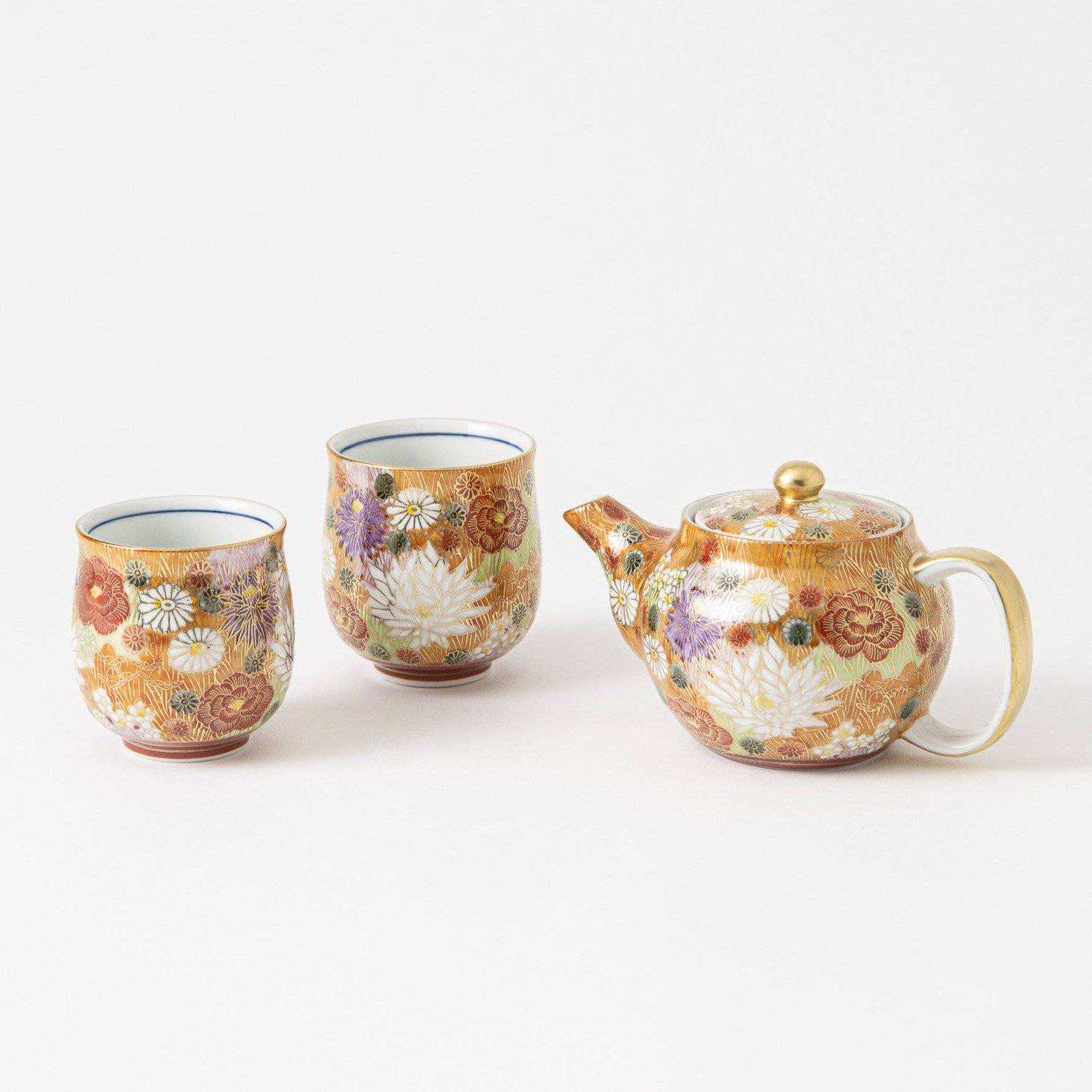
Over the years, Kutani ware has developed a variety of distinctive painting styles, reflecting changes in artistic taste and technique. Among the most renowned is the use of red and gold patterns, a lavish approach perfected by the artisan Kutani Shoza. This style became internationally recognized during the Meiji era (1868–1912 CE) under the name “Japan Kutani.”
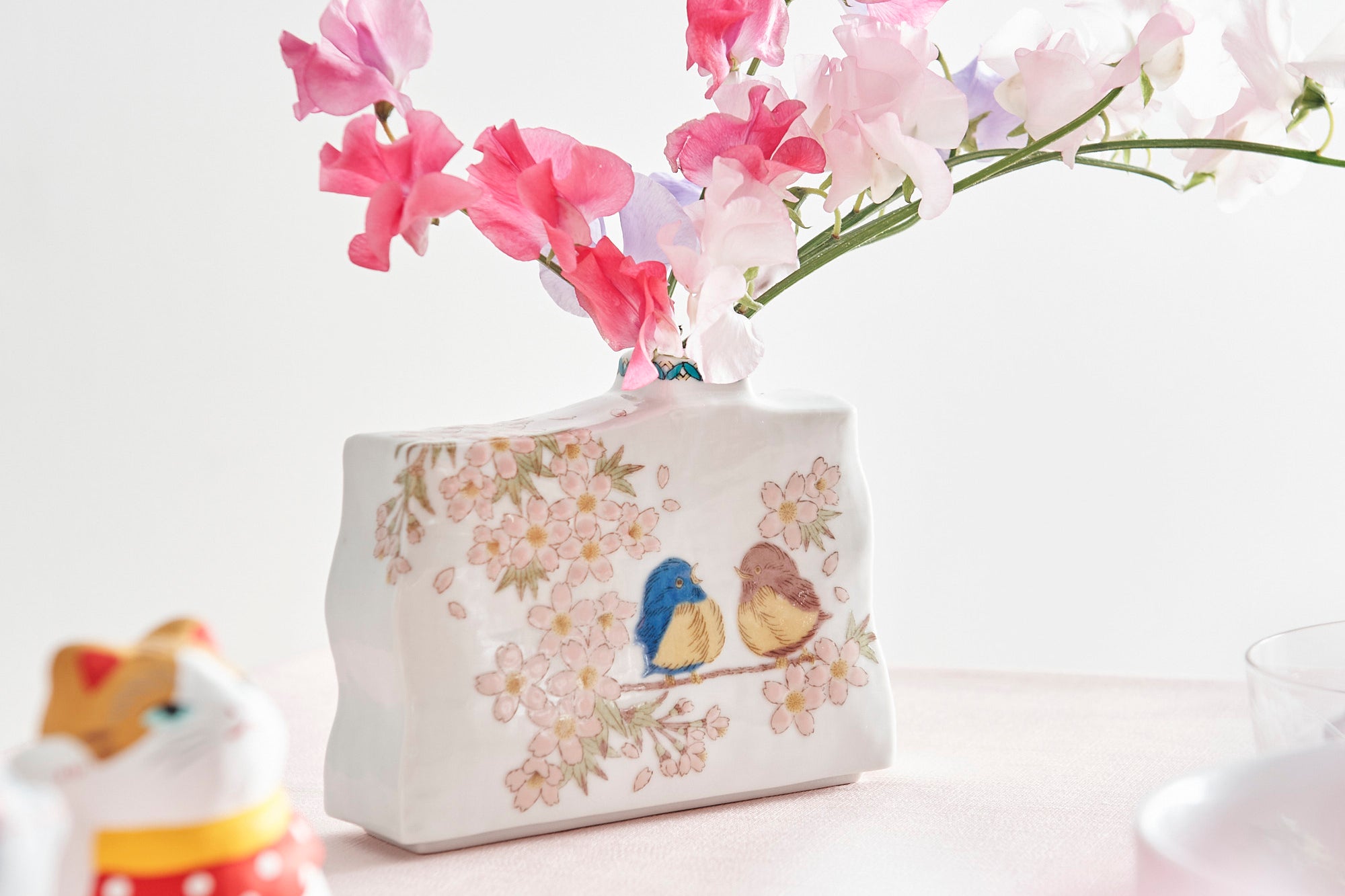

Through its long history, Kutani ware has preserved traditional techniques and aesthetics while continuing to evolve with modern advancements.
Kutani ware originated in 1655 during the early Edo period (1603–1868 CE), when Maeda Toshiharu, the first lord of the Kaga Daishoji Domain, established a kiln in the village of Kutani. This initiative followed the discovery of suitable pottery stones at the Kutani gold mine. The porcelain produced there soon became known as Kutani ware, named after its place of origin.
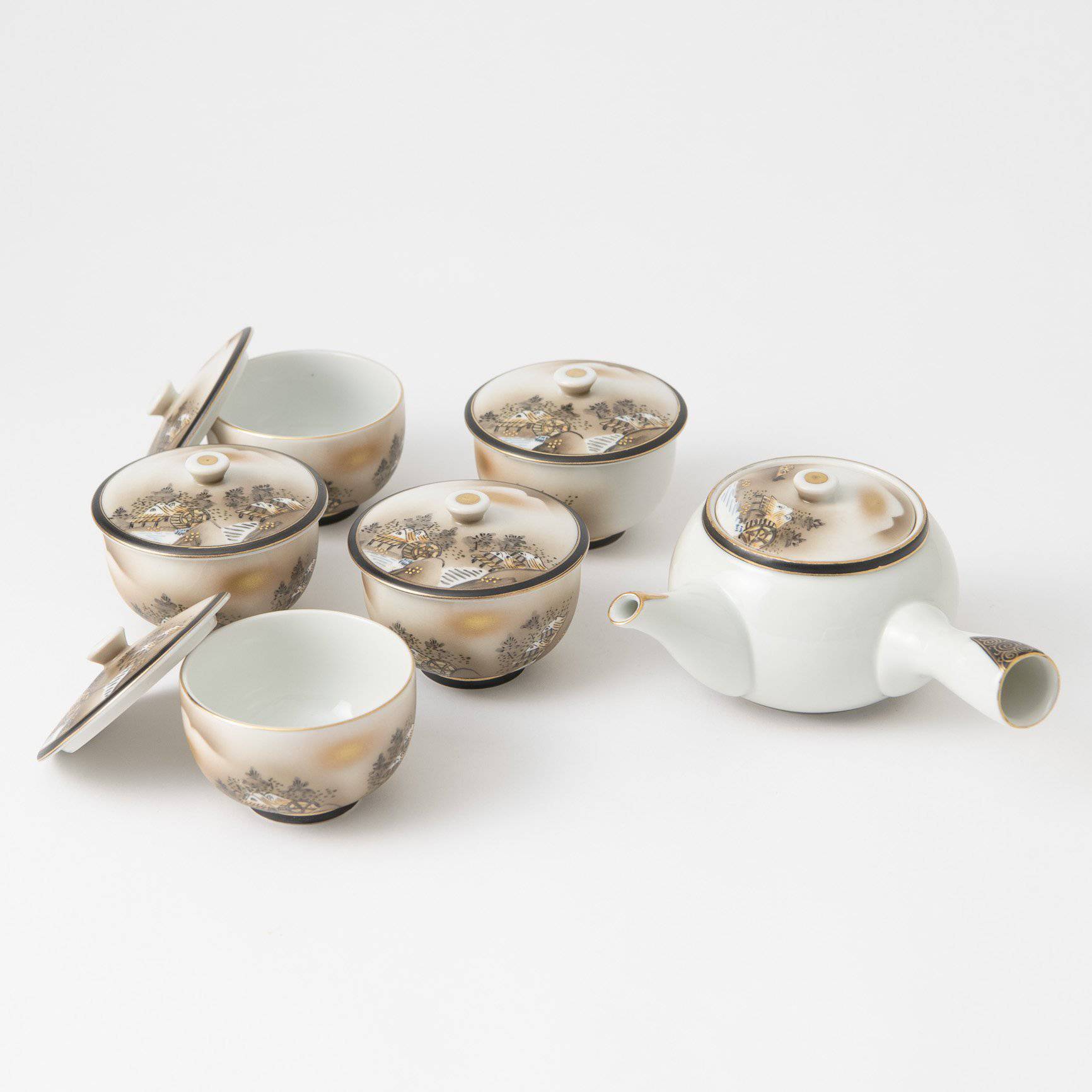
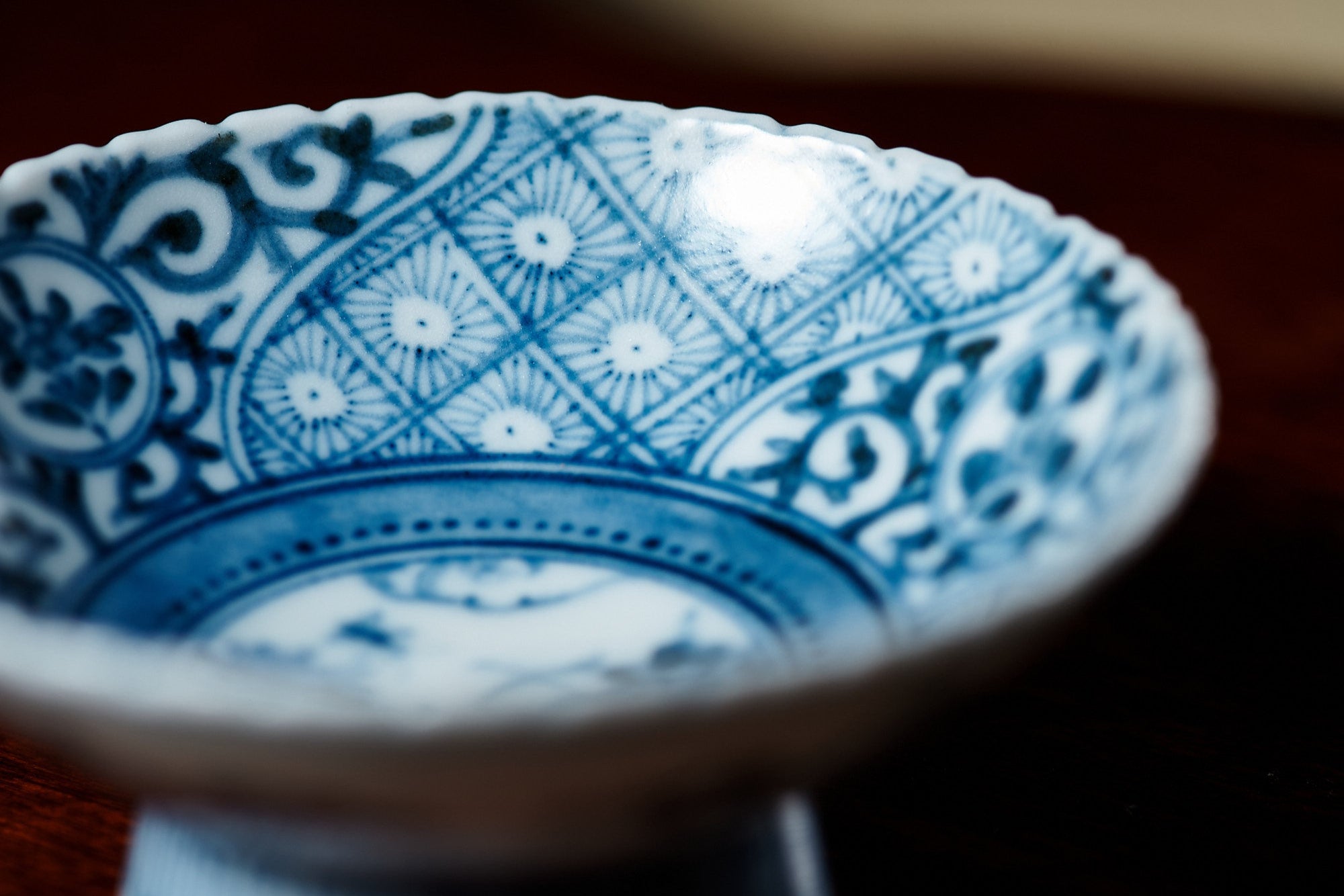
The kiln in Kutani village quickly gained a strong reputation and became a symbol of the Kaga Daishoji Domain. However, it was closed down approximately fifty years after its founding. The works produced during this brief but influential period are known as ko-Kutani, or “Old Kutani.” These pieces are highly valued today for their vibrant overglaze painting in the signature five-color palette of navy blue, red, purple, green, and yellow—marking an important foundation in the history of Japanese colored porcelain.
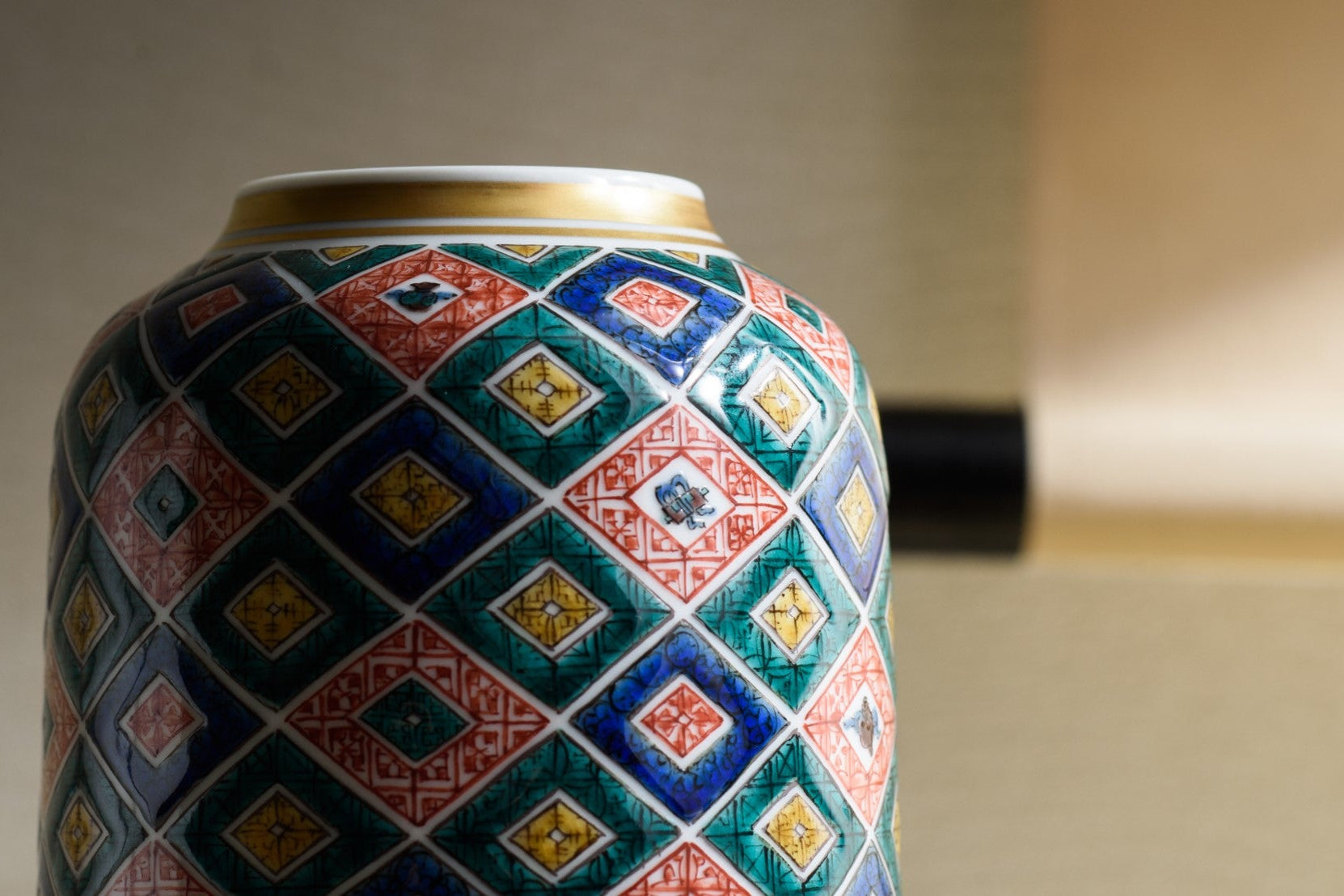

The reasons behind the early closure of the kiln remain uncertain. Several theories have been proposed, including the death of Maeda Toshiharu, economic hardship caused by famine, political conflict within the domain, and possible interference by the Tokugawa shogunate. To this day, the true cause remains a mystery.
Roughly a century later, a revival began as numerous new kilns producing overglaze porcelain were established with support from the Maeda family. This resurgence, known as the Revival of Kutani, introduced new artistic approaches and technical innovations, including both richly colored overglaze porcelain and elegant sometsuke (blue-and-white) porcelain. Over time, the diverse styles developed by individual kilns blended together, laying the groundwork for the modern expression of Kutani ware that flourished after the Meiji era.
For a deeper exploration of Kutani ware’s history, we invite you to read our interview with Nakaya Shinichi, Director of the Kutani Porcelain Art Museum.

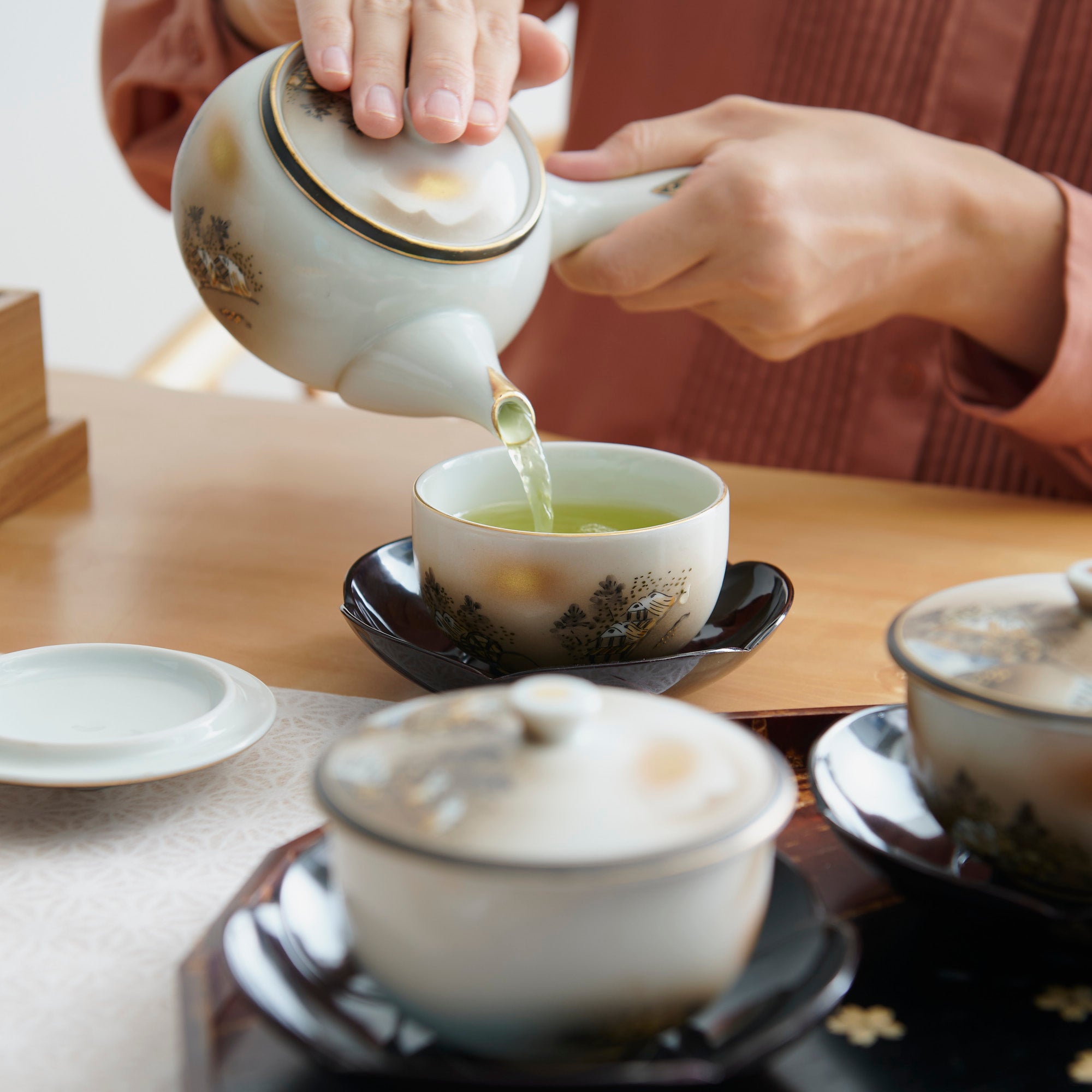
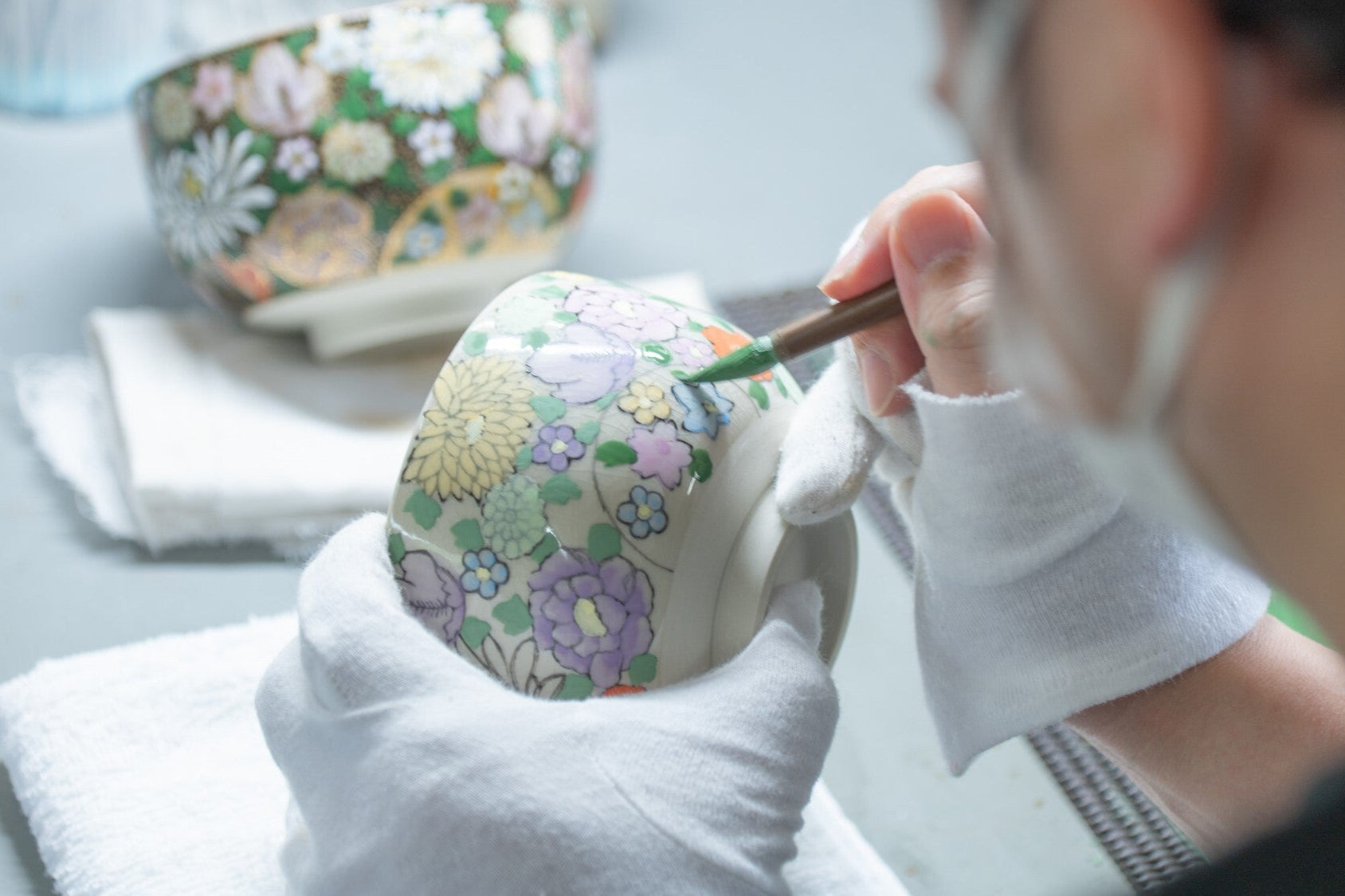
Known for its vivid colors and bold patterns, Kutani ware is crafted through a series of skilled processes: quarrying, clay preparation, molding, firing, and painting. Each step requires precision and dedication, with traditional techniques passed down through generations.

Related posts

A Classicist of Sometsuke: Yamamoto Choza
Kutani ware craftsman Yamamoto Choza blends traditional techniques with current trends to craft sometsuke masterpieces.
Read more
7 Actually Useful Table Accessories That You Didn’t Know You Needed
Discover 7 unique Japanese table accessories, from soy sauce dispensers to spice holders, that add charm to every meal.
Read more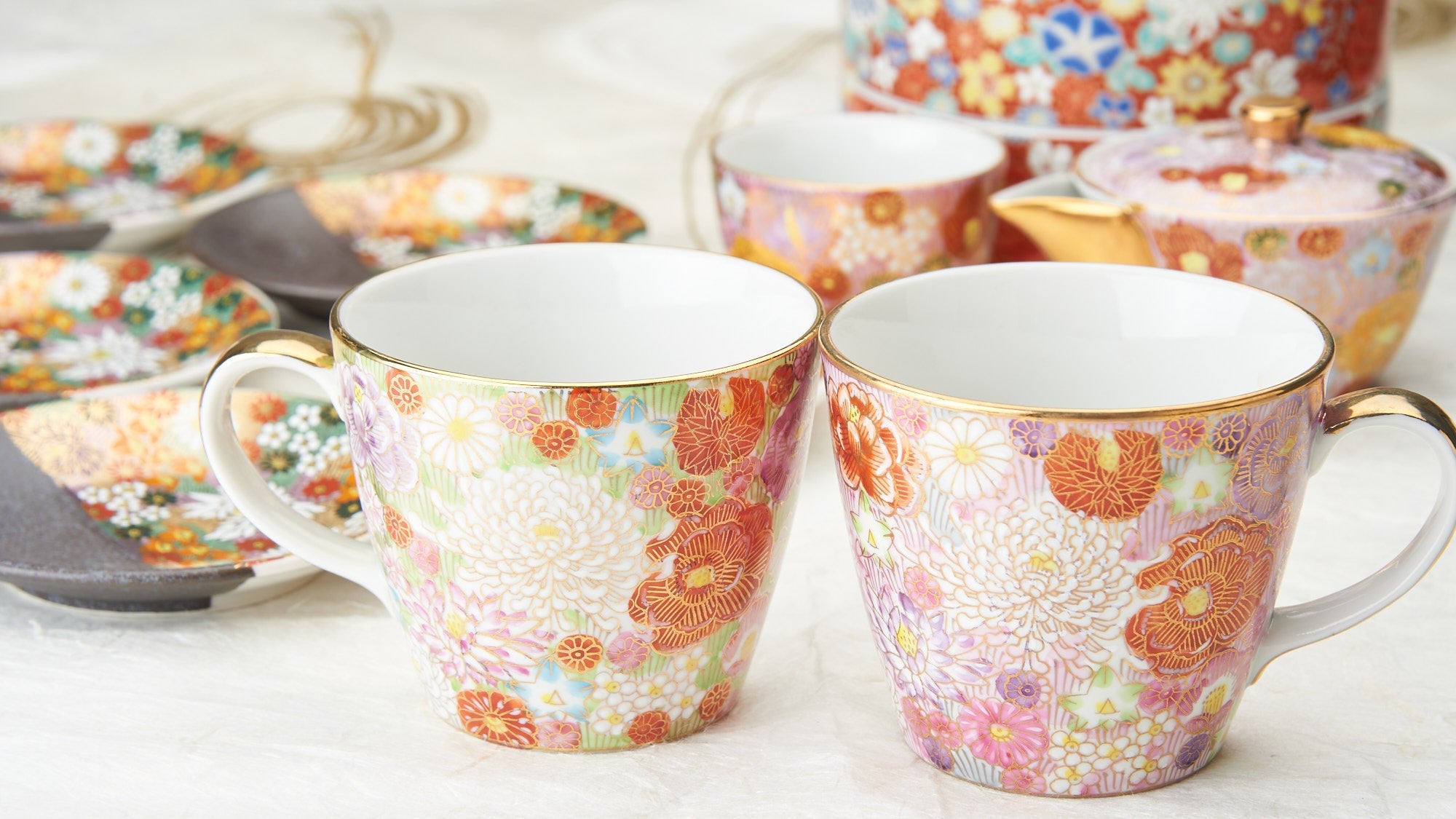
Fascinating Hanazume Gifts for Your Friends and Colleagues
Explore gifts ideas with hanazume, a traditional Kutani ware painting technique used to create vibrant floral designs.
Read more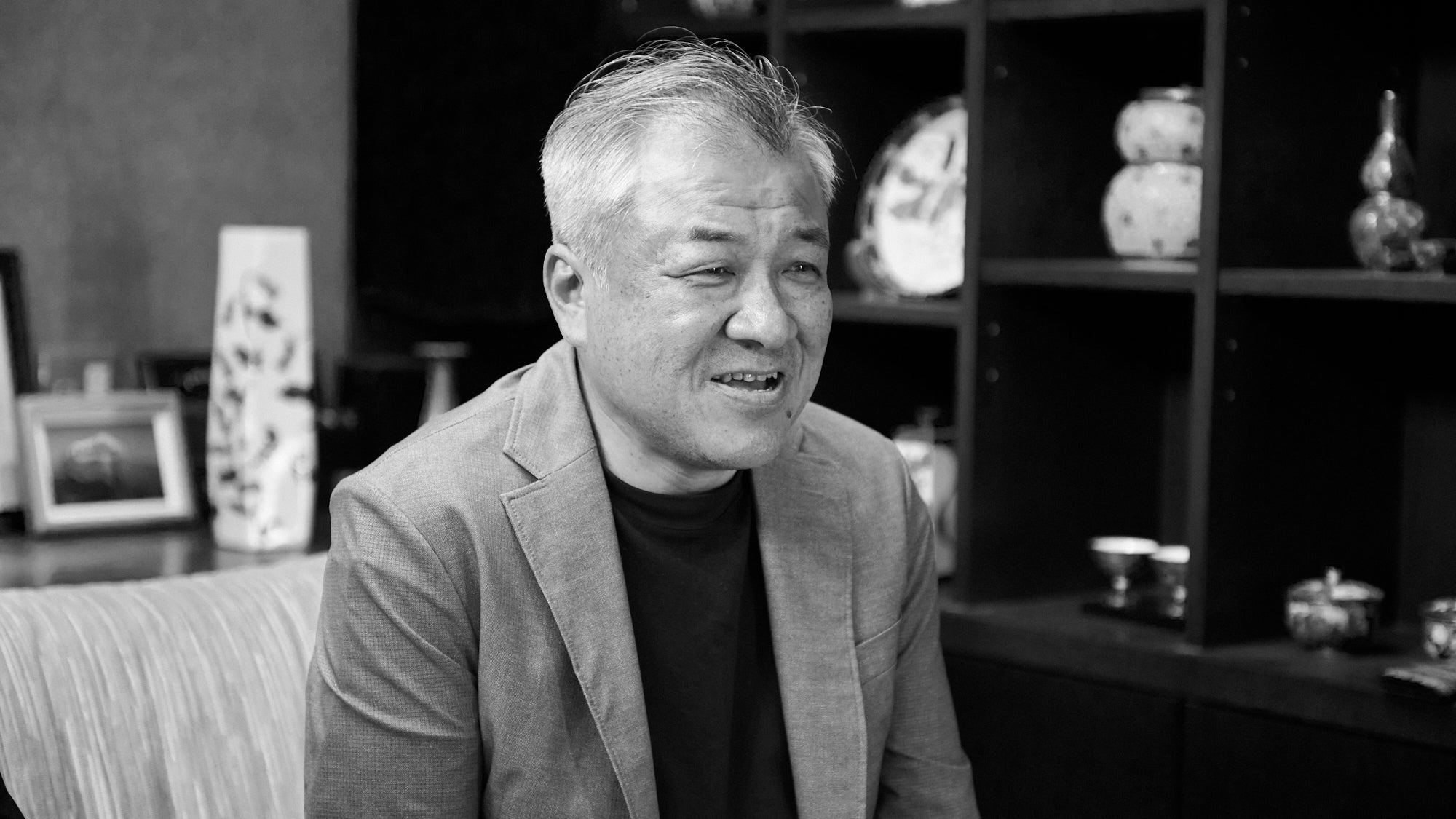
Taka Toshifumi: Bringing All Things Into Balance
Read about Taka Toshifumi's passion for Kutani ware, his family's rich legacy, and his exciting vision for the future.
Read more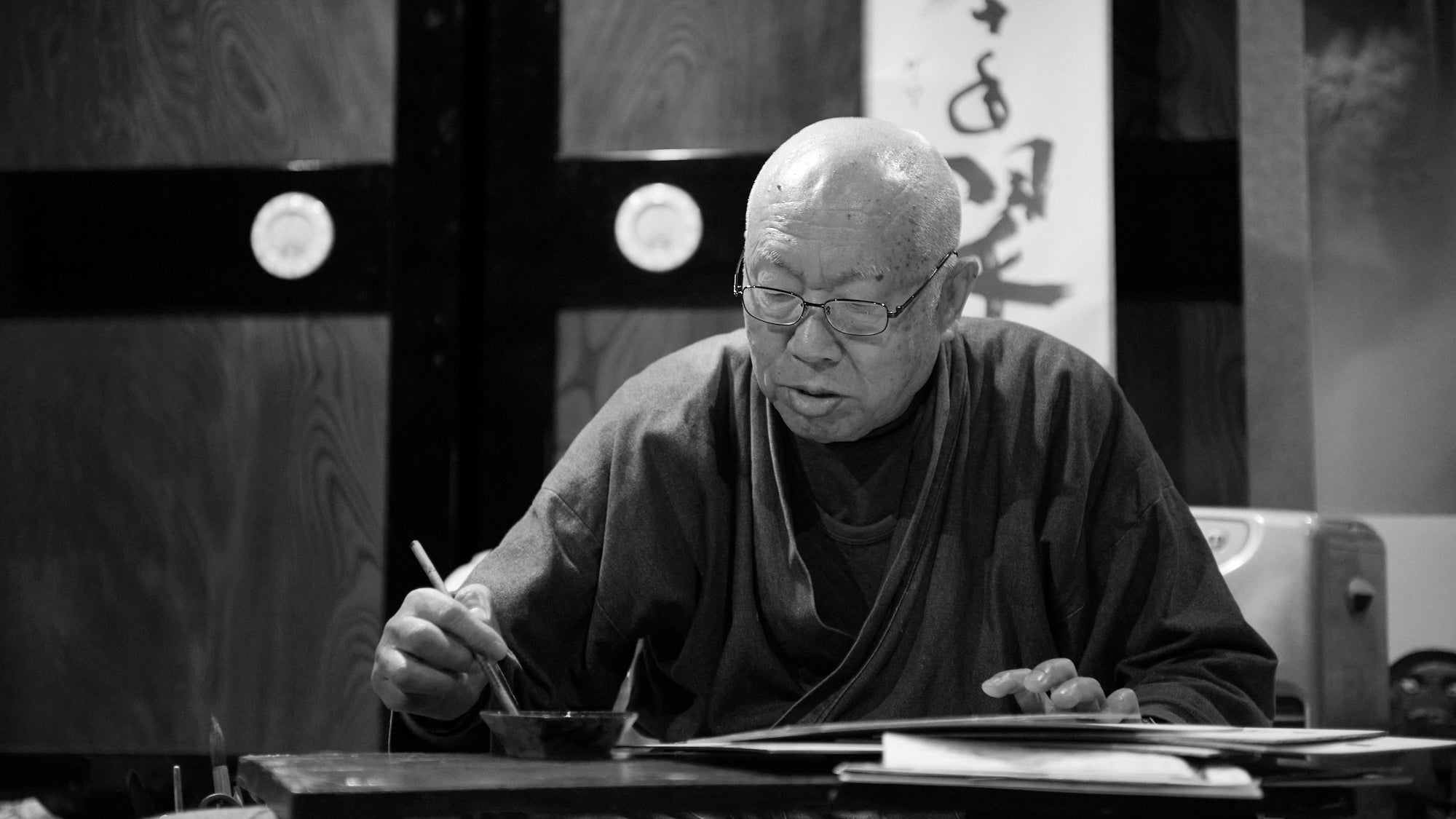
Painter of the Northern Seas, Art and Life of Kitamura Takashi
Kutani ware master Kitamura Takashi speaks on his journey and taking inspiration from Edo-period ships and Japan’s seas.
Read more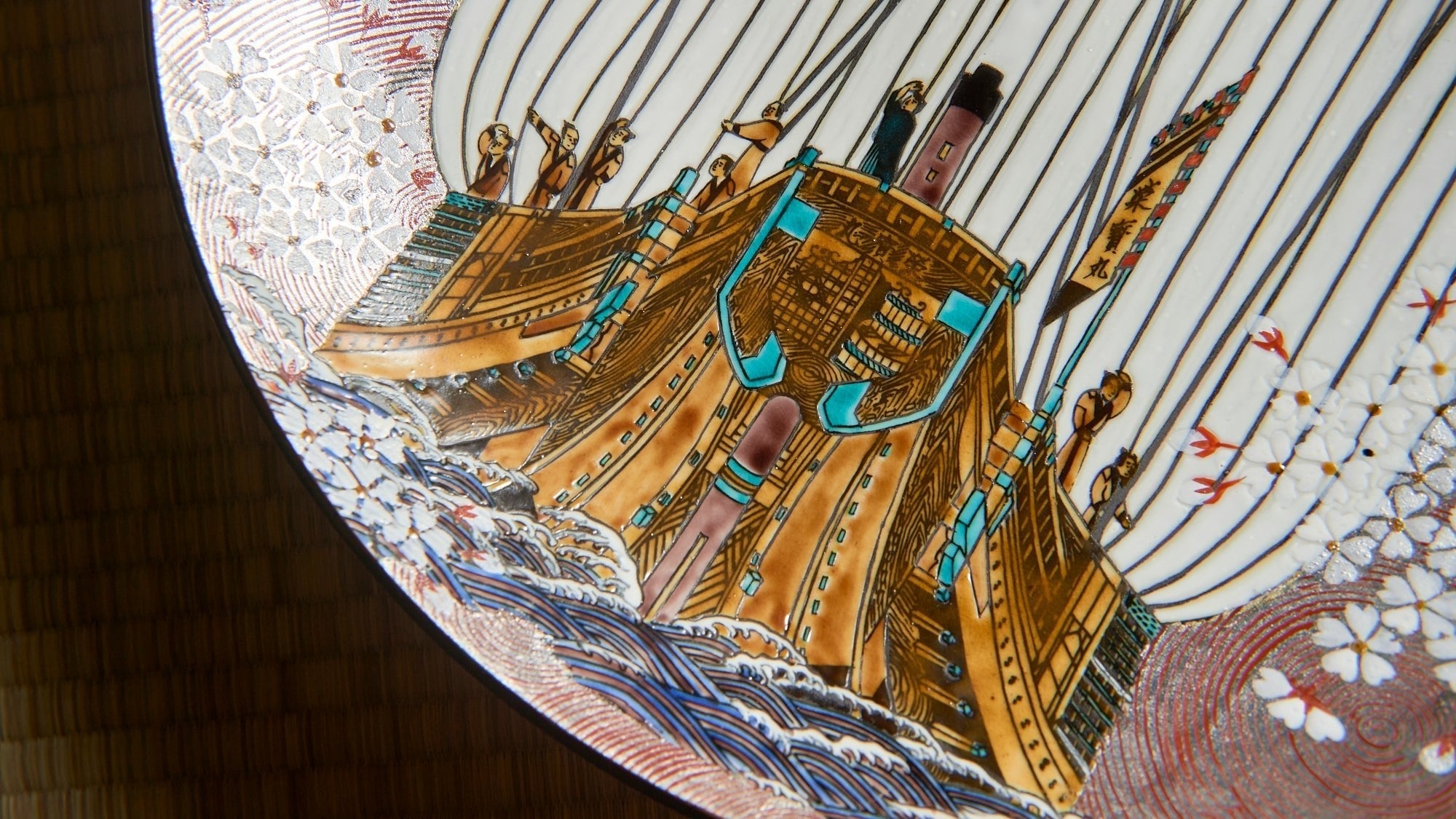
Voyages of Prosperity: The Kitamaebune Unveiled
Learn about kitamaebune, Edo-period merchant ships that sailed Japan's seas and inspired master artisan Kitamura Takashi.
Read more
Mitsui Tatsuya: Guardian of Kutani Ware's Eternal Beauty
Mitsui Tatsuya bridges past and present, preserving Kutani ware's legacy through vibrant ko-Kutani overglaze painting.
Read more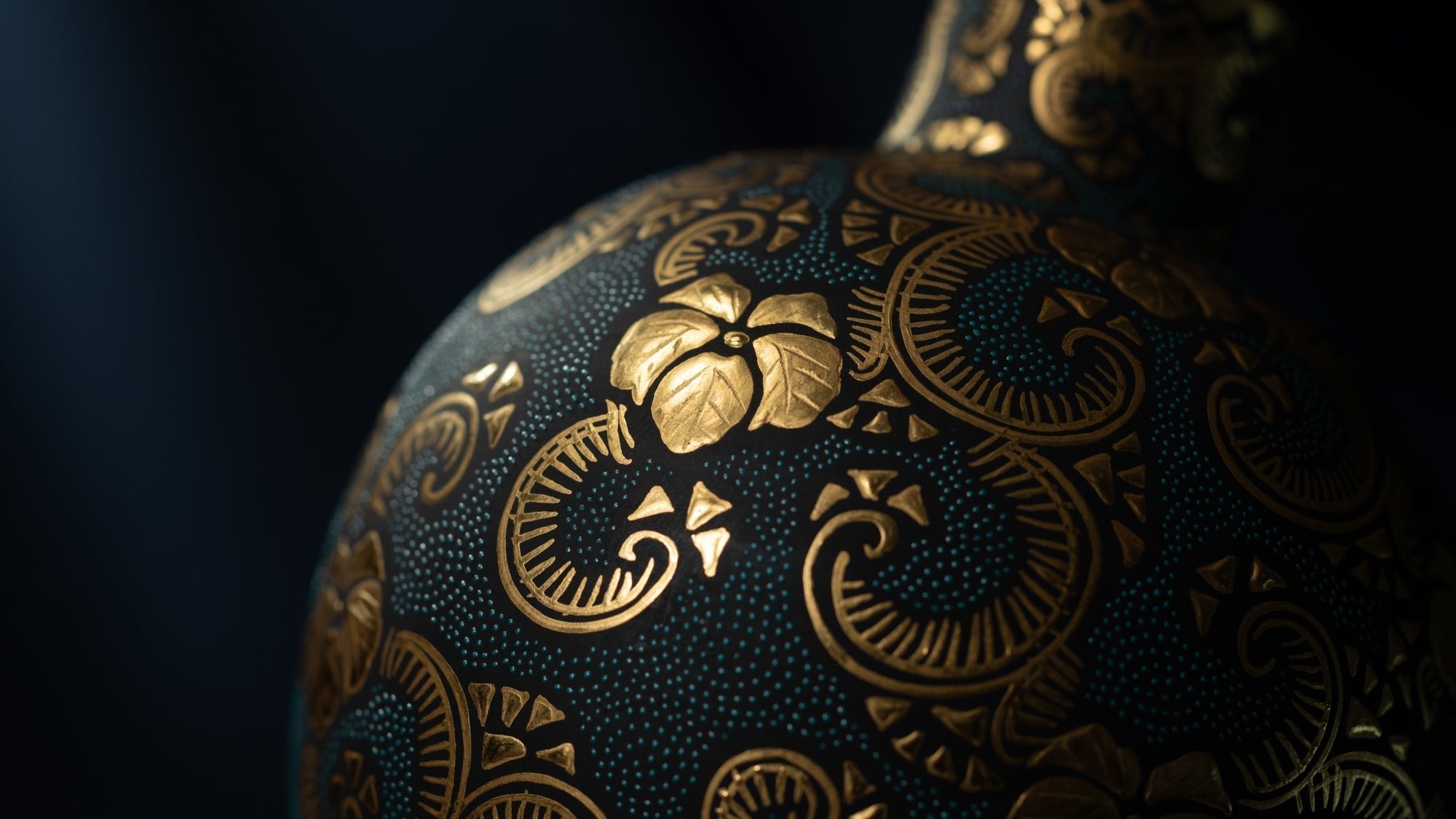
Swirling Elegance: The Artistic Mastery of Kutani Aochibu Style
Discover the art behind the elegant, eye-catching patterns of Kutani aochibu style.
Read more
Nakada Kingyoku: The Evolving Legacy of Kutani Ware's Decorative Paintings
Our interview with the artist innovating Kutani aochibu style by mixing it with the elegant morikin design.
Read more
We introduce five vases, traditional and modern, that will add Japanese flair to your springtime decor.
Read more
Realms of Enchantment: Life and Art of Yoshita Minori
Yoshita Minori brought extraordinary artistry to this prestigious Japanese craft, particularly through his mastery of the yuri kinsai technique.
Read more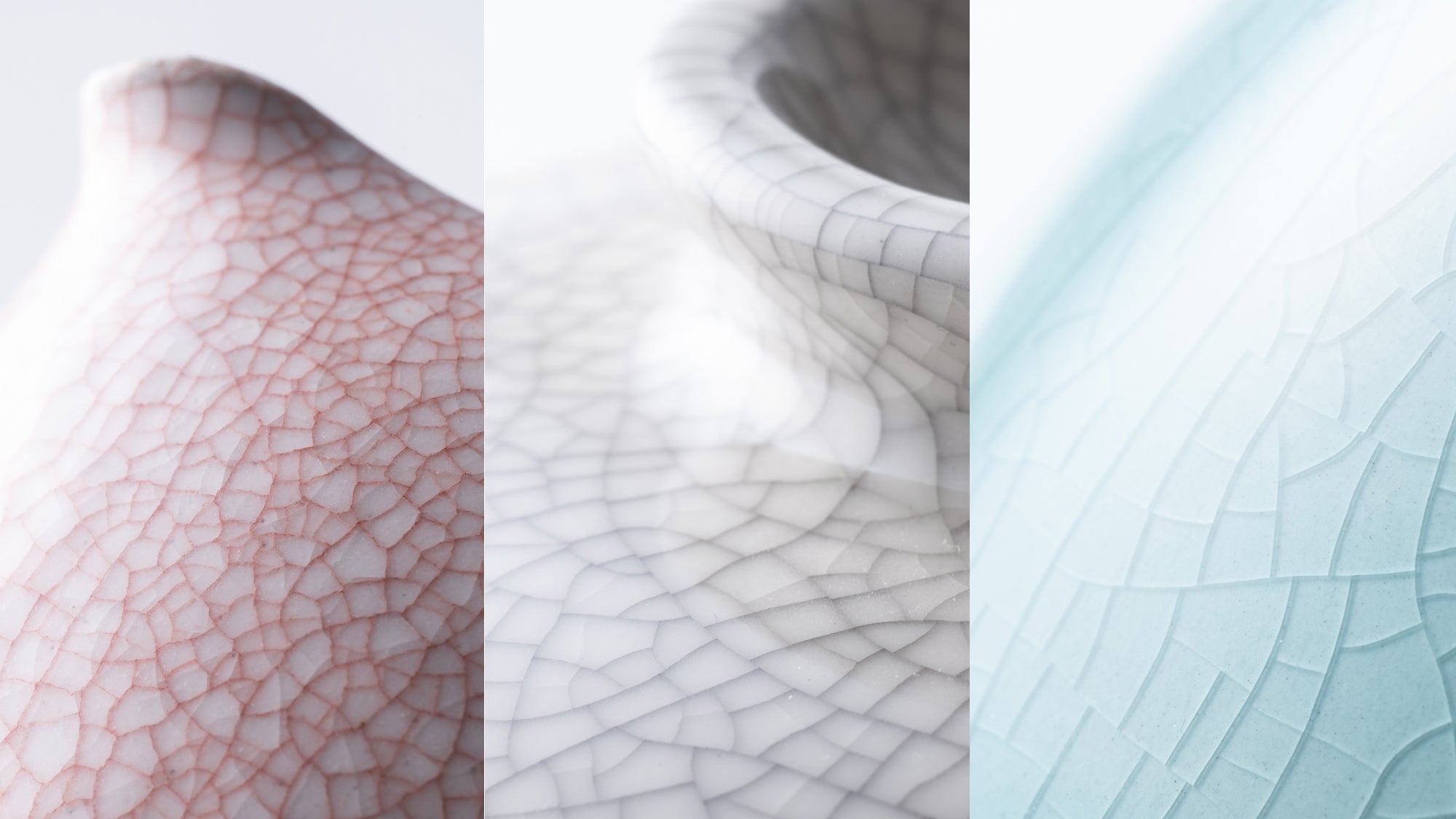
Imperfect Beauty: Cracking the Code of Kannyu
Discover the history of kannyu, the name of the crackled finish on glazed ceramic, dating as far back as the 10th century.
Read more
Hidden Gems of Kutani Ware: A Visit to Komatsu City's Artisans
This time, we embarked on a two-day, one-night trip to visit Kutani ware artists in Nomi City and Kaga City.
Read more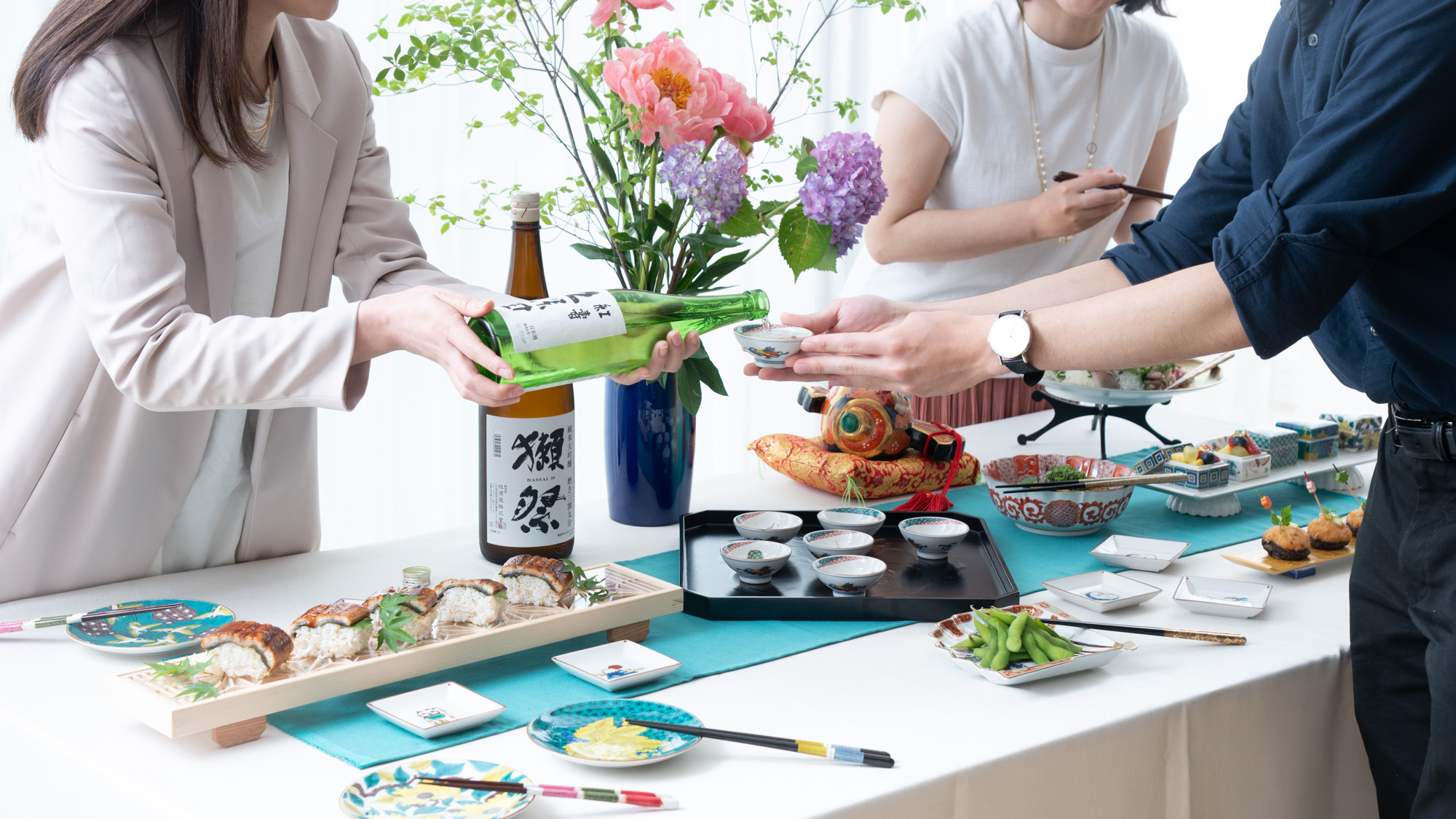
Kutani Elegance: An Exquisite Table Decor for a Sophisticated Office Party
Enjoy the elegance and sophistication of exquisite Kutani tableware with this unique office party buffet table.
Read more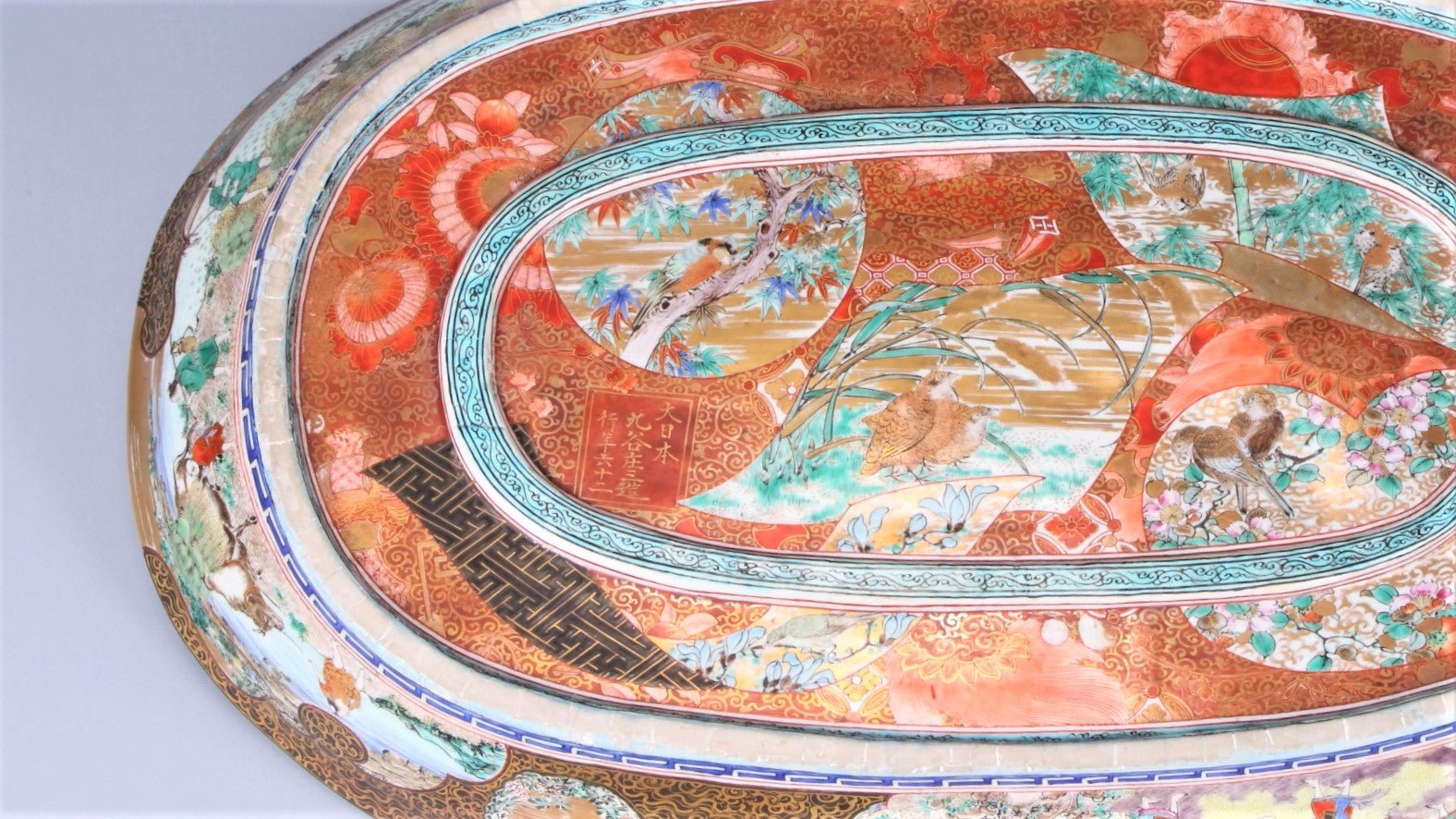
The Shoza style is a fine and gorgeous style of painting that uses Western-style paints in addition to the traditional Kutani Gosai.
Read more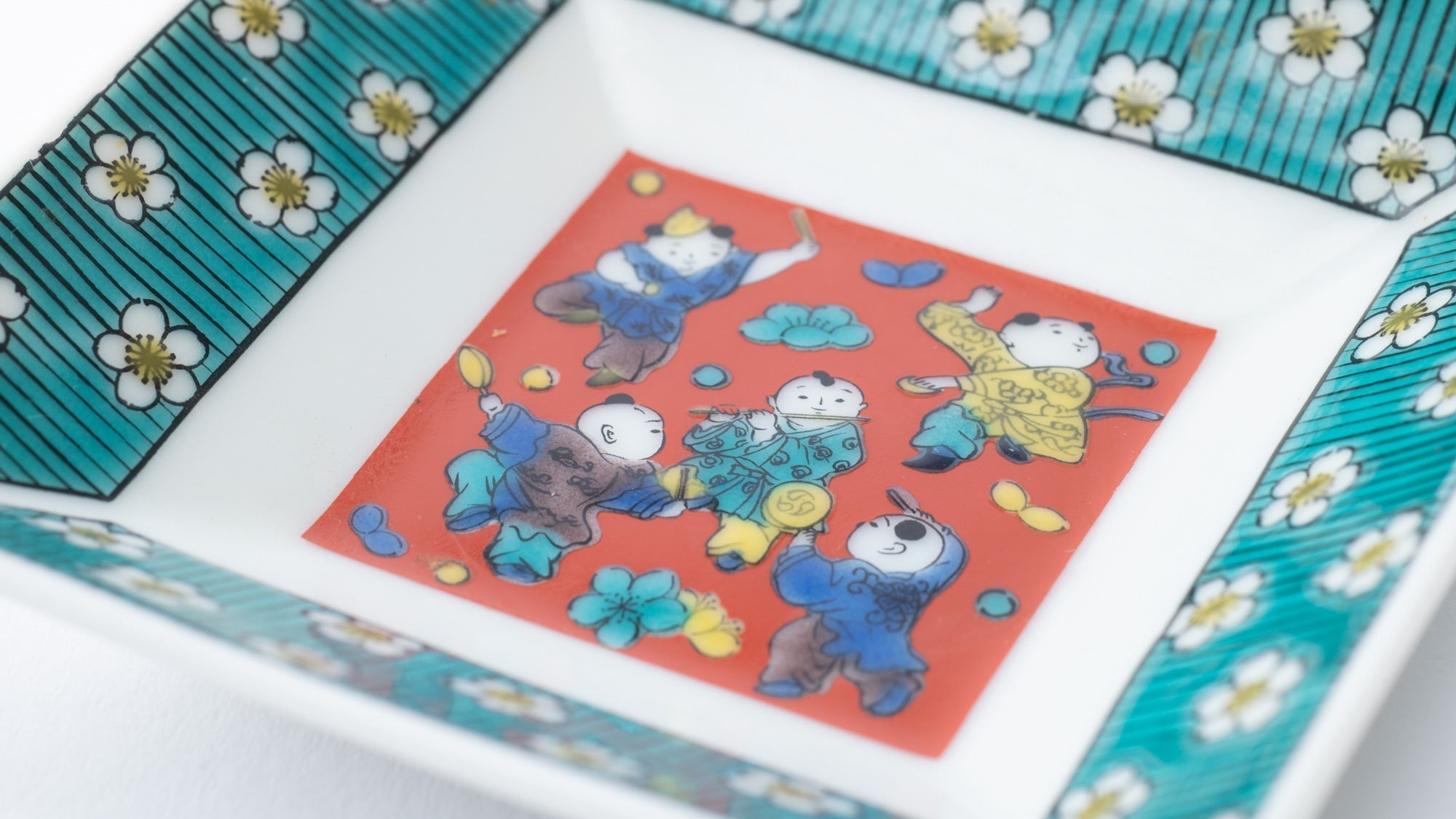
Mokubei is a style characterized by filling blank spaces with calming red pigments.
Read more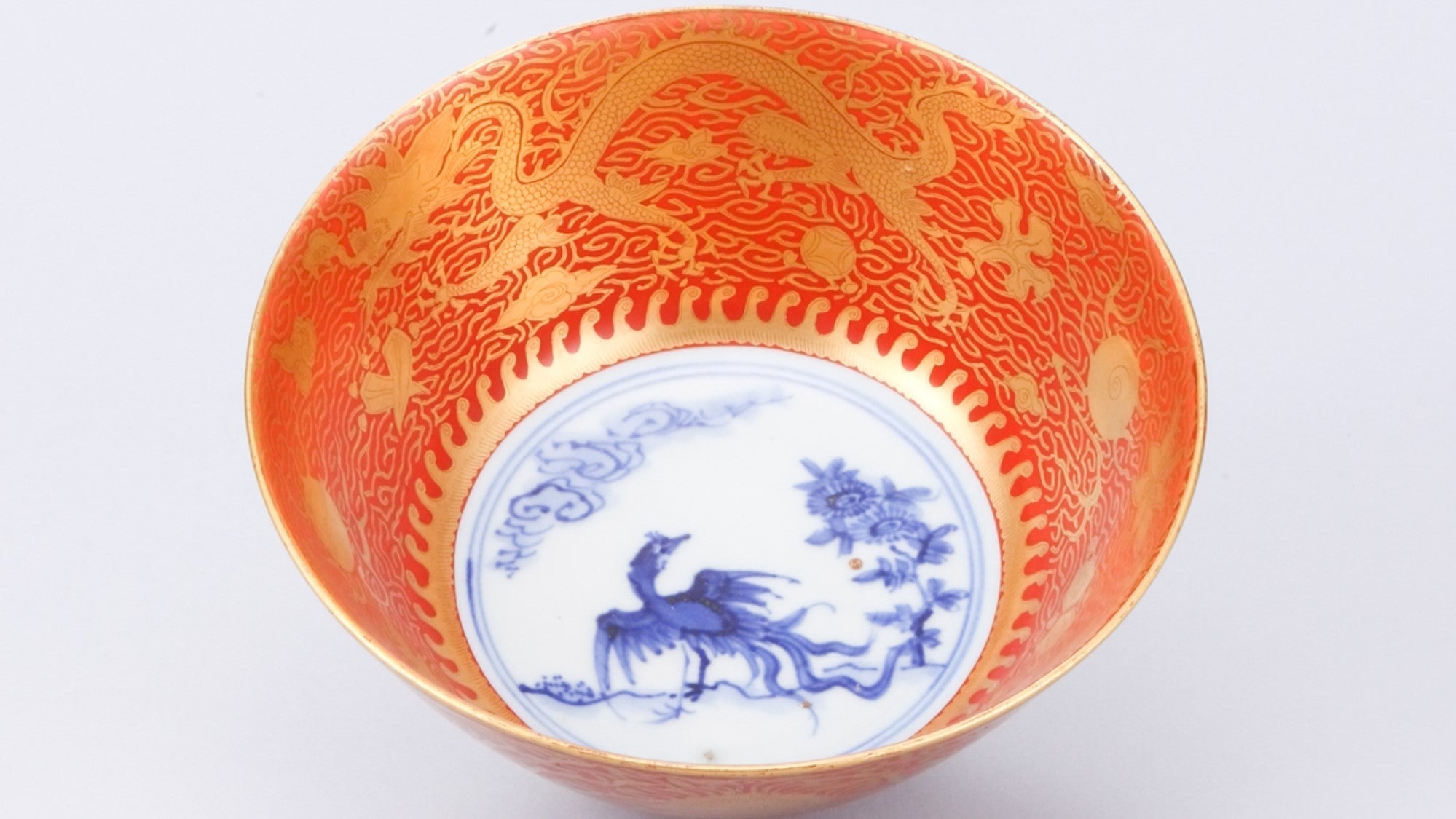
What is Akae-Kinrande "Eiraku" Style?
Akae-kinrande is a gorgeous, sophisticated, and graceful style of Kutani ware. It has a gold design with a red background.
Read more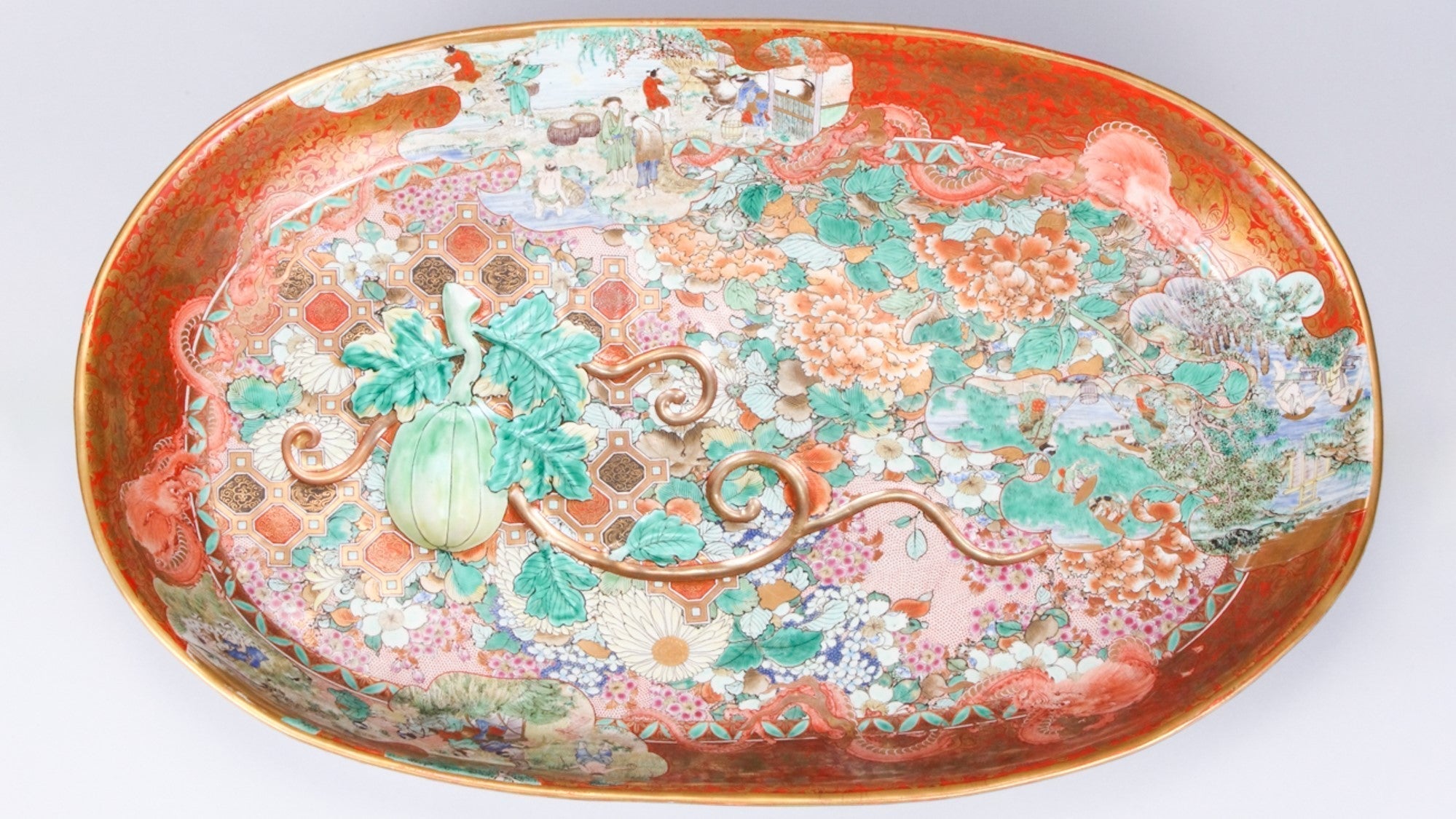
Interview with Nakaya Shinichi, Specialist of Kutani Ware - History Part 2
Shin-ichi Nakaya, Director of The Kutani porcelain Art Museum discusses historical stories and painting styles of Kutani ware.
Read more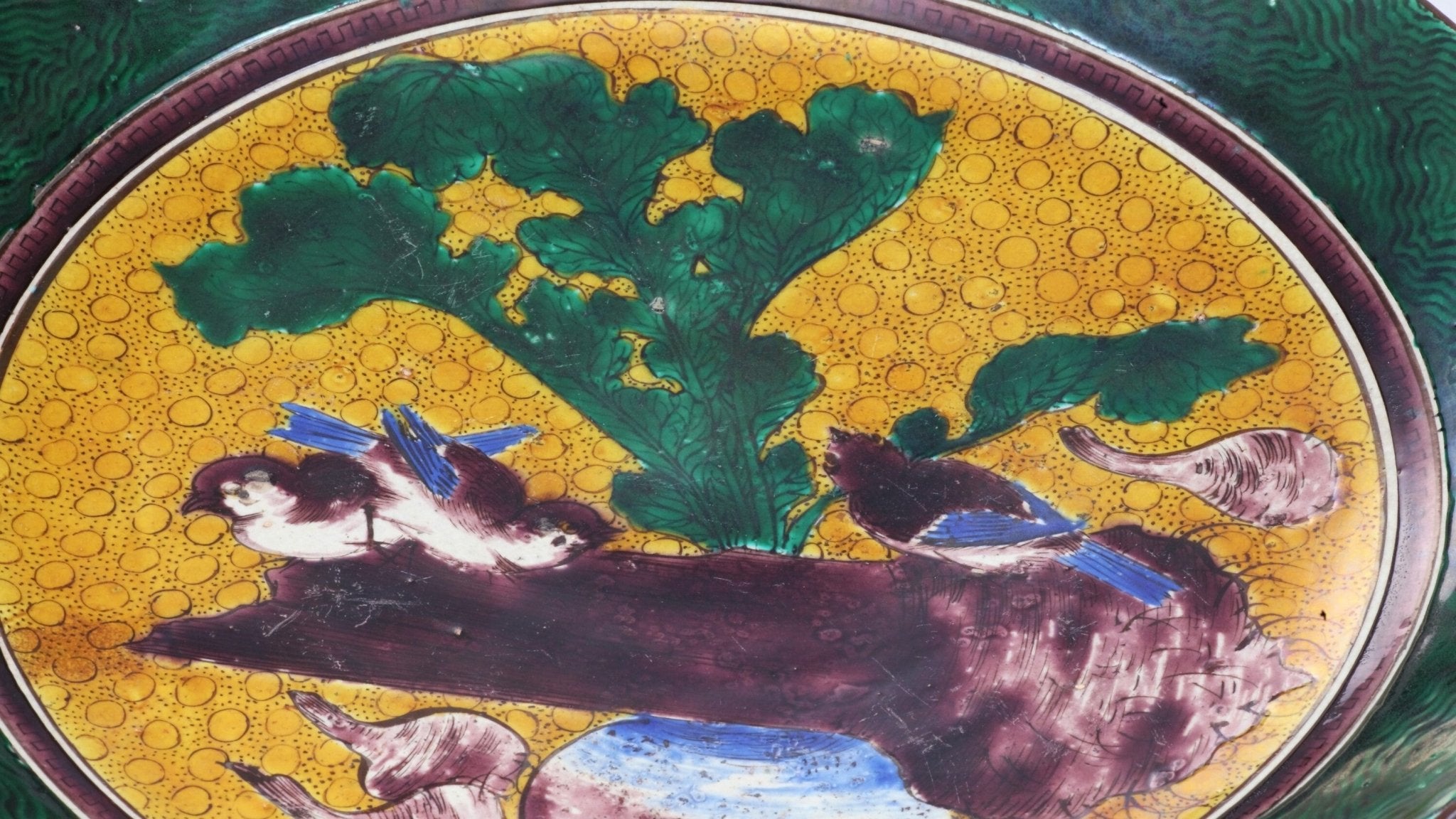
What is Kutani Yoshidaya Style?
Yoshidaya style’s charm is its use of translucent pigment and delicate painting style, as well as its refined designs.
Read more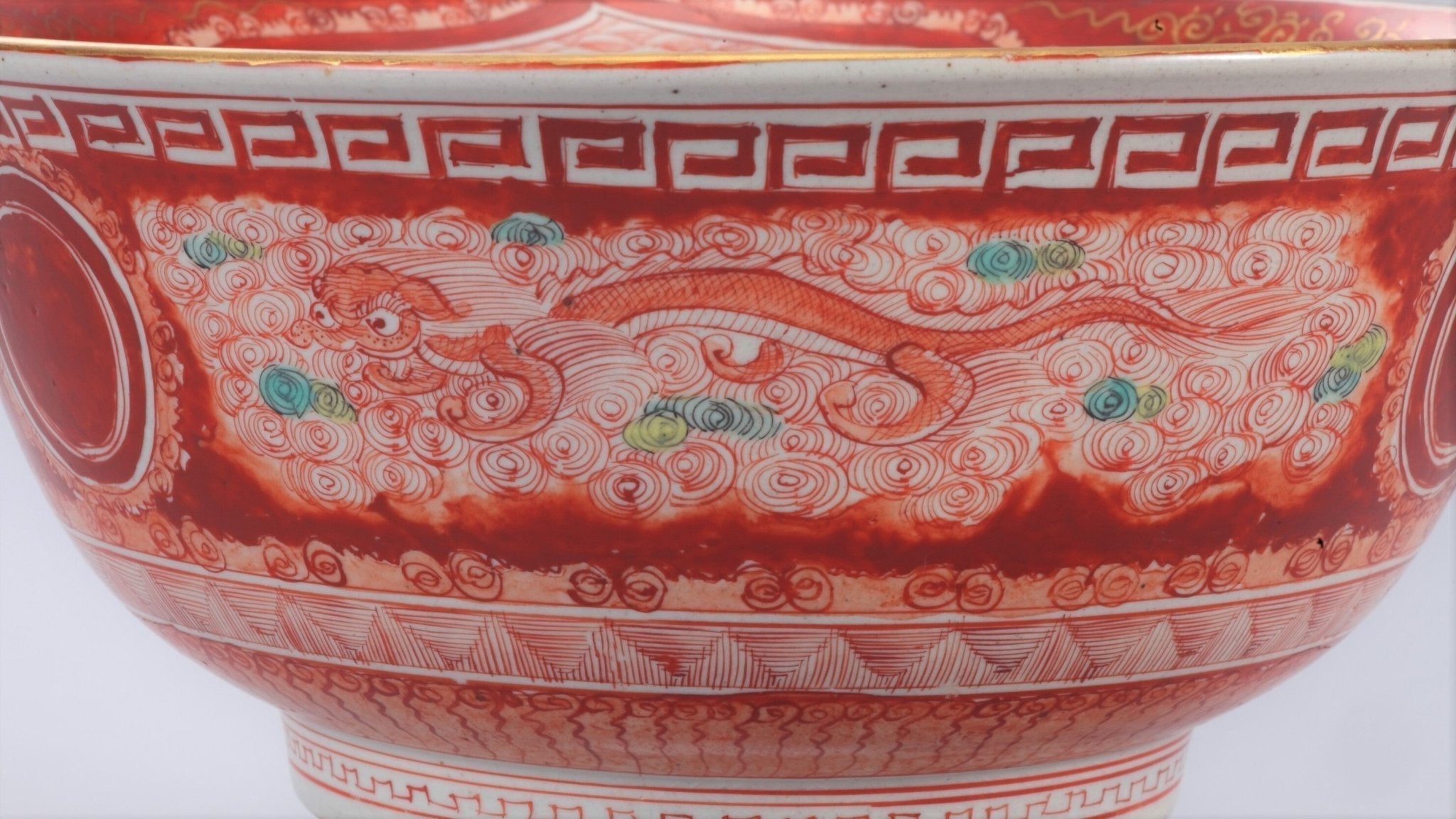
What is Akae-Saibyo "Iidaya" style?
Akae-saibyo–red dots and lines with intricate detalization–has an eye-catching, detailed beauty.
Read more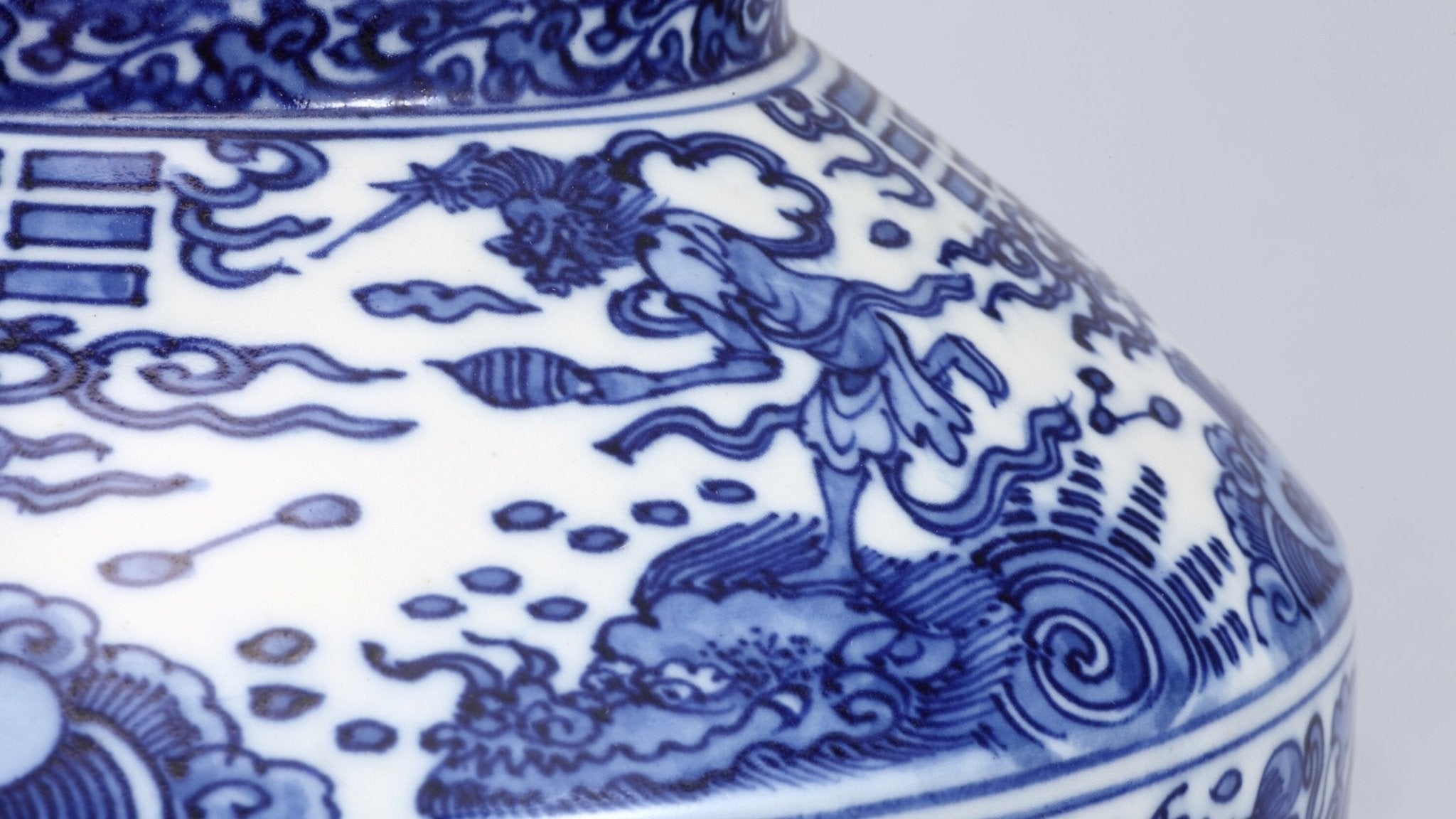
What is Kutani Sometsuke Style?
Sometsuke is a style that paints a canvas only in indigo pigments. The beauty of this style attracts the viewer with its subtleness.
Read more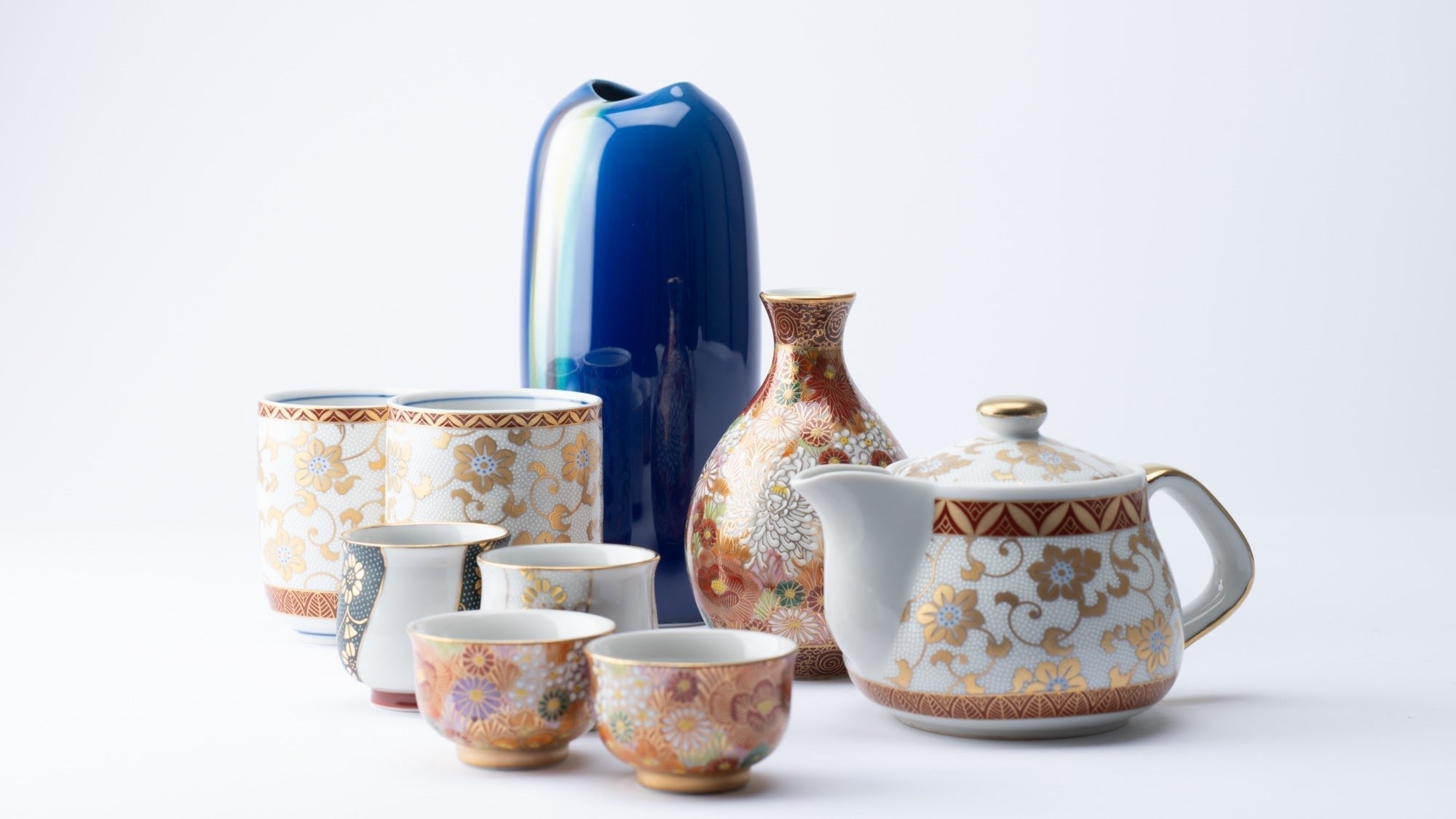
Kutani Ware Styles Born from Japan's Modernization
There are various Kutani ware styles and techniques, ranging from gosai-de derived from Ko-Kutani, to the popular Akae–fine red painting.
Read more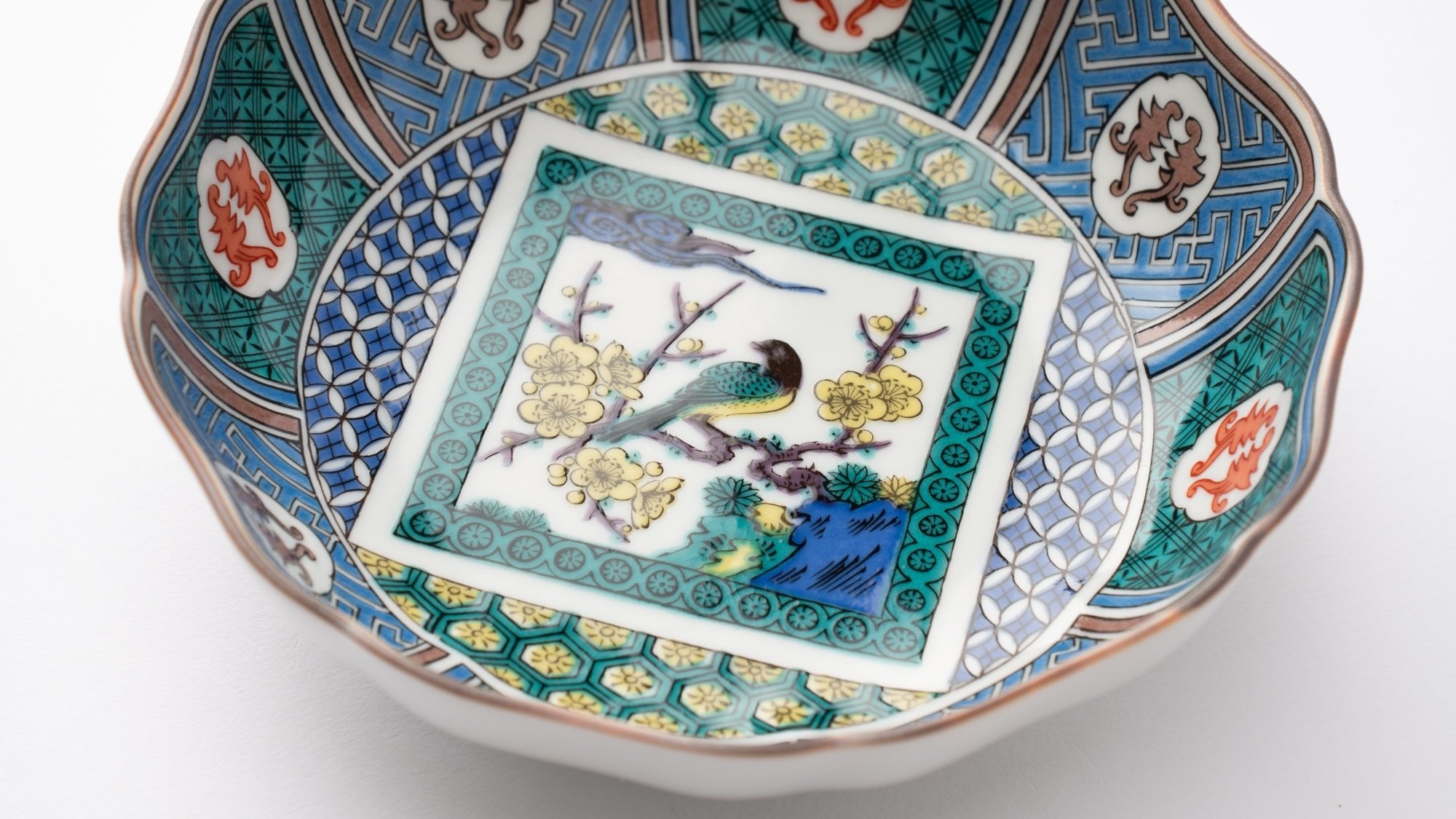
Discover the bold colors and dynamic brushwork of Ko-Kutani style, the vibrant origin of Kutani ware still admired today.
Read more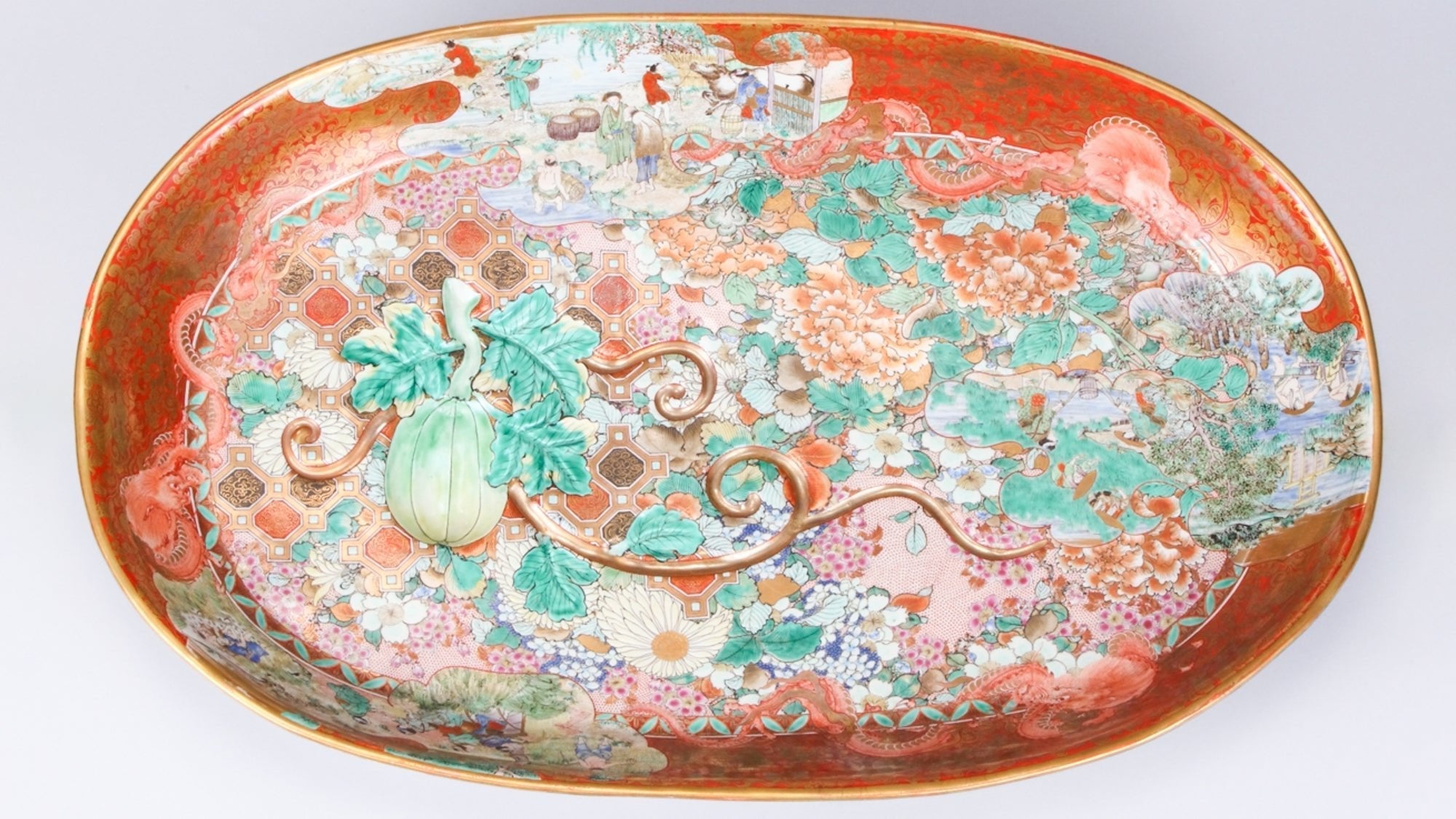
Interview with Nakaya Shinichi, Specialist of Kutani Ware - History Part 1
Kutani ware was introduced in 1655, during the early Edo period (1603-1868), by Maeda Toshiharu, the Lord of Kaga-Daishoji Domain.
Read more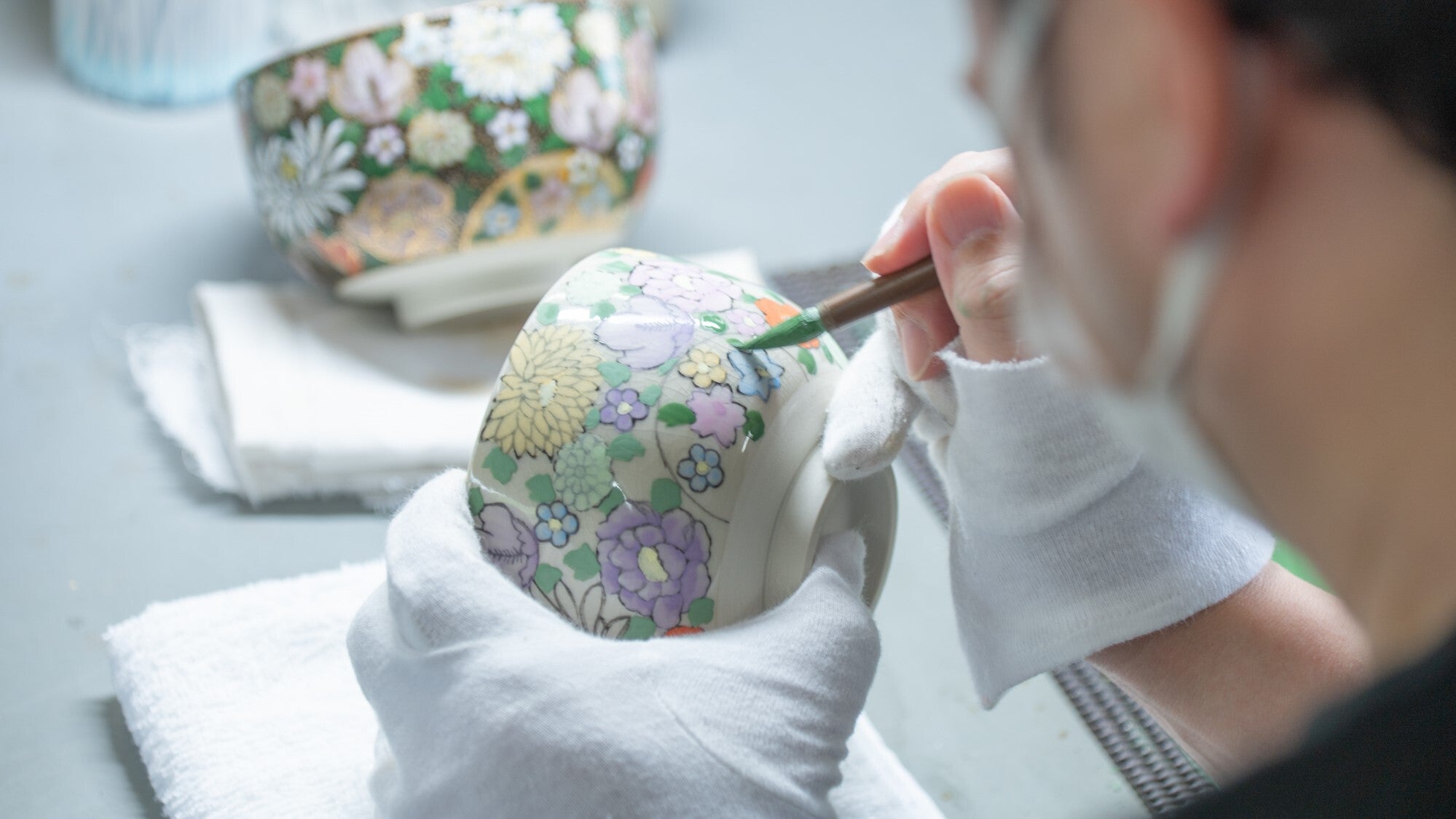
The Process of Making Kutani Ware
Kutani ware, while its vivid hues and bold patterns set it apart among Japanese ceramics, is produced through many processes.
Read moreFilters